▷ General
Tuberculosis (TB) is an airborne bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, spreading when someone with active lung disease releases droplets through coughing, speaking, or even breathing, and turning
that person into a carrier as long as active bacteria remain in the lungs. After an incubation period that can stretch from weeks to months, most people enter a silent phase called latent TB, where the bacteria are present
but symptoms are absent and the person is not contagious. Active TB, however, brings a recognizable set of symptoms: a persistent cough, chest pain, coughing up blood, fever, night sweats, fatigue, and weight loss, with
the illness sometimes affecting organs beyond the lungs such as the kidneys, spine, or brain. The course of TB varies—latent infection may never progress, while active disease can worsen gradually over months and become
life‑threatening without treatment. Management relies on a combination of antibiotics taken for several months, typically including isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol, with strict adherence essential to
prevent drug resistance. TB is both preventable and curable, and global health agencies emphasize early diagnosis, consistent treatment, and vaccination in high‑burden regions as key strategies for controlling a disease
that remains widespread worldwide.
Sleeping sickness moves with an unsettling patience: Trypanosoma brucei parasites enter the body through the bite of an infected tsetse fly, slip into the bloodstream, and eventually infiltrate the lymphatic system and
central nervous system, turning the infected person into a carrier as long as parasites circulate in blood or other bodily fluids. After an incubation period that can range from about a week to several months—sometimes even
longer—the illness begins with fever, headaches, joint pain, and swollen lymph nodes before shifting into its more ominous second stage, where the parasites cross into the brain and disrupt sleep cycles, mood, concentration,
and coordination. The course of the disease unfolds in two distinct acts: an early blood‑borne phase that may seem deceptively ordinary, followed by a neurological phase marked by confusion, personality changes, and the
characteristic sleep disturbances that give the disease its name. Treatment depends on the stage, using specific antiparasitic medications that target either the bloodstream form or the central‑nervous‑system form, paired
with careful monitoring to prevent complications, allowing the body to reclaim its equilibrium once the parasites are cleared.
Cholera, an acute diarrheal illness caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, begins when contaminated water or food introduces the organism into the digestive tract, allowing it to multiply rapidly in the small intestine
and release toxins that trigger massive fluid loss. An infected individual becomes a carrier while the bacteria are present in stool, enabling spread in areas with inadequate sanitation or crowded living conditions. After an
incubation period that typically ranges from a few hours to five days, symptoms can appear suddenly, most notably profuse watery diarrhea, vomiting, leg cramps, and rapid dehydration that can progress with alarming speed.
The course of illness varies from mild, almost unnoticed infection to severe dehydration and shock within hours if fluids are not replaced. Treatment centers on urgent rehydration with oral rehydration solutions or intravenous
fluids in more serious cases, along with antibiotics in certain situations to shorten the duration and reduce bacterial shedding, while preventive measures such as clean water, proper sanitation, and vaccination help curb
outbreaks and limit transmission.
Conjunctivitis, often called pink eye, develops when the conjunctiva—the thin membrane lining the eyelid and covering the white of the eye—becomes inflamed due to infection by viruses, bacteria, or irritation from allergens
or chemicals. A person with infectious conjunctivitis becomes a carrier while the virus or bacteria are active in eye secretions, allowing spread through direct contact, shared items like towels or makeup, or contaminated
surfaces. After an incubation period that typically ranges from one to three days for viral causes and up to a few days for bacterial forms, symptoms emerge as redness, itching, tearing, a gritty sensation, and discharge that
may be watery in viral cases or thicker and yellow‑green in bacterial ones. The condition often progresses over several days, with viral conjunctivitis tending to resolve gradually and bacterial conjunctivitis sometimes worsening
without treatment, while allergic conjunctivitis may flare with ongoing exposure to triggers. Treatment depends on the cause: viral cases rely on supportive care such as cool compresses and artificial tears, bacterial infections
may require antibiotic eye drops, and allergic conjunctivitis responds to antihistamine or anti‑inflammatory eye medications, all aimed at easing irritation as the inflammation subsides.
Dengue, caused by any of four related dengue viruses transmitted primarily through the bites of Aedes mosquitoes, begins when the virus enters the bloodstream and multiplies, turning an infected person into a temporary carrier
capable of passing the virus to mosquitoes that feed during the infectious period. After an incubation period that usually lasts 4 to 10 days, the illness often starts abruptly with high fever, intense headache, pain behind the
eyes, muscle and joint aches, nausea, vomiting, and a characteristic rash that may appear as the fever rises or falls. The course of dengue typically unfolds in three phases: a febrile stage marked by high temperature and general
discomfort; a critical stage in which some individuals experience plasma leakage, abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, or bleeding tendencies; and a recovery stage where fluids re‑enter the bloodstream and the rash may intensify
before fading. Treatment focuses on supportive care—rest, hydration, and fever management—while severe cases require careful medical monitoring, fluid replacement, and management of complications, allowing the body to stabilize
as the immune system clears the virus.
Diphtheria, caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, begins when the bacteria enter the body through the nose, throat, or skin, allowing them to produce a potent toxin that damages tissues and creates the illness’s distinctive
thick gray membrane in the throat. An infected individual becomes a carrier while the bacteria are present in respiratory droplets or skin lesions, enabling spread through coughing, sneezing, close contact, or shared items,
especially in crowded settings. After an incubation period that usually ranges from 2 to 5 days, symptoms emerge with sore throat, fever, swollen glands, and difficulty swallowing, sometimes accompanied by a hoarse voice or
nasal discharge, while severe cases may progress to breathing problems, heart inflammation, or nerve damage as the toxin circulates. The illness can advance quickly, with the membrane thickening over several days and systemic
complications developing if the toxin spreads unchecked. Treatment relies on prompt administration of diphtheria antitoxin to neutralize circulating toxin, paired with antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria, along with supportive
care to manage breathing difficulties and other complications, allowing recovery as the toxin’s effects subside and the infection clears.
A world of medical mysteries unfolds in the realm of rare diseases, where more than 7,000 conditions exist but only a handful reach the extreme edge of rarity—like Fields Condition, documented in just three people,
or ribose‑5‑phosphate isomerase deficiency, seen only four times in 27 years, while the hauntingly rapid‑aging disorder Hutchinson–Gilford Progeria Syndrome affects only a few hundred children worldwide;
together these conditions form a landscape as fascinating as it is fragile, a reminder of how astonishingly diverse—and sometimes bewilderingly scarce—human biology can be.
Rare diseases encompass a broad range of over 7,000 known conditions, including genetic, neurological, skeletal, immune-related, and ultra-rare disorders, affecting roughly 350–400 million people globally and about 30 million
in the U.S.—half of whom are children. Diagnosis of rare diseases can be extremely challenging, often requiring years and multiple misdiagnoses before reaching accuracy. Examples include Cystic Fibrosis, Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy,
Fabry Disease, Huntington’s Disease, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Aplastic Anemia, and even unusual conditions like Alice in Wonderland Syndrome and Progeria. These diseases often pose significant diagnostic challenges and are
frequently life-threatening or debilitating, yet only about 5% currently have FDA-approved treatments, making early detection, research, and advocacy critical to improving outcomes for patients worldwide.
Mary E. Brunkow , Fred Ramsdell , and
Shimon Sakaguchi were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2025 for their discovery of regulatory T cells and their role in maintaining immune tolerance.
Their groundbreaking research revealed how these specialized cells prevent the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues, a mechanism crucial for preventing autoimmune diseases. By understanding and harnessing this process,
scientists are now developing therapies that can restore immune balance, offering new hope for patients with conditions like type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Their work is also enhancing outcomes in cancer
immunotherapy and stem cell treatments by improving immune regulation and reducing rejection risks.Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman , awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2023,
revolutionized vaccine development by discovering how to modify nucleosides in mRNA, making it stable and non-inflammatory when introduced into the human body. This breakthrough enabled the safe and effective use of synthetic mRNA in vaccines,
leading directly to the creation of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines. Their work allowed for rapid vaccine production without growing viruses in labs, helping to curb the global pandemic and save millions of lives. Beyond COVID-19,
their discovery has opened new possibilities for treating cancer, genetic disorders, and other diseases using mRNA technology.Harvey J. Alter , Michael Houghton , and
Charles M. Rice were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2020 for their groundbreaking discovery of the Hepatitis C virus, a major cause of chronic liver disease.
Their work enabled the development of highly accurate diagnostic tests and effective antiviral treatments, which have dramatically reduced the risk of liver failure and liver cancer for millions of people worldwide. By identifying the virus
and understanding its biology, they paved the way for curative therapies that have transformed public health and saved countless lives.James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2018 for
their pioneering work in cancer immunotherapy, which transformed the way cancer is treated by enabling the immune system to recognize and attack tumor cells. Allison discovered how blocking the CTLA-4 protein could unleash immune responses
against cancer, while Honjo identified PD-1, another immune checkpoint that, when inhibited, boosts the body’s ability to fight tumors. Their discoveries led to the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors—drugs that have significantly
improved survival rates for patients with various cancers and revolutionized oncology by offering new hope where traditional treatments had failed.William C. Campbell and Satoshi Ōmura were awarded the Nobel Prize
in Medicine in 2015 for their discovery of ivermectin, a groundbreaking drug used to treat roundworm infections. Their work led to the near eradication of devastating parasitic diseases such as river blindness and lymphatic filariasis, particularly
in developing countries where these conditions were widespread. By targeting the parasites responsible for these illnesses, ivermectin has dramatically improved the health and quality of life for millions of people across the globe.Youyou Tu was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2015 for her discovery of artemisinin, a powerful antimalarial compound derived from sweet wormwood. Her breakthrough
provided an effective treatment for malaria, especially in regions where the disease is endemic and resistance to older drugs was widespread. Artemisinin-based therapies have become the global standard for malaria treatment, saving millions of
lives and significantly reducing mortality rates in tropical and subtropical areas. Her work stands as a remarkable fusion of traditional Chinese medicine and modern pharmacology.As of 2024, approximately 87% of Americans experience foot pain at some point in their lives, with issues ranging from mild discomfort to chronic conditions like plantar fasciitis, bunions, and heel pain. Women remain
disproportionately affected—up to four times more likely to report foot problems than men—largely due to lifelong patterns of wearing high heels and ill-fitting shoes. Despite the prevalence, only a small percentage seek
professional care, with many relying on self-treatment or ignoring symptoms altogether. These problems often stem from neglect and poor footwear choices rather than congenital issues, and they can significantly impact mobility,
weight, and overall health.
In 2024, the United States recorded approximately 1.0 billion physician office visits, maintaining a rate of 320.7 visits per 100 people, consistent with the previous year. The proportion of visits made to primary care physicians
held steady at 50.3%, reflecting a continued shift toward specialists, urgent care centers, and telehealth services. Chronic health conditions—especially hypertension, diabetes, and joint pain—remained the leading reasons for seeking
care, surpassing acute issues like cough. Essential hypertension continued to be the most frequently diagnosed condition, underscoring its widespread impact and the healthcare system’s growing focus on managing long-term illnesses
rather than isolated symptoms.
If you were admitted to hospital your chances of being subjected to an error (no dying) in your care would be something like 1 in 10.
These can range from medication mistakes and diagnostic delays to surgical mishaps and communication breakdowns. As for fatal outcomes, a widely cited Johns Hopkins study estimated that medical errors may be the third leading cause
of death in the U.S., responsible for over 250,000 deaths annually—which roughly translates to 1 in every 300 hospital patients dying due to preventable mistakes. Your chances of dying due to an error in health care would be 1 in 300.
A study published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that men who watched more than 20 hours of television per week had 44% lower
sperm concentration than those who watched none, suggesting that sedentary behavior may negatively impact fertility. In contrast, men who engaged in 15
or more hours of vigorous physical activity weekly had sperm counts 73% higher than those who exercised less than 5 hours per week. The findings highlight how lifestyle factors like screen time and regular exercise can significantly
influence reproductive health, independent of other factors such as diet, body weight, and smoking.
People who have blood types A, B, or AB have a slightly
higher risk of heart diseases compared to those with type O. The increased risk for blood type AB is about 20% higher risk of cardiovascular events, including heart attack and stroke; type B, around 11% increased risk; and type A,
roughly 8% higher risk. people with type O blood tend to have lower levels of von Willebrand factor, a protein involved in blood clotting, which may offer some protection against heart disease.
The population of people having blood type A include 40% of whites, 26% of blacks, 31% of Hispanics and 28% of Asians; type B: 11% of whites,
19% of blacks, 10% of Hispanics and 25% of Asians; type AB: 4% of whites, 4% of blacks, 2% of Hispanics and 7% of Asians; and type O: 45% of whites, 51% of blacks, 57% of Hispanics and 40% of Asians.
The longest living cells in the body are brain cells which can live an entire lifetime. Most neurons in your brain are formed before birth and can last your entire lifetime. Unlike skin or blood cells, which regenerate frequently,
neurons are largely non-dividing. That’s why damage from neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s can be so devastating—once these neurons are lost, they’re often not replaced.
In 2024, the human circulatory system remains one of the most astonishing feats of biological engineering. While the commonly cited figure suggests the body contains around 60,000 miles (96,500 kilometers) of
blood vessels —including arteries, veins, and capillaries—this estimate is more symbolic than precise. Recent scientific analyses suggest the actual length may be
closer to 9,000 to 19,000 kilometers (5,600 to 11,800 miles), varying by body size, vascular density, and measurement techniques. Regardless of the exact number, this intricate network plays a vital role in sustaining life: it delivers
oxygen and nutrients to trillions of cells, removes metabolic waste, regulates temperature, and supports immune function. Whether stretched across a continent or scaled to fit within our bodies, the circulatory system remains a marvel
of efficiency and design.
In 2024, the health profile of high-income countries continues to be dominated by non-communicable diseases, reflecting both medical progress and the challenges of aging populations. Ischaemic heart disease remains the leading
cause of death, though mortality rates have slightly declined due to improved prevention and treatment. Stroke and other cerebrovascular diseases persist as major concerns, particularly among older adults. Alzheimer’s disease and
other dementias have become increasingly prominent, driven by demographic shifts and better diagnostic awareness. Despite declining smoking rates, lung cancers (trachea, bronchus, and lung) remain among the top cancer-related killers,
alongside colorectal cancer, which continues to rank high despite improved screening. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), especially among former smokers, and diabetes mellitus, fueled by rising obesity and sedentary
lifestyles, remain significant threats. Kidney diseases, often linked to diabetes and hypertension, and breast cancer, still a leading cause despite improved survival rates, round out the top causes. Lower respiratory infections
continue to affect vulnerable populations, and while COVID-19 is no longer in the top 10, it still contributes to excess mortality in some regions.
In 2024, middle-income countries continued to experience a shifting health landscape, with non-communicable diseases (NCDs) firmly dominating mortality statistics. Ischaemic heart disease remained the leading cause of death,
driven by aging populations, poor diets, and sedentary lifestyles, followed closely by stroke and other cerebrovascular diseases, especially in regions with underdiagnosed or poorly managed hypertension. Chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD) persisted as a major concern in areas with high rates of smoking and air pollution, while diabetes mellitus climbed further due to rising obesity and metabolic risk factors. Though lower respiratory infections still
posed a threat, improved vaccination and treatment efforts helped reduce their mortality impact. Kidney and liver diseases, often linked to diabetes, hypertension, alcohol use, and hepatitis, gained recognition as significant
contributors to death. Road traffic injuries remained a leading cause among young adults, and hypertensive heart disease continued to be prominent. Tuberculosis showed a gradual decline thanks to strengthened public health initiatives,
and HIV/AIDS dropped further in the rankings due to expanded access to antiretroviral therapy, though it still imposes a notable burden in some regions.
In 2024, the leading causes of death in low-income countries continued to reflect a dual burden of infectious diseases and non-communicable conditions, though the balance is gradually shifting. Lower respiratory infections
remained the top cause of death, especially among children under five, while stroke and ischaemic heart disease gained prominence, signaling the growing impact of chronic illnesses. Malaria remained a major killer in sub-Saharan
Africa, with hundreds of thousands of deaths annually, and preterm birth complications, birth asphyxia, and birth trauma continued to threaten newborns. Diarrhoeal diseases and tuberculosis persisted as significant risks despite
improvements in sanitation and care. HIV/AIDS declined in rank due to expanded access to antiretroviral therapy, though it still contributes meaningfully to the disease burden in certain regions. Meanwhile, COVID-19, while no
longer dominant, remained present in mortality data, and the rise of non-communicable diseases like heart disease and stroke reflects evolving health challenges in these countries.
According to the Global Asthma Report 2025, it's now estimated that over 260 million people worldwide live with asthma ,
a chronic disease of the the air passages of the lungs which inflames and narrows them. Most asthma-related deaths occur in low- and lower-middle income countries, where people often lack access to inhalers, preventive care,
or emergency treatment.
The human feet have 52 bones, which is 25% of all the bones in the body. The foot is an intricate structure containing 26 bones with thirty-three joints,
107 ligaments, 19 muscles and multiple tendons that hold the structure together and allow it to move in a variety of ways.
As of 2024, the number of Americans waiting for organ transplants remains critically high, with over 105,000 individuals on the national transplant waiting list. Despite a record-breaking year with more than 48,000 organ transplants
performed, the demand continues to outpace supply. A new person is added to the waiting list approximately every eight minutes, and 13 people die each day waiting for a suitable organ. This persistent gap underscores the urgent need for
expanded donor outreach, improved organ preservation, and continued reform of the transplant system.
In 2023, the number of Americans waiting for organ transplants remains high, with over 100,000 people on the national transplant waiting list. Below is a snapshot of the breakdown by organ type. These numbers
reflect a persistent gap between the number of people who need transplants and the availability of donated organs. Despite advances in transplantation and a record number of transplants performed in recent years, a new person
is added to the waiting list every 8 minutes, and over a dozen people die each day waiting for an organ. It's noted that more than 110,000 Americans are listed as waiting for organs, including 87,995 for kidneys; 16,108 for liver;
3,209 for heart; 1,802 for lung; 1,398 for pancreas; and 258 for intestine.
Kidney: 91,506
Liver: 9,003
Heart: 3,746
Lung: 904
Pancreas: 806
Intestine: 175
Kidney/Pancreas (combined): 2,293
As of August 2025, there are over 106,000 people on the national organ transplant waiting list in the United States. This number far exceeds the commonly cited figure of 87,000 and reflects the growing demand for life-saving transplants.
Every eight minutes, another person is added to the list, and tragically, 13 people die each day waiting for an organ that never comes. The need for donors remains urgent, and each registered donor has the potential to save up to eight lives and
enhance many more.
In 2024, the United States set another record in organ transplantation, performing over 48,000 transplants, a 3.3% increase from 2023. This growth was driven by improvements in donor outreach, surgical techniques, and organ
preservation. The breakdown included 27,759 kidney transplants, 11,458 liver transplants, 4,572 heart transplants, and 3,340 lung transplants, with lung transplants showing the largest proportional growth at 10.4%. Despite these
advances, wait times remain highly variable: kidneys still have the longest average wait at 3 to 5 years, livers typically take 6 to 12 months, hearts and lungs are usually transplanted within 3 to 6 months, and pancreas and
intestine transplants range from 1 to 2 years and 6 months to 1 year, respectively. Meanwhile, the organ transplant system is undergoing major reforms following federal investigations into ethical and procedural failures, aiming
to improve safety, transparency, and accountability across the network.
Scientists have developed advanced blood tests capable of detecting a single cancer cell circulating in the bloodstream, offering oncologists a powerful diagnostic tool for monitoring the spread of cancer. Known as circulating
tumor cell (CTC) tests or liquid biopsies, these technologies identify cancer cells that have separated from a primary tumor, providing critical insights into early metastasis and treatment response. While not yet standard for
initial diagnosis, tests like the FDA-cleared Cellsearch are already helping clinicians track progression in patients with metastatic breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers, and hold promise for broader applications in
personalized cancer care.
A report released on November 10, 2010 by the CDC found that around 49.9 million Americans aged 18-64 went at least part of the last twelve months without health care insurance coverage. As of early 2024, the CDC reported that
more than 8% of Americans were without health insurance, translating to approximately 27.1 million people. This marks an increase of about 3.4 million uninsured individuals compared to the same period in 2023, when the uninsured
rate was around 7.7%1. This uptick breaks a streak of record-low uninsured rates that followed the COVID-19 pandemic. A key factor behind the rise is the end of pandemic-era policies, such as the pause on Medicaid eligibility checks.
As states resumed these checks, many people lost coverage—a process known as Medicaid “unwinding”. Despite this recent increase, the broader trend since 2019 still shows improvement. Between 2019 and 2023, the number of uninsured
Americans dropped by 8.2 million, and the uninsured rate among working-age adults (18–64) fell from 14.7% to 10.9%.
Around 46 million Americans under the age of 65 were without health insurance since 2007. In 2024, the number of Americans under age 65 without health insurance is estimated to be around 27.1 million, or just over 8% of the population.
That’s a significant drop from the 46 million figure in 2007, reflecting long-term gains in coverage due to policy changes like the Affordable Care Act and expanded Medicaid access. However, this year has seen a slight reversal. The uninsured
rate has ticked up from 7.7% in 2023, largely due to the end of pandemic-era protections like continuous Medicaid enrollment—a process known as Medicaid “unwinding”. So while the overall trend since 2007 is positive, 2024 is a reminder that
coverage gains can be fragile.
In 2025, there is no federal COBRA premium subsidy like the one provided during the 2009 economic stimulus or the temporary 100% subsidy under the American Rescue Plan Act in 2021. Currently, individuals who elect COBRA
continuation coverage are generally responsible for paying the full premium cost, which includes both the employee and employer share, plus a 2% administrative fee. That said, COBRA still allows eligible individuals—such as
those who lose their job or experience reduced work hours—to maintain their employer-sponsored health insurance for 18 to 36 months, depending on the qualifying event. But without a subsidy, it can be quite expensive.
If COBRA feels out of reach financially, you might want to explore alternatives like (1) Marketplace plans through HealthCare.gov, which may offer subsidies based on income; (2) Medicaid, if your income qualifies;
and Short-term health plans, though these come with limitations. It's noted that in the past, people who lost their jobs can keep COBRA coverage under their former employer's plan for up to 18 months, visit the U.S.
Department of Labor’s COBRA page or call 1-866-444-3272 for personalized help.
If you've ever been hospitalized, do not make any decisions before you have received, and analyzed, all the bills. Once you've determined what you can afford, ask the hospital's credit officer for interest-free payments. If
the debt is truly unwieldy, ask for the Medicare rate (not the insurance rate) or a charity write-off.
In 2023–2024, global mortality data show that out of every 1,000 deaths, approximately 807 occurred in low- and middle-income countries, while 193 were from high-income countries. This means over 80% of all global deaths
took place in lower-income regions, reflecting persistent disparities in healthcare access, disease burden, and demographic trends. These proportions have remained relatively stable into 2024, with only slight shifts driven
by population aging and improvements in health systems in some areas.
As of 2024, the United States still lags behind many peer nations in physicians per capita, with approximately 3.13 practicing physicians per 1,000 people—well below countries like Austria (5.2), Germany (4.3), and Switzerland (4.3).
In contrast, the U.S. maintains a relatively high number of licensed nurses, with about 11.9 per 1,000 people, though this is lower than the 17.5 per 1,000 reported in 2020 and trails countries like South Korea (20.5) and
Sweden (19.7). U.S. hospitals also remain heavily staffed, employing around 5.92 million people, or roughly 17.3 hospital employees per 1,000 people, with a significant share still working in administrative roles.
While the U.S. health system is resource-intensive, much of its workforce remains concentrated in non-clinical functions, contributing to high costs without necessarily improving care delivery.
As of 2025, the United States has approximately 1.1 million active physicians, including about 566,700 specialists—with emergency medicine being the most common specialty—and an estimated 535,000 primary care physicians,
based on recent workforce trends. California continues to lead the nation with the highest number of practicing physicians, while North Dakota remains among the states with the fewest, though updated state-level figures are
still being finalized. For historical context, in 2019, the U.S. had 1,005,295 active physicians, comprising 479,856 primary care doctors and 525,439 specialists. At that time, California had the largest physician
workforce (112,906), while North Dakota had the smallest (2,015).
Dr. Daniel Hale Williams (January 18, 1856 – August 4, 1931) was the first African American
general surgeon , who in 1893 performed the first documented, successful
pericardium surgery in the United States to repair a wound. A pericardial window is a
cardiac surgical procedure to create a fistula –
or "window" – from the pericardial space to the pleural cavity to allow a
pericardial effusion
(usually malignant) to drain from the space surrounding the heart into the chest cavity – where the fluid is not as dangerous; an untreated pericardial
effusion can lead to cardiac tamponade and death.
Graduated from Northwestern University Medical School , Dr. Williams opened a private practice where his patients were white
and black. Black doctors, however, were not allowed to work in American hospitals at that time; as a result, in 1891, Dr. Williams founded the
Provident Hospital and training school for nurses in Chicago, IL.
Dr. Henry Dalton was the first American to
successfully perform pericardium surgery to repair a wound. Earlier successful surgeries to drain the pericardium, by performing a pericardiostomy were done by
Dr. Francisco Romero in 1801 and Dr. Dominique Jean Larrey in 1810.As of 2025, the global health workforce is estimated to exceed 104 million people, a substantial increase from the 60 million reported in 2010. This includes 12.8 million physicians, 29.8 million nurses and midwives,
4.6 million dentistry personnel, 5.2 million pharmaceutical personnel. This growth reflects global efforts to strengthen health systems, especially in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and the push toward universal health coverage.
However, the distribution remains highly uneven—many low- and middle-income countries still face critical shortages, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
A 2018 study led by MIT economist Amy Finkelstein found that medical expenses directly cause only about 4% of personal bankruptcies among non-elderly adults in the U.S.—a stark contrast to earlier claims that pegged the
figure as high as 60%. The researchers employed a more rigorous approach by linking hospitalization data with credit reports, enabling them to isolate the causal impact of medical events on bankruptcy filings. While the study
confirmed that medical issues often lead to financial strain, reduced income, and job loss, it concluded that bankruptcy is a relatively uncommon outcome of medical hardship.
In 2025, medical billing overcharges remain a widespread concern. According to patient advocacy groups like Medical Billing Advocates of America and PatientRightsAdvocate.org, many hospital bills still contain inflated
or erroneous charges, despite federal price transparency rules. Recent analyses of itemized bills have uncovered examples such as $15 for a single Tylenol, $53 for a pair of non-sterile gloves, $8 for a plastic bag to hold personal
items, $10 for a disposable medicine cup, $23 per alcohol swab, and $93.50 for use of an overhead surgical light. Advocates report that up to 80% of medical bills contain errors or unjustified charges, often buried in complex billing
systems that make it difficult for patients to verify costs. Despite regulations requiring hospitals to publish standard prices, enforcement remains inconsistent, and many charges still fall outside publicly listed rates
Although hospital list prices —also known as chargemaster rates—are rarely the actual amounts paid by
patients or insurers, they still serve as a starting point for negotiations with commercial payers. These publicly posted rates reflect the hospital’s standard charges for services, but the final payments vary widely depending
on the payer, whether it's a private insurer, Medicare, Medicaid, or an individual paying out of pocket. Under current federal transparency rules, hospitals must now disclose both their list prices and payer-specific negotiated
rates, enabling consumers to better compare costs and understand the often significant differences in what various payers are charged.
The prices on a hospital's chargemaster bear little relationship to the amount most patients are asked to pay. That's because commercial insurers or government (e.g.; Medicare, Medicaid) negotiate discounts with healthcare
providers on behalf of their members, and the costs are often less than the actual cost of care. Hospitals' rising list prices primarily affect the uninsured and people with coverage but who seek care at hospitals outside of
their insurance network. Many hospitals often allow low-income patients who are uninsured to receive free care or care for a reduced charge.
When facing with a medical issue, choosing between the emergency room (ER) and urgent care can make a big difference in both treatment and cost. If a condition could permanently harm the health
or is life-threatening, go to the ER, and if it’s urgent but not critical, urgent care is often the better option.
Emergency room is best for life-threatening conditions like heart attacks, strokes, severe injuries, major allergic reactions, difficulty breathing, or sudden loss of consciousness; it's
available 24/7, equipped to handle severe trauma and complex medical issues; however, wait time can be long, as patients are treated based on severity, not arrival time, and cost ($1,000 - $3,000+)
is typically higher due to advanced medical equipment and specialist care.
Urgent care is best for non-life-threatening conditions like minor fractures, sprains, infections, flu symptoms, cuts needing stitches, or mild asthma issues. It's generally open extended hours,
including evenings and weekends, but not 24/7; wait time is usually shorter than ER, as patients are treated on a first-come, first-served basis; and cost ($100 - $250) is more affordable than
ER visits, often similar to a regular doctor’s appointment.
More than 4,000 preventable mistakes occur in surgery every year in the U.S. These include serious mistakes like operating on the wrong body part,
performing the wrong procedure, or leaving surgical instruments inside a patient. A Johns Hopkins study found that foreign objects (like sponges or towels) are left inside patients about 39 times a week, and wrong-site or wrong-procedure
surgeries happen around 20 times a week.Before the introduction of penicillin in 1943, syphilis was a widespread and deadly disease that killed thousands each year and caused serious
long-term health issues. The first major outbreak in Europe occurred in 1495 during the French invasion of Naples, Italy, where it became known as the “Disease of Naples.” As the epidemic spread, different countries blamed one
another for its origin, giving rise to stigmatizing names: the English called it the “French disease,” the French called it the “Spanish disease,” Germans dubbed it the “French evil,” Russians referred to it as the “Polish disease,”
Poles blamed the “Turkish disease,” Turks labeled it the “Christian disease,” and the Japanese named it the “Chinese pox.” These shifting names reflected national biases and social stigma long before the disease was scientifically
understood or effectively treated.
Arsenic poisoning is a medical condition that occurs due to elevated levels of arsenic
in the body. If exposure occurs over a brief period of time symptoms may include vomiting , abdominal
pain , encephalopathy , and watery diarrhea that contains
blood . Long-term exposure can result in thickening of the skin, darker skin , abdominal pain,
diarrhea, heart disease , and numbness . Arsenic increases the risk of
cancer . Exposure is related to skin, lung, liver, and kidney cancer among others.Human papillomavirus (HPV) , the most common sexually transmitted infection, is found in about 99% of cervical
cancers, and is the second most common type of cancer for women worldwide. By the age 50 approximately 80% of women have been infected with some type of HPV;
more than 12,000 women in the United States is diagnosed with cervical cancer each year , and over 4,000 of women die annually.The human body has 206 bones in adulthood, with more than half of them—54 in the hands and 52 in the feet—concentrated in the extremities, making these areas remarkably flexible and capable of intricate movement.
Each hand contains 27 bones (including those of the wrist, palm, and fingers), while each foot comprises 26 bones (found in the ankle, arch, and toes). Fascinatingly, babies are born with approximately 270 bones, many of
which are made of cartilage; as they grow, several bones—especially in the skull and spine—gradually fuse together, resulting in the standard 206 bones found in adults.
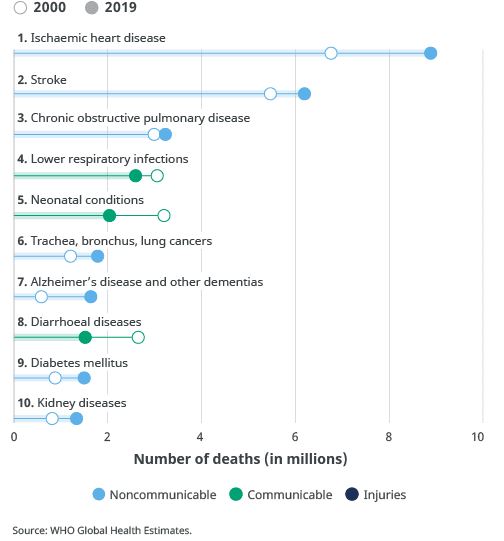
According to recent data from the World Health Organization, the top 10 leading causes of death globally include ischaemic heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lower respiratory infections,
neonatal conditions, trachea, bronchus, and lung cancers, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, diarrhoeal diseases, diabetes mellitus, and kidney diseases. While HIV/AIDS and road injuries remain significant public health
concerns, they no longer rank within the top 10 globally, and hypertensive heart disease is typically grouped under broader cardiovascular categories. This list reflects shifting global health trends due to advances in
treatment, aging populations, and evolving disease burdens.
Diagnostic errors are the leading cause of medical malpractice claims in the U.S., accounting for approximately 26.6% of all allegations, and are associated with particularly serious outcomes—39% of such claims
involve patient death. Each year, millions of Americans are affected by misdiagnoses, with estimates suggesting that up to 795,000 people die or suffer permanent disability as a result. The overall diagnostic error rate
across diseases is around 11.1%, with conditions like stroke, sepsis, and lung cancer being especially vulnerable to misdiagnosis due to their complex presentations and time-sensitive nature, highlighting a critical
area for improvement in patient safety and healthcare quality.
Body temperature naturally varies by person and time of day—typically about 1°F higher in the afternoon than early morning. While 98.6°F (37°C) has long been considered "normal," newer research suggests the average
is closer to 97.5°F (36.4°C). Despite these variations, a temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher is widely recognized as a clinical fever and often signals infection or illness.
As of 2025, UnitedHealth Group is under criminal investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice for
potential Medicare fraud . The probe, reportedly active
since mid-2024, centers on allegations that the company pressured physicians to assign diagnoses that would trigger higher Medicare Advantage reimbursements. If substantiated, this practice—known as upcoding—could constitute fraud
by artificially inflating the severity of patients’ conditions to secure larger government payments. Such tactics have drawn scrutiny across the Medicare Advantage industry, where some insurers have been accused of exploiting
diagnostic coding to boost profits. UnitedHealth has previously faced civil investigations over its billing practices, and the current criminal inquiry marks a significant escalation in regulatory oversight. Despite the controversy,
UnitedHealth Group reported $400.3 billion in revenue for 2024, reflecting an 8% year-over-year increase—underscoring its dominant position in the healthcare market.
▷ Common Illnesses
Common illnesses span everything from fast‑moving infectious diseases to long‑term non‑infectious conditions, creating a landscape where viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites intersect with chronic disorders shaped by
genetics, environment, and daily habits. This mix includes familiar infections like colds, flu, and strep throat alongside enduring conditions such as asthma, diabetes, and hypertension. While infectious illnesses often
hinge on exposure and transmission, non‑infectious ones tend to emerge from internal imbalances or long‑term influences, making the contrast between them both practical and fascinating. Understanding how these categories
differ—one driven by microscopic invaders, the other by physiology and circumstance—reveals the diverse ways health can be challenged across a lifetime.
Influenza stands out as a viral illness that practically feeds on human interaction, moving swiftly through communities by hitching a ride on respiratory droplets released during everyday moments like talking, coughing, or sneezing.
Those droplets can settle on surfaces or drift through shared air, turning crowded indoor spaces and close contact into ideal opportunities for the virus to leap to a new host. Seasonal changes often amplify its reach, helping it
surge through schools, workplaces, and households with remarkable speed.
Asthma occupies a very different place in the landscape of illness, functioning as a chronic condition rather than something that passes from person to person. Its roots lie in a mix of genetic tendencies, immune system behavior,
and environmental triggers such as pollen, smoke, cold air, or physical exertion. When symptoms surge, the flare‑ups can be intense, but they stem from an individual’s sensitivity to irritants or allergens rather than any infectious
agent. Unlike illnesses driven by pathogens, asthma never spreads through contact or proximity; each episode is a personal reaction shaped by the body’s own responses and the surrounding environment.
Strep throat is an infectious illness driven by Streptococcus pyogenes, a bacterium that spreads readily from one person to another. It travels through respiratory droplets released during coughing, sneezing, or close conversation,
and it can also move through shared surfaces, utensils, or other objects touched in quick succession. Its contagious nature makes it especially common in places where people gather closely—classrooms, households, and workplaces
often see cases appear in clusters as the bacteria find new hosts with ease.
Allergies, unlike infectious illnesses, stem from the immune system reacting too strongly to harmless substances such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods. These reactions can produce symptoms that resemble being
sick—sneezing, congestion, even a scratchy throat—but no pathogen is involved, and nothing passes from one person to another. Each episode is sparked by direct exposure to an allergen, making it a personal immune response rather
than something that spreads through contact or proximity.
Chronic bronchitis, which isn’t infectious, is a long‑lasting inflammatory condition of the airways often tied to smoking, air pollution, or repeated exposure to lung irritants. Rather than being triggered by a pathogen, it
develops slowly as the bronchial tubes become persistently inflamed and begin producing excess mucus. The resulting cough and breathing difficulties can resemble symptoms of an infection, but the condition doesn’t spread between
people; each case reflects an individual’s history of exposure and the cumulative effects of long‑term airway irritation rather than any form of transmission.
Athlete’s foot, a common fungal infection caused by dermatophytes that thrive in warm, moist environments, typically begins when these fungi invade the outer layers of skin—often between the toes—after contact with contaminated
floors, towels, or footwear. An infected person becomes a carrier while the fungus is active on the skin, shedding microscopic spores that can spread the infection in shared spaces such as locker rooms or swimming areas. After exposure,
the incubation period can vary from a few days to a couple of weeks before symptoms appear, usually starting with itching, burning, or stinging sensations, followed by peeling, cracking, redness, or blistering of the affected skin.
The condition may progress slowly or flare in cycles, sometimes spreading to the soles or toenails if left unaddressed. Treatment focuses on antifungal creams, sprays, or powders, along with keeping the feet dry, changing socks
regularly, and avoiding tight footwear, while more persistent cases may require prescription antifungal medications to fully clear the infection.
Herpes, caused by herpes simplex viruses type 1 and type 2, begins when the virus enters tiny breaks in the skin or mucous membranes during close contact, establishing a lifelong presence in nerve cells where it can reactivate
periodically. An infected individual becomes a carrier for life, shedding the virus during active outbreaks and sometimes even when the skin appears normal, which allows transmission through kissing, oral contact, or sexual activity
depending on the viral type. After an incubation period that generally ranges from 2 to 12 days, symptoms may appear as clusters of painful blisters, burning or tingling sensations, swollen lymph nodes, fever, or general discomfort,
though many infections remain silent. The illness tends to follow a pattern in which initial outbreaks are more intense and prolonged, while later recurrences are shorter and milder as the immune system gains control. Treatment
focuses on antiviral medications that reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks, along with supportive measures to ease discomfort, helping the body manage the virus as it cycles between dormancy and reactivation.
Yellow fever moves with a kind of fierce elegance: the virus enters the body through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito, settles into the bloodstream, and turns the infected person into
a carrier during the period when the virus circulates at high levels—usually from shortly before symptoms begin until several days into the illness. After an incubation period of about 3 to 6 days, the first wave of symptoms arrives
abruptly with fever, chills, headache, back pain, nausea, and a general sense of bodily upheaval. Many cases stop there, resolving within a few days, but a smaller portion take a darker turn as the disease enters its toxic phase,
marked by jaundice, abdominal pain, bleeding, organ stress, and a return of high fever. The course can shift quickly, moving from mild illness to severe, life‑threatening complications as the liver and kidneys struggle under the
viral assault. Treatment focuses on supportive care—hydration, monitoring, and management of organ strain—since no antiviral cure exists, while prevention relies on the highly effective yellow fever vaccine, which remains the
strongest barrier against a disease that once reshaped entire regions with its sudden, intense outbreaks.
Impetigo, a highly contagious skin infection caused mainly by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, begins when these bacteria enter through small cuts, insect bites, or irritated skin, allowing them to multiply on
the surface and form the condition’s characteristic honey‑colored crusts. An infected person becomes a carrier while the bacteria are active in the lesions, spreading them through direct skin‑to‑skin contact or shared items such as
towels, clothing, or sports equipment. After an incubation period that typically ranges from 1 to 3 days for streptococcal infections and up to 10 days for staphylococcal ones, symptoms appear as red sores or blisters that quickly
rupture and form golden crusts, often accompanied by mild itching or tenderness. The illness usually progresses locally, spreading outward from the initial spot or appearing in new areas if the bacteria move across the skin, though
it rarely causes deeper complications. Treatment focuses on gentle cleansing of affected areas, topical or oral antibiotics depending on severity, and hygiene measures that limit further spread, allowing the skin to heal as the
bacterial load diminishes and the crusts gradually resolve.
Leprosy, caused by the slow‑growing bacterium Mycobacterium leprae, begins when the organism enters the body through prolonged close contact, often via respiratory droplets, eventually settling in the skin and peripheral nerves
where it triggers chronic inflammation. A person with untreated leprosy can act as a carrier while the bacteria are present in nasal secretions or skin lesions, though transmission requires extended exposure rather than casual contact.
After an unusually long incubation period—typically 3 to 5 years but sometimes stretching beyond a decade—symptoms emerge gradually as pale or reddish skin patches with reduced sensation, numbness in hands or feet, muscle weakness,
or thickened nerves, and in some forms, nodules or facial changes. The illness progresses slowly, with nerve damage accumulating over time if untreated, potentially leading to loss of sensation, injuries that go unnoticed, and
secondary complications affecting the eyes, limbs, or skin. Treatment relies on multidrug therapy using a combination of antibiotics provided through global health programs, which stops the infection and prevents further nerve
damage, while supportive care such as wound management, physical therapy, and protective measures helps restore function and limit long‑term effects as the body recovers.
Mumps unfolds like a small viral drama: the mumps virus slips in through respiratory droplets, settles into the upper airway, and quietly turns its host into a contagious carrier for several days before and after the trademark
cheek swelling appears. After an incubation stretch of roughly two to three weeks, the illness tends to announce itself with fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches before the parotid glands swell and create the classic chipmunk‑like
look. The infection usually moves through a predictable arc—first a subtle prodrome, then several days of gland tenderness, and finally a slow easing as the swelling fades—though it can occasionally wander into more serious territory
with inflammation of the testes, ovaries, pancreas, or even the nervous system. Care revolves around rest, hydration, cool or warm compresses, and general symptom relief while the body clears the virus, and widespread vaccination
remains the force that keeps this once‑common childhood infection from regaining its old momentum.
Plague begins when Yersinia pestis—a bacterium carried by fleas that feed on infected rodents—finds its way into the body, setting off an infection that can take the form of bubonic, septicemic, or pneumonic disease depending on where
it spreads. A person becomes a carrier when the bacteria circulate in the bloodstream or, in the case of pneumonic plague, when the lungs are involved and infectious droplets are expelled during coughing, making this form especially
dangerous in close quarters. After an incubation period that usually spans 1 to 7 days, symptoms strike with abrupt intensity: swollen and painful lymph nodes called buboes in bubonic plague, sudden fever and weakness in septicemic cases,
or rapidly worsening cough and chest pain in pneumonic disease. The illness can escalate quickly, with bubonic plague progressing over several days, septicemic plague causing shock or bleeding complications, and pneumonic plague advancing
at a pace that demands immediate attention. Treatment relies on prompt use of appropriate antibiotics along with supportive care to stabilize the body as the infection is brought under control, a combination that has transformed this
once‑devastating disease into a highly treatable condition when recognized early.
Rubella moves with a kind of deceptive lightness: the rubella virus slips into the body through respiratory droplets, settles in the throat, and quietly turns its host into a carrier who can spread it for about a week before the
telltale rash appears and for several days afterward. After an incubation period that usually runs 14 to 21 days, the illness often begins gently with low fever, swollen lymph nodes behind the ears or at the back of the neck, and a
sense of mild discomfort before a fine, pink rash sweeps across the face and travels downward. The course tends to be brief and understated, with the rash fading within three days and most symptoms resolving soon after, though joint
pain can linger in some adults. Treatment focuses on rest, fluids, and easing discomfort while the immune system clears the virus, and widespread vaccination remains the force that keeps this once‑circulating infection from regaining
its foothold.
Scarlet fever tends to sweep in with a dramatic flair: a Streptococcus pyogenes infection—usually starting as strep throat—releases a toxin that sparks the illness’s signature red rash, turning the host into a carrier who can spread
the bacteria through respiratory droplets while coughing, sneezing, or even talking. After an incubation period of roughly 2 to 4 days, the infection often announces itself with sudden fever, sore throat, swollen glands, and a “strawberry”
appearance of the tongue before the fine, sandpaper‑like rash races across the torso and limbs. The course usually unfolds over several days, with the rash deepening, then peeling as the fever settles and the throat pain eases, though
untreated cases can wander into more serious territory such as ear infections, abscesses, or inflammatory complications. Treatment relies on appropriate antibiotics to clear the bacteria, paired with rest, fluids, and soothing care for
the throat and skin, allowing the body to regain its balance as the vivid flush of the illness fades.
Skin fungus tends to creep in quietly, thriving in warm, damp corners of the body where dermatophytes or yeasts can settle in after contact with infected skin, animals, or contaminated surfaces, turning the host into a temporary
carrier as long as active fungal growth remains on the skin or nails. After an incubation period that typically ranges from a few days to about two weeks depending on the specific fungus, symptoms begin to surface as itching, redness,
scaling, or the classic ring‑shaped patches of tinea infections, while yeast‑driven rashes often appear in moist folds as red, irritated, sometimes oozing patches. The course of illness varies from mild, localized irritation to more
persistent or spreading lesions if moisture, friction, or untreated overgrowth give the fungus room to flourish, though deeper complications are uncommon. Treatment revolves around antifungal creams or powders for superficial infections
and oral medications for more stubborn or widespread cases, paired with simple but powerful habits—keeping skin dry, avoiding shared towels or clothing, and choosing breathable fabrics—to help the body reclaim its territory as the fungal
colonies fade.
Walking and regular exercise have been shown to lower Alzheimer’s risk by up to 45%, with even modest activity—such as 3,000 to 5,000 steps a day—delaying progression by about 3 years, while 5,000 to 7,500 steps can delay
decline by as much as 7 years. Just 20 minutes of exercise twice a week or daily activities like gardening and cooking can reduce dementia risk by 20%, and those who remain most active in later life are more than twice as
likely to avoid Alzheimer’s compared to the least active. The benefits extend beyond walking, as strength training helps regulate blood sugar and reduce diabetes risk, while balance and flexibility exercises prevent falls
that could accelerate cognitive decline. By boosting blood flow, oxygen delivery, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, exercise strengthens neurons, reduces inflammation, and counters the damaging effects of amyloid
plaques and tau tangles, making consistent physical activity one of the most powerful lifestyle defenses against Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease, the most common form of dementia, is a progressive brain disorder that usually begins after age 60 but can occasionally strike younger individuals, affecting more than 6.9 million Americans over 65. It
starts with short-term memory loss and gradually erodes judgment, language, and other intellectual functions until most people with advanced Alzheimer’s lose the ability to perform daily activities. The condition is marked by
excessive deposits of two proteins—amyloid plaques and tau tangles—that distort communication between brain cells, leading to widespread cell death and brain shrinkage. Scientists remain uncertain about the exact cause, but
research continues to uncover how these proteins trigger symptoms. With age, genetics such as the APOE-e4 gene, and cardiovascular health acting as major risk factors, Alzheimer’s represents one of the greatest medical
challenges of our time, driving global efforts to find treatments that slow progression and ultimately a cure.
Gut bacteria are emerging as key players in human health, with the young but rapidly expanding science of the microbiome revealing surprising links to conditions as varied as hypertension, diabetes, and depression. Studies
suggest that microbial imbalances may influence blood pressure regulation, insulin sensitivity, and even mood through complex pathways involving inflammation, neurotransmitters, and immune responses. Researchers have identified
specific bacterial strains that may contribute to both physical and mental health challenges, including Morganella morganii and Eggerthella, which are associated with inflammation and depressive symptoms. As scientists continue
to decode the gut-brain and gut-heart axes, the microbiome is proving to be a powerful frontier in understanding—and potentially treating—a wide range of chronic conditions.
Hepatitis A, caused by the hepatitis A virus that targets the liver, spreads when contaminated food or water introduces the virus into the body or when close contact allows exposure to microscopic traces of infected stool,
turning an infected person into a temporary carrier who can shed the virus before and during symptoms. After an incubation period that typically lasts 15 to 50 days, the illness often begins gradually with fatigue, nausea,
stomach discomfort, loss of appetite, low‑grade fever, and sometimes dark urine or pale stools, followed by the onset of jaundice as bilirubin builds up in the bloodstream. The course of hepatitis A usually spans several weeks,
with symptoms peaking and then slowly resolving as liver inflammation subsides, though full recovery can take months in some cases. Treatment focuses on supportive care—rest, hydration, and balanced nutrition—while the liver
heals on its own, and preventive measures such as vaccination and good hygiene remain the most effective tools for stopping transmission and protecting communities.
Cold sores are small, fluid-filled blisters that typically appear on or around the lips and are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV)—most often HSV-1, though HSV-2 can also be responsible. After the initial infection, which may
not produce any symptoms, the virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate later, leading to recurrent outbreaks. These outbreaks often begin with a tingling or burning sensation, followed by the appearance of blisters that
eventually crust over and heal within 7 to 10 days. If symptoms do occur during the primary infection, they can be more severe and may include fever, sore throat, painful gums, swollen lymph nodes, and muscle aches. Triggers for recurrence
include stress, illness, sun exposure, and fatigue.
Stomach flu, more accurately called viral gastroenteritis, develops when viruses such as norovirus or rotavirus infect the stomach and intestines, typically spreading through contaminated food or water, shared surfaces, or close
contact with an infected person who sheds the virus in stool or vomit. A carrier becomes contagious as soon as the virus begins multiplying in the digestive tract, often even before symptoms appear, which helps the illness move quickly
through households, schools, and other close‑contact settings. After an incubation period that usually ranges from 12 hours to 2 days, symptoms strike suddenly with nausea, vomiting, watery diarrhea, stomach cramps, low‑grade fever,
and general fatigue. The illness tends to run its course over one to three days, though lingering tiredness or mild digestive upset can persist a bit longer. Treatment focuses on supportive care—rest, steady hydration with fluids or
oral rehydration solutions, and gradual return to bland foods—while severe dehydration may require medical attention, especially in vulnerable individuals.
The flu, or influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. It typically comes on suddenly and can cause symptoms such as fever, chills, cough, sore throat, muscle aches,
fatigue, and headache. While most people recover within a week or two, the flu can lead to serious complications—like pneumonia—especially in young children, older adults, pregnant women, and those with chronic health conditions. Treatment
often involves rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. In some cases, doctors may prescribe antiviral drugs, which work best when taken within the first 48 hours of symptoms. The best defense is prevention:
getting an annual flu vaccine significantly reduces your risk of infection and severe illness.
Pneumonia is a lung infection that causes inflammation in the tiny air sacs of the lungs, known as alveoli, which then fill with fluid or pus, making it difficult to breathe and absorb oxygen. It’s most commonly caused by bacterial infections,
though viruses and fungi can also be responsible. Symptoms may develop suddenly within 24 to 48 hours or more gradually over several days, and can include cough with phlegm, fever, chills, chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. The
condition tends to be more prevalent during autumn and winter, especially among older adults, young children, and those with weakened immune systems. Treatment depends on the cause and severity, ranging from rest and fluids to antibiotics or
hospitalization for more serious cases.
A sore throat, medically known as pharyngitis, is a common condition characterized by pain, scratchiness, or irritation in the throat, often worsened by swallowing or talking. It’s most frequently caused by viral infections like the
common cold or flu, but can also result from bacterial infections (such as strep throat), allergies, dry air, or irritants like smoke. Symptoms may include redness, swelling, hoarseness, fever, cough, and swollen lymph nodes, depending on
the underlying cause. Most sore throats resolve on their own within a few days, but persistent or severe cases—especially those with high fever, difficulty swallowing, or white patches on the tonsils—should be evaluated by a healthcare
provider.
Cough isn’t a single disease but a reflex that shows up when something irritates the airways, and its story depends on what triggered it. Infection often begins when viruses or bacteria settle into the nose, throat, or lungs—common
culprits include cold viruses, influenza, pertussis, or, in some cases, bacterial pneumonia—setting off inflammation that makes the airway lining hypersensitive. A person becomes a carrier only when the cough is caused by an infectious
agent, shedding germs in droplets while talking, laughing, or coughing, especially during the early, most contagious days of a viral illness. Incubation varies widely: a simple cold may take just a couple of days to appear, while other
infections have longer lead‑ins, but the cough itself usually emerges as the airways react to swelling, mucus, or post‑nasal drip. Symptoms can range from a dry tickle to a deep, chesty rumble, sometimes accompanied by fever, congestion,
sore throat, or shortness of breath depending on the underlying cause. The course may be brief—fading within a week or two for most viral infections—or linger for weeks when airway sensitivity persists, allergies flare, or irritants
like smoke keep the reflex active. Treatment focuses on the root cause: rest and fluids for viral infections, targeted antibiotics only when a bacterial illness is confirmed, and supportive measures such as humidified air, throat
soothing, or cough suppressants when appropriate, all helping the airways settle as the underlying irritation resolves.
Whooping cough has a way of unfolding in sharp, memorable stages: Bordetella pertussis settles into the airways after being inhaled in respiratory droplets, turning the infected person into a carrier who can spread the bacteria long
before the signature coughing fits appear and for several weeks afterward. After an incubation period that typically runs 7 to 10 days—though it can stretch to nearly three weeks—the illness begins with what seems like an ordinary cold:
mild fever, runny nose, sneezing, and a light cough. Then the second act arrives, marked by violent, rapid coughing spells that empty the lungs until a forceful, high‑pitched “whoop” follows as air rushes back in; vomiting after coughing
and sheer exhaustion are common companions during this phase. The course can drag on for weeks or even months, with the paroxysmal cough slowly easing as the body clears the bacteria and the irritated airways heal. Treatment focuses on
targeted antibiotics to shorten contagiousness and supportive care to manage the relentless coughing, while vaccination remains the powerful shield that keeps this once‑devastating childhood illness from reclaiming its old reach.
A headache is a common condition involving pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck, and can range from mild pressure to intense throbbing. There are over 150 types, with the most frequent being tension headaches, migraines,
cluster headaches, and sinus headaches—each with distinct patterns and triggers such as stress, dehydration, lack of sleep, hormonal changes, or certain foods. While most headaches are not dangerous, sudden or severe ones accompanied by
symptoms like confusion, vision changes, or weakness should be medically evaluated. Understanding your headache type can help guide effective treatment, whether through lifestyle adjustments, medications, or targeted therapies.
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a potentially life-threatening condition in which the abdominal portion of the aorta—the body’s main artery—becomes weakened and bulges outward. Often developing slowly and without symptoms, AAAs
can cause deep abdominal or back pain and a pulsing sensation near the navel, especially if they grow large or rupture. Risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, advanced age (particularly over 65), male sex, and a family history
of aneurysms. Diagnosis is typically made through imaging such as ultrasound or CT scan, and men aged 65–75 who have ever smoked are advised to undergo screening. Treatment depends on the size and growth rate of the aneurysm, ranging from
regular monitoring to surgical repair, which may be performed through open surgery or a less invasive endovascular procedure.
Tapeworm infection begins when Taenia or other tapeworm species enter the body through undercooked meat, contaminated food, or contact with eggs shed in human or animal feces, allowing the parasite to settle in the intestine and quietly
turn the host into a carrier as long as segments or eggs continue to pass in stool. After an incubation period that can stretch from several weeks to a few months depending on the species, symptoms may range from subtle digestive discomfort,
nausea, or changes in appetite to visible tapeworm segments in stool, though many infections remain almost silent. The course of illness often unfolds slowly, with the parasite growing and shedding segments over time, and in rare
cases—especially when eggs rather than larvae are ingested—larvae can migrate into tissues and cause cysticercosis, a far more serious condition that can affect muscles, eyes, or the nervous system. Treatment relies on targeted
antiparasitic medications that eliminate the intestinal tapeworm, along with supportive care and, when necessary, additional therapies for tissue‑based infections, allowing the body to clear the parasite and return to equilibrium
once the life cycle is interrupted.
Typhoid fever begins when Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi slips into the body through contaminated food or water, settling first in the intestine and then spreading through the bloodstream, turning the infected person into a carrier
as long as the bacteria remain active in stool or, in some cases, the gallbladder. After an incubation period that usually spans 6 to 30 days, the illness often starts with a creeping fever, headache, abdominal discomfort, and profound
fatigue before giving way to more distinctive signs such as rose‑colored spots on the trunk, constipation or diarrhea, and a steadily rising temperature that can climb in a stepwise pattern. The course of typhoid can stretch over several
weeks if untreated, with fever lingering, the abdomen becoming increasingly tender, and complications such as intestinal bleeding or delirium emerging in severe cases, while chronic carriage may persist in a small number of individuals
even after symptoms fade. Treatment relies on targeted antibiotics to clear the infection, along with hydration and supportive care to steady the body as it recovers, and preventive measures such as vaccination and safe food and water
practices remain the strongest defense against this persistent, water‑borne disease.
Acute cholecystitis is a sudden inflammation of the gallbladder, typically caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct, which leads to a buildup of bile and irritation of the gallbladder wall. This condition can cause intense pain
in the upper right abdomen, often radiating to the back or right shoulder, along with fever, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness over the affected area. Symptoms often worsen after eating, especially fatty meals. If left untreated, it can lead
to serious complications such as infection, tissue death, or rupture of the gallbladder, which may be life-threatening. Diagnosis typically involves imaging like ultrasound or CT scan, and treatment usually requires hospitalization, with
options ranging from antibiotics and pain management to surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, begins when the organism infects mucous membranes of the urethra, cervix, rectum, throat, or eyes, allowing it to multiply and spread through
intimate contact. An infected individual becomes a carrier while the bacteria are active in genital, rectal, or throat secretions, making transmission possible even when symptoms are mild or absent. After an incubation period that typically
ranges from 2 to 7 days, symptoms may appear as burning during urination, increased genital discharge, pelvic discomfort, or, in some cases, rectal pain or sore throat, though many infections remain silent. The illness can progress from
localized irritation to more serious complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease or epididymitis if untreated, and it may also spread through the bloodstream in rare cases. Treatment relies on targeted antibiotics chosen to address
current resistance patterns, paired with partner notification and follow‑up testing to ensure the infection clears and further transmission is prevented.
Syphilis unfolds in distinct, almost theatrical stages: Treponema pallidum enters through tiny breaks in the skin or mucous membranes during intimate contact, establishing an infection that turns the host into a carrier as long as
the bacteria remain active in blood or lesions. After an incubation period that typically stretches from 10 to 90 days, the first act appears as a firm, painless sore—often unnoticed—at the site of entry, followed by a second stage
marked by rash, swollen lymph nodes, fever, and patchy hair loss as the bacteria spread more widely. The illness may then slip into a long, quiet latent phase, lingering silently for years before reemerging as tertiary syphilis, a
destructive form that can damage the heart, brain, nerves, or other organs. Treatment relies on targeted antibiotics that clear the infection at any stage, paired with follow‑up testing and partner management to halt transmission,
allowing the body to recover as the bacteria are eliminated and the disease’s progression is brought to a stop.
Trichomoniasis tends to unfold with a subtle, almost stealthy rhythm: Trichomonas vaginalis, a single‑celled parasite, passes from one person to another during sexual contact, settling into the urogenital tract and turning the
infected individual into a carrier as long as the organism remains active in vaginal or urethral secretions. After an incubation period that usually ranges from about 5 to 28 days, symptoms may surface—or remain entirely absent—with
possibilities including itching, burning, genital irritation, discomfort during urination or intercourse, and in some cases a frothy or unusual discharge, while many carriers experience nothing more than a vague sense that something
feels off. The course of the infection can be persistent, lingering for months or even years if untreated, with symptoms that may flare or fade unpredictably. Treatment centers on targeted antiparasitic medication that clears the
organism from the body, paired with partner management to prevent reinfection, allowing the infection’s quiet cycle to come to an end once the parasite is eliminated.
Candidiasis, a fungal infection caused by various Candida species—most commonly Candida albicans—takes hold when these normally harmless organisms overgrow on the skin, in the mouth, in the gastrointestinal tract, or in the genital
area, often after shifts in moisture, immunity, or the body’s microbial balance. An infected individual can act as a carrier while the fungus is active on the skin or mucous membranes, allowing spread through close contact, shared personal
items, or, in the case of oral or genital candidiasis, intimate contact, though many cases arise from internal overgrowth rather than transmission. After exposure or internal imbalance, the incubation period varies widely, with symptoms
emerging within days or developing gradually depending on the site. Manifestations range from white patches and soreness in oral thrush to itching, redness, and discharge in genital infections, or cracked, irritated skin in cutaneous
forms. The course of illness can be brief with prompt care or persistent when underlying factors—such as moisture, antibiotic use, diabetes, or weakened immunity—remain unaddressed. Treatment centers on antifungal medications applied
topically or taken orally, along with measures that reduce moisture, restore microbial balance, and address contributing conditions, allowing the affected tissues to recover as the fungal load returns to normal levels.
Acne is a widespread skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to various types of blemishes such as whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
It most commonly appears on the face, chest, shoulders, and back—areas with high concentrations of oil glands. Symptoms can range from mild spots and oily skin to painful, inflamed cysts and nodules that may feel hot or tender to the touch1.
While acne is most prevalent among teenagers due to hormonal changes, it can affect people of all ages and may persist into adulthood, especially in women. Effective treatments are available, and early intervention can help reduce the risk
of scarring and emotional distress.
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi—the main airways that carry air to and from the lungs—usually triggered by a viral infection following a cold, sore throat, or flu. It causes the airways to swell and fill with mucus, leading
to symptoms like a persistent cough, chest discomfort, wheezing, and sometimes mild fever or fatigue. While bronchitis can affect people of all ages, it’s especially common in children under 5 and tends to occur more frequently during the
winter months. Most cases are acute bronchitis, which resolve on their own with rest, fluids, and home care, though chronic bronchitis—often linked to smoking or long-term exposure to irritants—requires medical attention and ongoing management.
Tetanus begins when Clostridium tetani spores—often found in soil, dust, or animal waste—enter the body through a wound, where they germinate in low‑oxygen tissue and release a potent neurotoxin that disrupts normal muscle control.
A person with tetanus doesn’t become a carrier in the usual sense, since the bacteria don’t spread from person to person; the infection is tied entirely to environmental exposure and the toxin’s effects within the body. After an
incubation period that typically ranges from 3 to 21 days, early signs emerge as jaw stiffness, difficulty swallowing, irritability, and muscle spasms near the injury site before the toxin’s influence spreads more widely. The illness
then moves into a more dramatic phase marked by painful muscle rigidity, arching of the back, and spasms triggered by light, sound, or touch, with the severity depending on how much toxin has reached the nervous system. Treatment focuses
on neutralizing circulating toxin with antitoxin therapy, controlling muscle spasms, cleaning the wound to halt further toxin production, and providing supportive care while the nervous system slowly recovers. Vaccination remains the
cornerstone of prevention, transforming a once‑common and often fatal infection into a largely avoidable one.
Back pain is a common condition that often arises without a clear cause and is rarely due to serious disease or structural damage, as the spine is generally strong and resilient. Symptoms can vary widely and may include stiffness,
muscle spasms, and sensations such as hot, burning, shooting, or stabbing pain in the back, which can radiate into one or both legs or feet. Additionally, nerve irritation—often from conditions like a herniated disc or spinal compression—can
lead to pins and needles, numbness, or weakness in the affected areas. These symptoms may stem from issues like muscular strain, disc degeneration, or inflammation around nerve roots, such as in cases of radiculopathy or sciatica.
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, causing inflammation and damage across multiple organs—including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, and brain. The most common
form is systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which can manifest through symptoms like joint pain, fatigue, and a distinctive butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose. What makes lupus especially complex is its unpredictable nature:
symptoms can flare up and subside, vary widely between individuals, and often mimic other illnesses, making diagnosis difficult. While anyone can develop lupus, it disproportionately affects women of color, particularly Black and Hispanic
women, who tend to experience more aggressive disease progression and face systemic barriers to timely diagnosis and treatment.
Lupus is a master of disguise, often masquerading as other illnesses while quietly wreaking havoc across the body. Its symptoms range from relentless fatigue and joint pain to mysterious fevers and a signature butterfly-shaped rash
that blooms across the face. Beneath the surface, it can inflame kidneys, spark chest pain, and trigger neurological issues like confusion or memory lapses. Skin becomes hypersensitive to sunlight, hair may thin or fall out, and circulation
can falter, turning fingers ghostly white in cold weather. Even the mouth and eyes aren’t spared, with sores and dryness adding to the discomfort. What makes lupus especially challenging is its unpredictability—flaring up without warning,
then retreating into remission—making early recognition and tailored care essential for those navigating its complex terrain.
Many diseases continue to defy the best efforts of medical science, remaining incurable despite decades of research and innovation. Conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis), Parkinson’s disease,
and Multiple Sclerosis (MS) are progressive neurological disorders that can be managed but not reversed. HIV/AIDS, while no longer a death sentence thanks to antiretroviral therapy, still lacks a definitive cure. Huntington’s disease,
a genetic disorder, relentlessly deteriorates motor and cognitive function. Some cancers, especially in late stages, resist treatment and recur despite aggressive therapy. Rare genetic conditions such as Progeria, which causes accelerated
aging, and Ataxia, which impairs coordination, also remain without cures. Even diabetes and asthma, though manageable, are chronic conditions that persist for life. These diseases highlight the ongoing need for research, compassion,
and innovation—not just to treat symptoms, but to unlock the possibility of healing. Below is a list of diseases and conditions for which there is currently no known cure.
Alzheimer's disease: A progressive, fatal brain disorder that causes a decline in memory and thinking.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): Also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, this is a fatal neurodegenerative disease that leads to complete disability.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: A form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine.
Ataxia: A neurological condition resulting in a lack of muscle control and coordination.
Arthritis: A broad category of conditions causing joint pain, with over 100 different forms, none of which have a cure.
Ataxias: A non-specific neurological symptom indicating dysfunction of the cerebellum, the part of the brain that coordinates movement.
Cancer: While some cancers can be cured, others, particularly in advanced stages, do not have a cure.
Dementia: A general term for loss of memory, thought, and other cognitive abilities, including Alzheimer's disease.
HIV/AIDS: A virus that infects the immune system, with no current cure, though treatments can manage the virus.
Huntington's disease: A genetic disorder that leads to a breakdown of nerve cells in the brain.
Muscular Dystrophy: A group of genetic diseases that cause progressive weakness and loss of muscle mass.
Multiple Sclerosis: A chronic, often debilitating disease that affects the brain and spinal cord, with no cure but treatments to manage symptoms.
Parkinson's disease: A brain disorder that causes involuntary movements, stiffness, and balance issues, with no cure.
Polio: A serious viral infection that can cause paralysis, and for which there is no cure.
Progeria: A rare genetic condition causing rapid aging in children, with no cure but treatments to ease symptoms.
Alzheimer’s disease is a relentless, progressive brain disorder that gradually erodes memory, thinking, and reasoning skills, ultimately interfering with daily life and independence. It’s the most common cause of dementia,
triggered by the buildup of abnormal proteins—amyloid plaques and tau tangles—that damage and destroy brain cells over time. Early symptoms often include forgetting recent conversations or events, but as the disease advances,
individuals may struggle with language, decision-making, and even recognizing loved ones. Though there’s no cure, medications can help manage symptoms and slow cognitive decline, and support programs play a vital role in improving
quality of life for both patients and caregivers1. Alzheimer’s doesn’t just steal memories—it reshapes lives.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), famously known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a ruthless neurodegenerative condition that dismantles the body’s ability to move, speak, swallow, and eventually breathe, all while leaving the
mind heartbreakingly intact. It begins subtly—perhaps with a twitch or a stumble—and then accelerates, stripping away muscle control as motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord waste away. Though treatments like riluzole and edaravone
offer a glimmer of hope in slowing progression, ALS remains a fatal diagnosis, often leading to respiratory failure within a few years. Yet amid its cruelty, stories of resilience and advocacy shine, as those affected often become powerful
voices for awareness and research, defying the silence the disease tries to impose.
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic, inflammatory form of arthritis that targets the spine and sacroiliac joints, often beginning in early adulthood. What starts as persistent lower back pain and morning stiffness can evolve
into a fusion of vertebrae, leading to a rigid, hunched posture and reduced mobility. Unlike typical arthritis, AS may also affect the hips, shoulders, and even the eyes, causing complications like iritis or uveitis. The disease stems
from an autoimmune response, and while its exact cause remains elusive, a strong genetic link to the HLA-B27 gene has been identified. Though incurable, biologic therapies and physical activity can help manage symptoms and slow progression,
offering a path toward maintaining function and quality of life.
Ataxia is a neurological condition marked by a breakdown in muscle coordination, turning once-fluid movements into clumsy, uncertain gestures. It stems from damage to the cerebellum—the brain’s control center for balance and precision—
or its connections, and can affect walking, speech, eye movements, and even swallowing. Depending on the type, ataxia may arise from genetic disorders, strokes, tumors, vitamin deficiencies, or chronic alcohol use1. Symptoms often include
unsteady gait, poor fine motor skills, and slurred speech. Though incurable in many cases, therapies like physical rehabilitation and assistive devices can help preserve independence and improve quality of life.
Arthritis isn’t just one disease—it’s a sweeping category encompassing over 100 distinct conditions that all share a common thread: joint pain and inflammation. From the wear-and-tear of osteoarthritis to the immune system misfires of
rheumatoid arthritis, each form brings its own challenges, affecting joints in the hands, knees, spine, and beyond. Some types, like gout or psoriatic arthritis, come with sudden flares or skin symptoms, while others, such as juvenile
idiopathic arthritis, strike early in life. Despite the lack of a definitive cure, modern treatments—from anti-inflammatory drugs to biologics—can ease symptoms and help many lead active, fulfilling lives. Arthritis may be persistent,
but it doesn’t have to be paralyzing.
Ataxias are a group of neurological symptoms that signal trouble in the cerebellum—the brain’s finely tuned control center for movement, balance, and coordination. Rather than a single disease, ataxia describes a breakdown in motor
precision, often manifesting as unsteady gait, clumsy hand movements, slurred speech, or erratic eye motion. These symptoms can stem from a wide range of causes, including genetic mutations, autoimmune disorders, infections, strokes, or
toxic exposures. Some forms, like spinocerebellar ataxia, are inherited and progressive, while others may be reversible if caught early. Despite its broad definition, ataxia always points to a disruption in the brain’s ability to choreograph
smooth, purposeful motion.
HIV/AIDS is a chronic viral condition that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells that help the body fight infections. Left untreated, HIV gradually weakens the immune response, paving the way for opportunistic
infections and, ultimately, the development of AIDS—the most advanced stage of the disease. While there’s no cure, antiretroviral therapy (ART) has revolutionized treatment, allowing most individuals to suppress the virus to undetectable
levels, dramatically improving health and preventing transmission. Today, HIV is no longer a death sentence but a manageable condition, thanks to daily pills or long-acting injections that keep the virus in check and help people live long,
healthy lives.
Huntington’s disease is a hereditary brain disorder that slowly dismantles physical, cognitive, and emotional functioning, often during the prime of adult life. Caused by a mutation in the huntingtin gene, it triggers the progressive
death of nerve cells, especially in areas controlling movement, mood, and memory. Early symptoms may include subtle changes in coordination, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating, but over time, involuntary movements (chorea), severe
cognitive decline, and psychiatric disturbances take hold. The disease typically begins between ages 30 and 50 and worsens over 10 to 25 years, ultimately requiring full-time care. Though there’s no cure, treatments can help manage symptoms
and improve comfort.
Muscular Dystrophy refers to a family of over 30 genetic disorders that gradually rob the body of its strength by weakening and wasting away skeletal muscles. These conditions vary in onset, severity, and the specific muscles they
target—some begin in infancy, others in adulthood—but all share a relentless progression. Duchenne muscular dystrophy, the most common and severe form, typically affects boys and starts in early childhood, while Becker muscular dystrophy
follows a slower course. Other types, like myotonic dystrophy or limb-girdle dystrophy, bring their own unique challenges, from difficulty relaxing muscles to heart and lung complications. Though no cure exists, advances in therapy and
supportive care continue to improve mobility, independence, and life expectancy.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that disrupts communication between the brain and body by attacking the protective myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This damage leads to
a wide range of symptoms—muscle weakness, vision problems, numbness, fatigue, and cognitive changes—that can vary in intensity and come in unpredictable waves. MS unfolds in different forms, from relapsing-remitting episodes to steadily
worsening progression, and while there’s no cure, disease-modifying therapies can slow its advance and reduce flare-ups. With early diagnosis and personalized treatment, many individuals continue to lead active, fulfilling lives despite
the challenges MS presents.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that disrupts the brain’s ability to regulate movement, leading to tremors, muscle rigidity, slowed motion, and impaired balance. It stems from the gradual loss of dopamine-producing
neurons in the basal ganglia, a region critical for motor control. Symptoms often begin subtly—perhaps a slight hand tremor or reduced facial expression—and intensify over time, affecting walking, speech, and even handwriting. Though incurable,
treatments like levodopa and deep brain stimulation can significantly ease symptoms and improve quality of life. Beyond movement, Parkinson’s can also bring non-motor challenges such as sleep disturbances, depression, and cognitive changes,
making it a multifaceted condition that demands comprehensive care.
Polio, or poliomyelitis, is a highly infectious viral disease that targets the nervous system and can lead to irreversible paralysis, especially in the legs. While most infected individuals show no symptoms, a small percentage experience
flu-like signs that can escalate into severe muscle weakness and breathing difficulties2. In its most dangerous form, polio attacks the spinal cord and brainstem, sometimes resulting in death. Though there's no cure, global vaccination efforts
have dramatically reduced its prevalence, turning a once-feared epidemic into a near-eradicated threat. Yet in regions with low immunization rates, the virus still lurks, making continued vigilance essential.
Progeria, formally known as Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS), is an extraordinarily rare genetic disorder that accelerates aging in children at a startling pace. Caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, it leads to the production
of an abnormal protein called progerin, which destabilizes cells and triggers premature aging. Children with progeria typically appear healthy at birth but begin showing signs—such as growth delays, hair loss, aged-looking skin, and joint
stiffness—within the first two years of life. Though there’s no cure, treatments like lonafarnib, a drug that targets the buildup of faulty proteins, have shown promise in slowing disease progression and extending lifespan. Supportive therapies,
including physical therapy, nutritional support, and cardiovascular monitoring, help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Despite its severity, children with progeria often maintain sharp intellect and remarkable resilience, becoming
powerful symbols of strength and advocacy.
HDL cholesterol influences brain health in several important ways. It helps transport cholesterol into the brain, which is essential for maintaining the structure and function of nerve cells—particularly in areas related to
learning and memory. HDL also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can reduce brain inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are linked to cognitive decline and diseases like Alzheimer’s. Recent studies
have shown that higher levels of small-particle HDL are associated with greater gray matter volume and better cognitive function in middle-aged adults. However, HDL’s impact isn’t always straightforward—oxidized or dysfunctional
HDL may harm nerve cells, and very high HDL levels have been linked to memory problems in some cases. This suggests that not just the amount, but the quality and function of HDL are crucial for brain health.
Recent research suggests that both very high and very low levels of HDL cholesterol—the "good" cholesterol—may increase the risk of developing dementia, with mid-range levels offering the lowest risk. In a study of over 184,000
adults tracked for up to 17 years, individuals with HDL levels ≥65 mg/dL had a 15% higher risk of dementia, while those with levels between 11–41 mg/dL had a 7% higher risk compared to those around 53.7 mg/dL. Although HDL is known
for protecting blood vessels and removing excess cholesterol, extreme levels may disrupt vascular health and contribute to cognitive decline. LDL cholesterol showed no clear link to dementia except in statin users, where higher LDL
was slightly associated with increased risk. These findings highlight the importance of maintaining balanced cholesterol levels for both heart and brain health, though they reflect correlation rather than causation.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) significantly increases mortality risk, especially when kidney involvement like lupus nephritis develops, but even without it, over half of SLE patients experience chronic kidney disease (CKD),
which is linked to more hospitalizations and premature death. A major meta-analysis revealed that individuals with SLE have a 2.87-fold increase in all-cause mortality compared to the general population, with the most elevated
risks seen in renal disease (4.49×), infections (4.95×), cardiovascular disease (2.93×), and cancer (1.70×). These findings underscore that SLE is far more than an episodic autoimmune condition—it’s a serious systemic illness
that requires early detection and vigilant, long-term care.
Diffuse scleroderma, a severe form of systemic sclerosis, can rapidly affect internal organs—most dangerously the heart and lungs—leading to pulmonary hypertension (PH), which occurs when scarring or arterial narrowing
increases pressure in lung vessels and forces the right side of the heart to pump harder, potentially causing right heart failure. It may also contribute to left ventricular stiffness, pushing back pressure into the lungs and
exacerbating PH. Because this combination of lung fibrosis and vascular damage makes PH one of the leading causes of death in diffuse scleroderma, regular screening with echocardiograms and pulmonary function tests is crucial
for early diagnosis and management.
Vasculitis is a group of autoimmune disorders characterized by inflammation of blood vessels, which can cause the vessel walls to thicken, narrow, or scar—ultimately restricting blood flow and leading to organ damage.
When vasculitis affects the kidneys, it can impair their ability to filter waste, potentially resulting in kidney injury or failure. In the lungs, it may cause bleeding, shortness of breath, or coughing up blood due to damaged
pulmonary vessels. Specific types like microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) are especially prone to targeting small- to medium-sized vessels in the kidneys and lungs, making early diagnosis
and immunosuppressive treatment essential to prevent irreversible damage
Autoimmune myocarditis is a rare but potentially fatal condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the heart muscle, leading to inflammation, scarring, and impaired cardiac function. This inflammation can disrupt
the heart’s electrical system, triggering life-threatening arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, which are major causes of sudden cardiac death—especially in young, otherwise healthy individuals. In severe
cases, the heart may fail to pump effectively, resulting in cardiogenic shock or abrupt pump failure. Certain autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic sclerosis can predispose
individuals to this condition. Because symptoms like chest pain, fatigue, or palpitations may be subtle or absent, early diagnosis through cardiac MRI, biopsy, and blood tests is critical. Without timely intervention, autoimmune
myocarditis can progress rapidly, making it one of the most dangerous cardiac complications in autoimmune disorders.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that targets the brain and spinal cord, leading to inflammation, nerve damage, and progressive disability. While MS itself is rarely fatal, severe cases—especially
those involving advanced disability or frequent infections—can shorten life expectancy by approximately seven years compared to the general population2. The average lifespan for someone with MS is around 75 years, with most
deaths resulting from complications like pneumonia, urinary tract infections, or cardiovascular disease rather than MS directly1. Early and consistent use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs), along with lifestyle adjustments
such as exercise, smoking cessation, and infection prevention, can significantly improve prognosis and help individuals with MS lead long, fulfilling lives.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a long-lasting (chronic) disease of the central nervous system that attacks the myelin, the protective covering
surrounding nerves, resulting in a variety of symptoms, including weakness, loss of balance, pain, tingling and fatigue; MS is an unpredictable disease that affects people differently. Some people with MS may have only mild symptoms;
nearly a million Americans have MS; the condition is three times more common among women than men and often begins between ages 20 and 50, during the prime of life.Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a relentlessly progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness, paralysis,
and ultimately respiratory failure. While the average life expectancy after diagnosis is 2 to 5 years, about 20% of patients live beyond 5 years, 10% exceed 10 years, and a rare 5% survive 20 years or more2. The disease typically
begins with limb or bulbar symptoms, and its progression varies depending on factors like age at onset, genetic mutations, and respiratory function. Bulbar-onset ALS, which affects speech and swallowing early, tends to have a poorer
prognosis. Though there is no cure, treatments such as riluzole, edaravone, and noninvasive ventilation can modestly extend survival and improve quality of life3. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care are key to managing symptoms
and planning for long-term support.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's Disease, is a rare neurological, progressive
and incurable disease that affects motor neurons. It is caused by the death of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord that control the movement of muscles. Early symptoms include muscle twitches in the arm, leg, shoulder, or tongue,
muscle cramps, tight and stiff muscles (spasticity), muscle weakness affecting an arm, a leg, the neck, or diaphragm, slurred and nasal speech, and difficulty chewing or swallowing.The Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) disease often begins with muscle twitching and weakness in an arm or leg, trouble swallowing or slurred speech, but as it progresses it profoundly impacts on the ability to move, talk and even breathe.
The exact cause of the disease is still not known. A small number of cases are inherited. Most people with ALS die from respiratory failure, usually within three to five years from when the symptoms first appear. However, about 10 percent
of people with ALS survive for a decade or more.
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic autoimmune liver disease that gradually damages the small bile ducts within the liver. These ducts are responsible for transporting bile—a fluid that helps digest fats and remove waste.
When the ducts become inflamed and scarred, bile builds up in the liver, leading to tissue damage and, over time, cirrhosis. Though the condition progresses slowly and may not cause noticeable symptoms early on, it can eventually lead
to fatigue, itching, and complications related to liver function. While there’s no cure, medications like ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can help slow the disease’s progression and preserve liver health1. Building a strong support network,
staying informed, and working closely with healthcare providers are essential steps in managing PBC and maintaining quality of life.
The leading causes of death in the U.S. for 2015 vs. 2024.
Cause of Death # Deaths in 2015 # Deaths in 2024
Heart Disease ~633,000 688,117
Cancer ~595,000 561,107
Unintentional Injuries ~146,000 218,064
Chronic Respiratory Diseases ~155,000 102,121
Stroke ~140,000 180,456
Alzheimer’s Disease ~110,000 103,493
Diabetes ~80,000 106,105
Kidney Disease ~50,000 55,117
Suicide 44,193 50,123
Influenza & Pneumonia ~57,000 60,457
Many diseases, such as cancer. dementia, Alzheimer, advanced lung, heart, kidney, liver, stroke and other neurological diseases, including motor neurone disease and multiple sclerosis, still lack curative treatments;
however, there are treatments that can slow progression, manage symptoms, or improve quality of life, even if they can't fully cure the disease, for example,
Cancer - Some types are curable, especially when caught early; others can be managed long-term with chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted drugs.
Alzheimer’s & Dementia - No cure yet, but drugs like lecanemab and donanemab have recently been approved to slow early-stage Alzheimer’s progression; new therapies using cancer-inspired immune technology are also being explored.
Stroke - Emergency treatments like tPA can dissolve clots, and newer drugs are being tested to reduce brain damage and aid recovery.
Heart, Lung, Kidney, Liver Diseases - These often have extensive treatment options, including medications, surgeries, and transplants; while not always curative, they can significantly extend life.
Motor Neurone Disease (ALS) and Multiple Sclerosis (MS) - No cures, but drugs like riluzole (for ALS) and disease-modifying therapies (for MS) can slow progression and ease symptoms.
Coronary artery disease, stroke, lower respiratory infections, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease and dementia, tuberculosis, diarrheal diseases, and HIV/AIDS
are the most dangerous diseases in the world. Many of these diseases are preventable or manageable with proper healthcare, lifestyle changes, and early detection.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) – The leading cause of death globally, CAD occurs when blood vessels supplying the heart become narrowed, leading to heart attacks and heart failure.
Treatments – Managed with lifestyle changes, medications (such as statins and beta-blockers), and surgical procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
Stroke – A sudden blockage or rupture of an artery in the brain, strokes can cause long-term disabilities and are a major cause of death worldwide.
Treatments – Immediate treatment includes clot-busting drugs for ischemic strokes or surgery for hemorrhagic strokes. Rehabilitation focuses on physical therapy and speech therapy.
Lower Respiratory Infections – Diseases like pneumonia and bronchitis can be life-threatening, especially for young children and the elderly.
Treatments – Treated with antibiotics (for bacterial infections), antivirals (for viral infections), and supportive care like oxygen therapy..
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) – A progressive lung disease that makes breathing difficult and is often caused by smoking.
Treatments – Managed with bronchodilators, steroids, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes like quitting smoking.
Cancer – Various types of cancer, including lung, breast, and colorectal cancer, are among the leading causes of death.
Treatments – Treatment depends on the type and stage but may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
Diabetes – A chronic condition that affects blood sugar regulation and can lead to severe complications like kidney failure and heart disease.
Treatments – Managed with insulin therapy (for type 1), oral medications (for type 2), and lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia – These neurodegenerative diseases primarily affect older adults and lead to cognitive decline and death.
Treatments – No cure exists, but medications can slow progression and improve symptoms. Cognitive therapy and lifestyle adjustments help manage the condition.
Tuberculosis (TB) – A bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs and can be fatal if untreated.
Treatments – Treated with a long course of antibiotics, often lasting six months or more.
Diarrheal Diseases – Often caused by contaminated food or water, severe diarrhea can lead to dehydration and death, particularly in developing countries.
Treatments – Managed with rehydration therapy, antibiotics (if bacterial), and improved sanitation.
HIV/AIDS – Although treatments have improved, HIV/AIDS remains a deadly disease, especially in regions with limited access to healthcare.
Treatments – Treated with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which helps control the virus and prevent progression to AIDS.
Brain damage can result from a variety of causes, including prolonged hypoxia—a dangerous shortage of oxygen often triggered by cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, or suffocation—which can lead to irreversible harm
within minutes. Poisoning, such as exposure to carbon monoxide, heavy metals, or toxic substances, may impair brain function or destroy nerve cells. Infections like meningitis and encephalitis can inflame or directly damage
brain tissue. Neurological illnesses, including conditions such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's disease, or multiple sclerosis, can also progressively deteriorate brain cells over time. These factors disrupt vital processes like
oxygen delivery, neural communication, and immune response, contributing to a range of cognitive and motor impairments.
Every year, about 120 million people in the U.S. have high blood pressure (hypertension). Heart attacks occur in about 805,000 people
annually, with 605,000 being first-time events and 200,000 recurrent. As of 2022, an estimated 127.9 million U.S. adults—almost 1 in 2—had some form of cardiovascular disease (CVD), including heart failure, stroke, and coronary artery
disease. Cardiovascular conditions are incredibly widespread and remain the leading cause of death in the U.S., claiming over 940,000 lives in 2022 alone.
About 25% of Asian-American adults have hypertension (i.e.; having blood pressure greater than or equal to 140/90 millimeters (mm) mercury (Hg)).
Of which there is about 5.0% for the 20–39 age group, 26.5% for the 40–59 age group, and 59.6% for the 60 and over age group. There are around 15.4 million Asian people in the U.S., which primarily comprise persons of Chinese,
Asian Indian, Korean, Filipino, Vietnamese, and Japanese descent.High blood pressure is a risk factor for more than heart disease ; left uncontrolled,
you may wind up with a disability, a poor quality of life or even a fatal heart attack. High blood pressure can damage brain, kidneys, eyes, and heart; narrow arteries, cause sexual dysfunction and trouble sleep, and make bone loss.Having high blood pressure (HBP) and
coronary artery disease (CAD) puts you at a greater risk of a
heart attack or
stroke . You can have HBP for years without knowing it because HBP itself usually has no symptoms. If your blood pressure rises and stays high over time, it can damage your
heart ,
blood vessels ,
kidneys , and other parts of your body. The numbers in a blood pressure reading include
Systolic and Diastolic . Systolic (the top number) is the maximum pressure in the arteries when the heart is contracting or squeezing. Diastolic (the bottom number) represents the pressure in the
arteries when the heart is at rest. The recommended blood pressure goal is below 140/90 mmHg (millimeters of mercury). If your blood pressure is above that level, you may have HBP. The most common of medications to treat HBP in people who have CAD is
Beta-blockers , which slow the heart rate, reduce the heart's output of blood, and decrease the force of the heart beat.
People suffered from mild hypertension, which is a blood pressure reading of no higher than 160/100 mm Hg, took a 81-milligram tablet of aspirin in the evening had a significant reduction in their blood pressure. Those who took the aspirin in the morning had no reduction at all.
The most common and dangerous cause of blue skin on your face or body is
Cyanosis , which causes when the body is not able to put enough oxygen into the circulating blood. The
possible diseases include heart defects ,
lung defects and
blood disorder s (potential blood cancer ),
Chromhidrosis and
Pseudochromhidrosis .
There are three types of muscles in the human body: cardiac, smooth and skeletal. Cardiac muscle makes up the wall of the heart.
Smooth muscles make up the walls of the intestine, the uterus, blood vessels, and internal muscles of the eye. Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones; contraction of the skeletal muscles helps limbs and other body parts move.Acute Hepatic Porphyria (AHP) is a rare group of inherited disorders that disrupt the body’s ability to produce heme, a vital component of hemoglobin. This disruption leads to the buildup of toxic compounds in the liver, which can
spill into the bloodstream and affect the nervous system and skin. AHP includes four subtypes—Acute Intermittent Porphyria, Variegate Porphyria, Hereditary Coproporphyria, and ALAD Deficiency Porphyria—each caused by a different enzyme
deficiency1. While some individuals may experience few or no symptoms, others endure recurrent, debilitating attacks marked by severe abdominal pain, vomiting, neuropathy, and even seizures1. These episodes can be unpredictable and
profoundly impact daily life, work, and relationships.
Treatment of Acute Hepatic Porphyria (AHP) focuses on halting attacks quickly and managing symptoms. Options include intravenous hemin therapy to reduce the production of toxic precursors, pain management, anti-nausea medications,
and lifestyle adjustments to avoid known triggers like certain medications, fasting, or hormonal changes. Long-term care often involves regular monitoring and preventive strategies to reduce attack frequency. Though AHP is rare,
understanding its mechanisms and accessing proper care can make a significant difference in maintaining quality of life.
Mesothelioma is caused by exposure to asbestos ,
which is a mineral that was used in the United States. Mesothelioma is diagnosed in approximately 2,500 Americans each year with a life expectancy of twelve months to eighteen months from the time of diagnosis. There are four types of
mesothelioma: pleural , peritoneal ,
pericardial , and testicular , which impact
the cavity of lung, abdomen, heart and testes, respectively. Pleural and
peritoneal mesothelioma are the most common ones.Polydipsia is the medical term for extreme thirst, which does not improve no matter how much a person drinks. It is not a disease by itself but can be
an important symptom of certain health problems, such as diabetes . Common diabetes mellitus symptoms include polydipsia, polyuria, extreme and uncontrolled
hunger, blurred vision, extreme fatigue or lack of energy, genital itching, slow healing of wounds or cuts, weight change (gain or loss), frequent or returning infections, and tingling or numbness in the hands or feet.When treated by an older doctor, hospitalized patients 65 and older may face a slightly higher risk of dying within a month of their admittance than if treated by a younger physician.Clinical skills and knowledge accumulated by
experienced physicians can lead to better quality of care; however, doctors' skills and knowledge can also become outdated, as scientific technology and clinical guidelines change over time.
There are about 20 million new sexually transmitted infections (STIs) each year in the United States with young people aged 15–24 accounting
for nearly half of those cases. The most commonly reported STIs include
Chlamydia ,
Gonorrhea ,
Syphilis ,
Human papillomavirus (HPV) ,
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) , and
Human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV)
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause serious health problems if it is not treated.
The name for the disease , ‘syphilis’, originates from an epic Latin poem Syphilis,
sive morbus gallicus , ‘Syphilis, or the French disease'. The disease started with genital ulcers, then progressed to a fever, general rash and joint and muscle pains, then weeks or months later were followed by large, painful
and foul-smelling abscesses and sores, or pocks, all over the body. Muscles and bones became painful, especially at night. The sores became ulcers that could eat into bones and destroy the nose, lips and eyes. They often extended
into the mouth and throat, and sometimes early death occurred.Scratching skin creates a mild amount of pain (in the skin), that can interfere with itching — at least temporarily — by getting nerve cells in the spinal cord to carry pain signals to the brain instead of itch signals.
This mechanism is part of what’s known as the “itch-scratch cycle”: scratching relieves the itch momentarily, but it can also lead to inflammation or even more itching if overdone.
The "flu" or the seasonal flu is caused by the influenza virus and causes mostly upper respiratory problems while
the "stomach flu" is often caused by a number of viruses and causes
gastrointestinal problems, such as diarrhea and vomiting. While they share the word “flu,” they’re very different illnesses
with different causes, symptoms, and treatments.As of 2025, cardiovascular disease remains the nation’s leading cause of death, claiming over 941,000 lives in 2022 alone—of which 371,506 were due to coronary heart disease. Hypertension continues to escalate with age,
affecting 66.9% of adults aged 85 and older. Diabetes is also on the rise, particularly among older adults and men, reflecting broader shifts in chronic disease patterns. Meanwhile, arthritis has emerged as a major health
burden in the elderly, impacting 55.9% of those 85 and above, making it the second most common chronic condition in that age group and a significant contributor to age-related disability.
Each year, approximately 500,000 people in the United States are diagnosed and treated for Lyme disease, though many cases go unreported. About 96% of reported cases are concentrated in just 19 states, mainly in the Northeast,
Upper Midwest, and parts of the Mid-Atlantic. These include Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Vermont, Virginia, Wisconsin, Ohio, Michigan, Illinois,
Iowa, as well as emerging hotspots like North Carolina and Kentucky—areas where the tick populations that transmit Lyme disease are most prevalent and the risk of exposure is highest.
During sleep—especially during deep, slow-wave stages—the body boosts production of cytokines , essential signaling proteins that govern immune activity
and inflammation. Among these are pro-inflammatory molecules such as interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), which are vital for combating infections, facilitating tissue repair, and coordinating
immune responses. Quality sleep functions as a critical period for immunological maintenance, fortifying the body's defenses and enhancing its capacity for healing and protection.
Most adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night to function at their best, and chronic sleep deprivation—getting less than 7 hours consistently—can seriously harm both physical and mental health. In the short term,
inadequate sleep impairs concentration, memory, mood, and immune response, while long-term effects are linked to increased risks of heart disease, obesity, type 2 diabetes, depression, anxiety, and even Alzheimer’s disease.
Research shows that sleep is far more than rest; it’s a vital biological process during which the body repairs tissues, balances hormones, consolidates memories, and strengthens the immune system. Ongoing sleep loss may
even reduce lifespan, making regular, restorative sleep essential for long-term health and well-being.
Cholera is an acute diarrhea disease that can kill within hours if left untreated. As of 2025, the World Health Organization reports that from
January to late May, there were already over 211,000 cholera cases and 2,754 deaths across 26 countries. Outbreaks remain severe in areas with poor sanitation, limited healthcare access, or conflict—like Sudan, Angola, and
the Democratic Republic of Congo, which together account for the majority of 2025’s reported cases.Asthma is a chronic disease of the bronchial, the air passages leading to and from the lungs. It is the most common chronic disease among children.
Over 260 million people worldwide live with asthma. Asthma can range from mild to life-threatening, and while it's often manageable with inhalers and medication, many people still struggle with underdiagnosis or poor control.In 2024, chronic pain remains a major public health challenge in the United States, affecting an estimated 51.6 million adults, or 21% of the population. Of these, approximately 17.1 million suffer from high-impact chronic
pain, meaning their pain frequently limits daily life or work activities. While this reflects a slight decrease from 2023’s figures, chronic pain still exceeds the combined number of Americans living with diabetes, heart disease,
and cancer, and continues to be the leading cause of long-term disability. The economic toll remains staggering, costing the U.S. up to $635 billion annually in healthcare expenses, lost productivity, and disability payments.
Chronic pain is also linked to increased risks of anxiety, depression, sleep disturbances, and even suicide, underscoring the urgent need for better pain management, research funding, and equitable access to care.
Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are linked to a wide range of serious health conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, depression, and increased risk of premature death. OSA disrupts normal
sleep patterns and oxygen flow, impairing glucose metabolism and increasing insulin resistance—raising the risk of type 2 diabetes. Repeated oxygen drops during sleep also activate stress responses that elevate blood pressure,
even in otherwise healthy individuals. The cardiovascular system is further strained, contributing to a higher likelihood of heart attacks, arrhythmias, heart failure, and strokes. Additionally, poor sleep quality and chronic
fatigue from OSA are strongly associated with mood disorders like depression and anxiety. Left untreated, sleep apnea significantly elevates the risk of early mortality, especially from cardiovascular causes, underscoring the
need for timely diagnosis and management.
Night sweats can stem from a wide range of causes—some harmless, others more serious. While menopause is a common trigger, especially in women, other potential culprits include infections (like tuberculosis, HIV,
and endocarditis), cancers such as lymphoma and leukemia, and certain medications that affect temperature regulation. Anxiety, hyperactivity, and respiratory issues like sleep apnea may also play a role, as can thyroid disorders
(notably hyperthyroidism) and, less commonly, conditions like atopic dermatitis. Though rarely a direct cause, systemic diseases affecting the eyes may indirectly contribute. Persistent or intense night sweats—particularly when
accompanied by symptoms like fever or weight loss—warrant medical evaluation.
As of 2024, asthma continues to affect a growing number of Americans, with an estimated 29 million people living with the condition—up from 28 million in 2023. Among adults aged 18 and older, 9.9% currently have asthma, with
rates as high as 13% in states like Rhode Island, Maine, and New Hampshire. For children under 18, asthma prevalence varies by state, ranging from 4.1% in Nebraska to 16.0% in Puerto Rico. The condition remains a major burden on
the healthcare system, contributing to over 1.4 million emergency department visits and thousands of deaths annually. Environmental factors, urban living, and improved diagnostic awareness continue to drive these trends.
In 2024, joint replacement surgeries in the United States continued to rise, with the American Joint Replacement Registry reporting over 3.7 million total hip and knee arthroplasty procedures performed nationwide since 2012,
driven by growth in outpatient surgeries and robotic-assisted techniques. In 2023 alone, surgeons performed approximately 793,000 hip replacements (a 3.8% increase from 2022) and 1.36 million knee replacements (up 5.1%), i
ncluding 1.13 million primary knee procedures (up 4.9%) and a notable 8.4% rise in revision knee surgeries—the fastest-growing segment. These procedures are highly effective, but many patients will require revision or replacement
of their implants within 10 to 20 years, depending on factors such as age, activity level, and implant type.
A routine cardiac imaging stress test should not
be performed on asymptomatic patients. Routine cardiac imaging stress tests are not recommended for patients without
symptoms, particularly those at low risk for heart disease. Leading medical organizations advise against this practice because it often results in false positives, which can prompt unnecessary and potentially risky follow-up procedures
such as angiography or interventions. These tests also carry avoidable costs, stress, and radiation exposure without clear benefit. Studies have shown that asymptomatic individuals with abnormal results have similar mortality rates to
those with normal tests, suggesting little clinical value. Instead, guidelines emphasize managing risk factors like blood pressure and cholesterol through lifestyle changes and informed discussions between patients and healthcare providers.
Routine cardiac imaging stress tests are generally not recommended for individuals without symptoms,
as they offer little benefit in low-risk cases and may lead to unnecessary procedures, false positives, and increased healthcare costs. Leading medical organizations—including the American College of Cardiology and the U.S.
Preventive Services Task Force—advocate against using such tests as routine screening tools in asymptomatic patients unless there are specific risk factors or clinical concerns that warrant further evaluation. Stress testing
is far more effective when guided by symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath, or in patients with known or suspected heart disease.
Women who suffer from both depression and diabetes face a significantly increased risk of heart attacks and cardiovascular mortality over time. Depression amplifies the effects of diabetes-related inflammation, poor glucose
control, and vascular damage, all of which strain the heart. A large observational study found that women with depression had a 64% higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease compared to women without depression, and their
hazard ratios for heart attacks, stroke, and heart failure were consistently higher than those of men. This compounded risk underscores the importance of integrated care that addresses both mental and physical health, especially
in women with chronic conditions like diabetes.
Childhood obesity significantly increases the risk of developing serious health conditions in adulthood, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic disorders. Studies show that children with
obesity are more likely to experience early vascular aging, insulin resistance, and impaired glucose control, which can lead to long-term complications such as heart disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A recent meta-analysis
confirmed that childhood obesity is positively associated with adult blood pressure, triglyceride levels, and inversely associated with HDL cholesterol, suggesting a strong link to future cardiovascular risk. Additionally, genetic
research has identified polygenic risk scores that can predict obesity as early as age five, offering opportunities for early intervention to prevent these chronic conditions.
Long-term stress increases the risk of both diabetes and depression by disrupting hormonal balance and behavior. Chronic stress elevates cortisol and adrenaline levels, which raise blood sugar and impair insulin sensitivity,
contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes. It also promotes unhealthy habits like poor diet, lack of exercise, and sleep disturbances, which further worsen glucose control. For those already living with diabetes, stress
can make disease management more difficult and lead to higher A1C levels. At the same time, the emotional burden of managing diabetes can trigger depression, creating a bidirectional relationship where each condition exacerbates
the other. This cycle highlights how stress can entangle physical and mental health, making both diabetes and depression harder to treat.
A 2016 study presented by the American Academy of Neurology found that the overall rate of ischemic stroke was 8% higher during the first two days after a daylight saving time transition. The risk was especially elevated among
vulnerable groups: cancer patients were 25% more likely to suffer a stroke during that period, and people over age 65 had a 20% increased risk. Researchers believe this spike may be due to disruptions in the body's circadian rhythm,
which can affect blood pressure, inflammation, and vascular function. While the increase was temporary, the findings highlight how even small shifts in sleep and biological timing can have serious health consequences.
Palliative care , which helps the gravely ill make the most of the time they have left, provided a surprising bonus for terminal
lung cancer patients. The patients who started soon after their diagnosis on palliative care along with usual cancer care lived nearly three months longer than people given only
standard cancer care . More than half of lung cancer patients have incurable diseases by the time they are diagnosed.While muscle pain is a possible side effect of taking a statin medication; however, researchers found that it’s uncommon, and
most pain stems from something other than the cholesterol-lowering drug.
About 25% of people reported muscle pain whether they took statins or not.
Lipodystrophy is a rare disorder marked by the loss or abnormal distribution of body fat. In severe forms—such as congenital
generalized lipodystrophy or acquired generalized lipodystrophy—there is a near-complete absence of subcutaneous fat, which can lead to a strikingly gaunt and prematurely aged appearance, especially in children and adolescents.
In extreme cases, a 13-year-old may appear decades older due to the lack of fat beneath the skin and the prominence of muscles and veinsAs of 2024, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women at average risk begin biennial mammogram screenings at age 40, reflecting updated guidance aimed at improving early detection as breast
cancer rates rise among younger women. For those at higher risk—including women with BRCA gene mutations, dense breast tissue, or a family history of breast cancer—earlier or more frequent screening, possibly including MRI
in addition to mammography, may be advised. Screening plans should be tailored based on individual risk factors, and some providers may still recommend annual screening.
There are 30 different blood types . However, most people have blood types: O, A, B and AB. Type O blood is the most common, it can help other Os and also people
with AB, A and B blood types.The next common one is type A, which can help other As and also people with AB blood types. Type B is one of the rarest blood types, it can help people with B, O, A and AB blood types.
Type AB is the rarest blood type of 4 common ones, it can help people with AB, O, B and A blood types. The major common blood types in the U.S. include O+: 37.4%; O-: 6.6%; A+: 35.7%; A-: 6.3%; B+ 8.5%; B-: 1.5%; AB+: 3.4% and AB-: 0.6%. ▷ Autism
Life expectancy in autistic people reads less like a medical limitation and more like a story shaped by environment, support, and overall health, since autism itself doesn’t shorten life and instead sits alongside the same factors
that influence longevity for anyone—access to healthcare, safety, social inclusion, and the presence or absence of other medical conditions. Studies that report lower averages point toward external pressures rather than autism as a
biological cause, highlighting barriers to care, co‑occurring conditions such as epilepsy, chronic stress from navigating an often inflexible world, and social determinants like housing stability or employment. When those barriers
fall away and supportive structures are in place, autistic people tend to live lives that align far more closely with the general population, a reality that modern research increasingly emphasizes as it shifts from deficit‑focused
thinking toward understanding how society can remove obstacles rather than treating autism itself as the source of reduced lifespan.
Autism doesn’t have a single, simple cause; instead, it emerges from a complex interplay of biology, development, and environment that shapes the brain long before birth. Research points strongly toward genetics as the central driver,
with hundreds of genes involved in brain development contributing in different combinations, sometimes inherited and sometimes arising spontaneously during early embryonic growth. Alongside this genetic foundation, certain prenatal
influences—such as advanced parental age, pregnancy complications, or exposure to specific infections or medications—can increase the likelihood of autism, not by “creating” it outright but by nudging developmental pathways in ways that
interact with underlying genetic factors. What science consistently shows is that autism is not caused by parenting style, vaccines, or social environment; instead, it reflects natural variations in how the brain organizes itself, with
multiple biological threads weaving together long before a child takes a first breath.
Autism rates don’t cluster neatly by country, but some nations report higher percentages because of stronger diagnostic systems, broader awareness, and better access to evaluation rather than a true difference in how often autism
occurs. High‑income countries tend to identify autism more frequently, not because autism is more common there, but because screening is widespread and services are easier to reach. The United States, the United Kingdom, Sweden, Denmark,
South Korea, and Australia often appear near the top of reported prevalence lists, with figures in some regions reaching 1–3 percent of the population. Meanwhile, many low‑ and middle‑income countries report far lower rates simply because
diagnostic resources are limited, cultural stigma suppresses reporting, or health systems focus on more immediate medical needs. The global pattern reflects differences in recognition rather than biology, painting a picture in which
autism exists everywhere, but only some places have the tools and awareness to see it clearly.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a lifelong neurodevelopmental condition that affects how individuals perceive
the world and interact with others. It influences communication, social behavior, and information processing, often presenting through a wide range of symptoms and abilities—hence the term “spectrum.” People with autism may experience
challenges in social interaction, repetitive behaviors, sensory sensitivities, and unique ways of learning or problem-solving. Symptoms typically appear in early childhood, though diagnosis can occur at any age. Living well with autism
involves understanding individual strengths and needs, accessing supportive therapies and services, and fostering inclusive environments that celebrate neurodiversity.Diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children involves a comprehensive evaluation that typically includes both parental input and professional observation. According to the CDC, clinicians rely on descriptions of the child’s
developmental history from caregivers, alongside direct behavioral assessments. There’s no single medical test to confirm autism; instead, specialists—such as developmental pediatricians, child psychologists, or neurologists—use
standardized tools and criteria from the DSM-5, which requires persistent deficits in social communication and interaction, plus restricted and repetitive behaviors. Evaluations may also include hearing and language tests, developmental
screenings, and sometimes genetic testing to rule out related conditions like Rett syndrome or fragile X syndrome. Early diagnosis is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention and support, which can significantly improve long-term
outcomes.
Medical experts and organizations—including the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Autism Science Foundation—have responded with caution to claims linking acetaminophen to autism, emphasizing that
current research is limited, conflicting, and inconclusive. They stress that autism is a complex neurodevelopmental condition shaped by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and not attributable to any single
cause or exposure.
There is no scientific evidence linking vaccines to autism. This misconception originated from a 1998 study by Andrew Wakefield that falsely claimed a connection between the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine and autism.
That paper was later fully retracted, and Wakefield lost his medical license due to ethical violations and flawed methodology. Since then, dozens of large-scale studies conducted across the globe—including by the CDC, World Health
Organization, and Johns Hopkins University—have consistently found no causal relationship between vaccines or their ingredients and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). For example, a 2013 CDC study showed that children with and without
autism received the same number of vaccine antigens in early childhood. Despite this overwhelming evidence, misinformation persists, often fueled by social media and public figures who promote vaccine skepticism. This has contributed
to vaccine hesitancy, which poses serious public health risks, including outbreaks of preventable diseases like measles.
Vaccines do not cause autism. Extensive research has confirmed that there is no causal link between vaccines and autism. Numerous large-scale scientific studies have thoroughly examined this issue and found no link between
vaccines and autism, and vaccines are safe and essential for public health. The idea that vaccines might cause autism originated from a fraudulent 1998 study that has since been debunked and retracted.
The exact causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) remain unknown, but research suggests a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors may contribute to its development.
The complexity of ASD means there is likely no single cause, but rather a combination of factors interacting in unique ways for each individual.
Parental age: Older parents, particularly fathers over 40, may have a higher likelihood of having a child with autism.
Maternal health: Certain maternal infections, vitamin deficiencies, and exposure to toxins during pregnancy have been investigated as possible contributors.
Brain development: Autism is linked to differences in brain development that affect communication and social interaction.
Having a family history of autism or other developmental disorders can increase the likelihood of an ASD diagnosis; genetic factors play a significant role in ASD; research suggests that autism is highly heritable,
with studies estimating that around 80% of autism cases are linked to genetics.
Differences in brain structure and function, as well as prenatal influences like maternal health during pregnancy, may play a role of the likelihood of an ASD diagnosis; biological factors contributing to ASD include
differences in brain structure, function, and development; these biological factors often interact with genetic and environmental influences, making autism a complex and multifaceted condition.
Exposure to certain toxins, infections, or complications during pregnancy or early childhood could contribute to the likelihood of an ASD diagnosis, though these links are still being studied; environmental factors,
including prenatal exposure, toxins, parental age, and birth complication, can play a role in ASD, though they are not the sole cause; these factors interact with genetic predispositions, and no single environmental factor has
been definitively proven to cause autism.
Adults can be diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). While autism is typically identified in childhood, many individuals go undiagnosed until adulthood, especially if they have milder symptoms or developed strategies
to mask their traits. Increased awareness has led to more adults seeking evaluations and receiving diagnoses later in life. For some, an adult diagnosis can bring clarity to lifelong challenges, such as difficulties with social
interactions, sensory sensitivities, or managing routines. Receiving an autism diagnosis as an adult can help explain experiences and behaviors that might have felt confusing or isolating before. For many, it offers a sense
of validation, helping them understand why they might have struggled with things like socializing, processing sensory input, or maintaining daily routines.
Both parents’ ages are linked to autism risk. Studies consistently show that fathers over 40 face
a significantly higher likelihood of fathering a child with autism—up to 5.75 times greater than fathers under 30. Maternal age also plays a role: women over 35 or 40 have a 40–80% higher risk compared to younger mothers.
When both parents are older—for example, a mother over 35 and a father over 40—the combined risk increases further, though the exact magnitude varies across studies. Interestingly, one large study found that when the father
is over 40 and the mother is under 30, the risk of autism increases by 59%, suggesting that certain age combinations may amplify risk more than others.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is not an illness or disease—it is a lifelong condition that represents a variation in neurodiversity. It is possible for an individual with autism to experience mental health challenges, such as anxiety or depression,
which are co-occurring conditions; however, autism itself is not a mental illness. Autism is not "cured" but rather supported with interventions that help individuals thrive based on their unique needs.
Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder
characterized by impaired social interaction , verbal and
non-verbal communication , and restricted and repetitive behavior. In other words, autism is a neurodevelopmental condition, meaning it relates to
differences in how the brain develops and functions. Autism prevalence varies significantly across countries, influenced by factors like diagnostic practices, healthcare infrastructure, and societal awareness. In the U.S., approximately
1 in 36 children were identified with autism in 2024, about 1.5% of children (one in 68) were diagnosed with autism in 2014, a 30% increase from one in 88 in 2012. In other countries like Japan, South Korea
and the U.K., reported high rates, with around 1 in 33, 1 in 38, and 1 in 57 children were identified with autism in 2024, respectively.There is no cure for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), about 20 to 30 percent of children with autism develop epilepsy by the time they reach adulthood.
Autism is diagnosed approximately four to five times more often in boys than in girls. Over the last decade, autism rates have shown a significant increase globally, largely due to improved diagnostic practices, heightened awareness,
and broader definitions of ASD.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) prevalence varies across countries, influenced by diagnostic practices, healthcare infrastructure, and societal awareness. Some countries with notably high reported rates include Qatar, which reports the highest rate globally,
with approximately 151 cases per 10,000 individuals, and United Arab Emirates follows closely with 112 cases per 10,000 individuals. Marriage among relatives, known as consanguinity, is common in these countries and may contribute to
higher autism rates in these countries. Consanguinity increases the likelihood of genetic conditions, as closely related individuals are more likely to share genetic mutations. Studies have shown that parental consanguinity is associated
with a higher risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, including ASD.
Having babies close together may increase the risk of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Research shows that short interpregnancy intervals—especially less than 12 months—are linked to a significantly higher risk of ASD compared
to spacing of 36 months or more. One study found that children conceived within a year of an older sibling were nearly twice as likely to be diagnosed with autism. Interestingly, very long gaps between pregnancies—typically
over 5 or 6 years—may also elevate the risk, though the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Experts believe that maternal factors such as nutrient depletion, inflammation, and hormonal imbalances during closely spaced pregnancies
may affect fetal brain development. While birth spacing is just one of many factors influencing autism risk, it plays a meaningful role in shaping early neurodevelopment.
Early intervention for symptoms associated with autism spectrum disorder is
critical
for helping families improve outcomes for their children. Children diagnosed with developmental disorders should be identified as children with
special health care needs, and chronic-condition management should be initiated. Specific autism screenings are recommended at the same time as typical well-child visits from infancy through school age, and at any age thereafter.
Developmental surveillance should be performed if concerns are raised about social acceptance, learning, or behavior. Developmental evaluation is required whenever a child fails to meet any of the following milestones: babbling by
12 months; gesturing (e.g., pointing, waving bye-bye) by 12 months; single words by 16 months; two-word spontaneous (not just echolalic) phrases by 24 months; loss of any language or social skills at any age.
There is inadequate evidence to recommend an electroencephalogram study in all individuals with autism . Reflecting social
communication, ADHD, anxiety, food selectivity, and sleeping disorders could provide early signs of autism. Eating and sleeping issues can be identified long before autism is diagnosed. Some children with more typical language skills
may not be identified until they enter school and social requirements are greater.
The causes for the increased Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) incidence are not completely understood though a possible connection to childhood vaccines (which has been resoundingly rejected by rigorous scientific studies). Although
scientists are still trying to understand why some people develop ASD and others don’t, some risk factors include the child has very low birth weight, a sibling with ASD, older parents, and certain genetic conditions. People with
ASD have difficulty with communication and interaction with other people, restricted interests and repetitive behaviors, and symptoms that hurt the person’s ability to function properly in school, work, and other areas of life.
28% of people on the autism spectrum are left-handed, compared to roughly 10% in the general population. That’s a significant difference,
and it suggests a meaningful link between neurodiversity and handedness. Interestingly, mixed-handedness—using different hands for different tasks without a strong preference—is also more common among autistic individuals.
Scientists believe this may be tied to early brain development, since both handedness and language processing are shaped during similar stages in utero.
As of 2025, the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in major global regions shows notable variation. In China, the rate is approximately 638 cases per 100,000 people (0.64%), with underdiagnosis still common due to limited
awareness and uneven access to care. India reports around 715 per 100,000 (about 1 in 36 children), though actual numbers may be higher due to inconsistent reporting and rural healthcare challenges. Across the European Union, the average
prevalence is about 590 per 100,000 (0.59%), with significant variation among countries: France reports 693 per 100,000 (1 in 144), Northern Ireland has rates as high as 1 in 40 children, Poland reports 1 in 160, and Iceland is closer to
1 in 100. These differences reflect disparities in diagnostic criteria, healthcare infrastructure, cultural attitudes, and public awareness.
As of 2025, the countries with the highest reported rates of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are those with advanced healthcare systems and widespread diagnostic practices. Singapore leads with approximately 1,460 cases per 100,000
people, followed closely by South Korea and Japan, each with 1,450 per 100,000. Brunei reports 1,390, while Australia and New Zealand show rates of 1,160 and 1,140, respectively. Canada has 1,070, Chile reports 1,060, the United States
stands at 1,050, and Ireland rounds out the top ten with 1,040 per 100,000. These elevated rates reflect improved awareness, expanded diagnostic criteria, and greater access to evaluations and services, rather than a true increase in
incidence.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD ) is a developmental condition that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction.
While autism can be diagnosed at any age, it is classified as a developmental disorder because symptoms typically emerge within the first two years of life. In the United States, the prevalence of ASD has steadily increased over the past
decade: approximately 1 in 68 children aged 8 were diagnosed in 2010, rising to 1 in 54 in 2015, 1 in 36 in 2024, and 1 in 31 in 2025. This upward trend reflects enhanced public awareness, expanded diagnostic criteria, and improved access
to screening, evaluations, and support services.
In 2025, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, led by Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., ignited controversy by banning thimerosal—a widely studied vaccine preservative deemed safe by decades of research—based on
discredited claims linking it to autism and miscarriage. Despite overwhelming scientific consensus that vaccines do not cause autism, Kennedy appointed individuals with anti-vaccine backgrounds, including David Geier, to influential
positions, raising alarms about politicized science and eroding public trust. While Kennedy maintains his stance is about vaccine safety, critics argue these actions legitimize debunked theories and threaten the integrity of public
health policy.
▷ Cancers
Comparison of common cancers by survival expectation, 5‑year relative survival rates (all stages combined):
Cancer Type
Approx. 5‑Year Survival Notes
Prostate >95% Often detected early;
highly treatable.
Breast
(female) ~90% Screening improves
early detection.
Melanoma (skin) ~93% Very high if caught
early; drops sharply if metastatic.
Colorectal ~65% Strongly
stage‑dependent; screening helps.
Kidney ~77% Improved therapies have
raised survival.
Lung
(non‑small cell) ~28% Historically low;
improving with new treatments.
Lung
(small cell) ~7% Very aggressive; often
diagnosed late.
Pancreatic ~12% One of the lowest; late
detection common.
Liver ~22% Survival has improved
from 7% in the 1990s.
Ovarian ~50% Often diagnosed at
advanced stages.
Leukemia (varies by type) 40–90% Some types now
near-normal life expectancy with targeted drugs.
Cancers known for rapid progression—such as pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma, small‑cell lung cancer, esophageal cancer, liver cancer, stomach cancer, mesothelioma, and gallbladder cancer—tend to have life expectancies measured in months
rather than years once they reach advanced stages, largely because they grow quickly, spread early, and are often diagnosed only after symptoms appear late in the disease. Pancreatic and gallbladder cancers frequently lead to survival
measured in months, while glioblastoma typically offers a median survival of about a year despite aggressive treatment. Small‑cell lung cancer can progress so fast that extensive‑stage disease often results in survival of less than a year,
and advanced esophageal, liver, and stomach cancers follow similarly short timelines. Mesothelioma, though sometimes slower than the others, still carries a median survival of roughly one to two years. Across all of these cancers, limited
early symptoms, few effective screening tools, and resistance to standard therapies combine to shorten life expectancy dramatically.
Cancers with the fastest and deadliest progression tend to share the same brutal traits: they grow aggressively, spread early, and rarely announce themselves until they’ve already advanced. Pancreatic cancer is among the most lethal,
often discovered only after it has spread, leaving surgery possible for a small minority of patients. Glioblastoma follows a similarly devastating path in the brain, with rapid recurrence even after surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Small‑cell lung cancer spreads quickly through the body, while esophageal, liver, stomach, mesothelioma, and gallbladder cancers often remain silent until late stages, when treatment options narrow sharply. Across all of these, the
combination of subtle early symptoms, limited screening tools, and resistance to standard therapies creates a pattern of late detection and high mortality that makes them some of the most dangerous cancers known.
In 2025, glioblastoma remains one of the most relentless primary brain cancers, defined by its rapid infiltration into healthy tissue and a median survival that still hovers around 12 to 18 months. Yet the therapeutic landscape is evolving,
driven by increasingly sophisticated, technology‑enabled strategies. Although five‑year survival continues to sit below 10%, prognosis is now shaped more precisely by molecular signatures such as MGMT promoter methylation and by
surgical innovations like fluorescence‑guided resection that push the limits of safe tumor removal. The long‑standing Stupp Protocol—radiation paired with temozolomide—has expanded into a more layered approach that incorporates
Tumor Treating Fields and a wave of 2025 breakthroughs, including focused ultrasound to transiently open the blood‑brain barrier and hypofractionated proton therapy for more targeted radiation delivery. Alongside these advances,
experimental viral‑mediated gene therapies are emerging as bold attempts to reprogram the tumor’s biology itself. Together, these developments signal a shift from merely slowing an aggressive disease to mounting a more precise,
multi‑front campaign against its microscopic and persistent recurrence.
In 2025, small‑cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains one of the fastest‑moving malignancies in oncology, defined by its near‑immediate tendency to metastasize, yet the therapeutic landscape is shifting toward more durable,
immune‑driven approaches. Median survival for extensive‑stage disease has long hovered between 6 and 12 months, but the routine incorporation of immunotherapies such as durvalumab or atezolizumab alongside platinum‑based
chemotherapy is now extending survival for a meaningful subset of patients. In limited‑stage SCLC, aggressive chemoradiation paired with prophylactic cranial irradiation can push survival into the 2‑ to 3‑year range,
while new 2025 advances—most notably tarlatamab, a DLL3‑targeting BiTE therapy—are offering renewed hope for those confronting relapse. With these immunotherapy innovations and increasingly precise targeting of DLL3‑expressing
tumor cells, clinicians are working to slow the explosive trajectory of SCLC and carve out longer, more sustainable treatment horizons.
In 2025, esophageal cancer remains a formidable clinical challenge, largely because it advances quietly until symptoms such as dysphagia or unintentional weight loss finally force a diagnosis—often at an already advanced stage.
Metastatic disease still carries a typical survival of less than a year, yet the therapeutic landscape has been reshaped by the routine use of immunotherapies like nivolumab and pembrolizumab, which have demonstrated meaningful
survival gains when paired with traditional chemotherapy. For the smaller group diagnosed early, endoscopic resection or the CROSS protocol—preoperative chemoradiation followed by surgery—offers a far more favorable path toward
long‑term survival. As the field moves through 2025, momentum is shifting toward earlier detection and molecular profiling, particularly the identification of HER2‑positive tumors, enabling more precise, targeted treatments that
push beyond the constraints imposed by late‑stage discovery.
Esophageal cancer carries a five-year survival rate of just 21.6%, largely because it’s often diagnosed at advanced stages when treatment options are limited and the disease has already spread. Its symptoms—difficulty swallowing, chest
pain, or unintended weight loss—tend to emerge only after significant progression, making early detection rare. By the time it's caught, surgery may no longer be viable, and chemotherapy or radiation become the primary tools to slow its advance.
Despite medical strides, this cancer remains a formidable challenge, lurking quietly until its grip is hard to break.
Esophageal cancer affects the esophagus and has a poor prognosis due to late detection. Esophageal cancer can present with a range of symptoms, though they often appear only in later stages. These symptoms can overlap
with less serious conditions, making early detection challenging.
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) – This is often the first noticeable symptom; it may start as trouble swallowing solid foods and progress to difficulty with liquids.
Unintentional weight loss – Many people with esophageal cancer lose weight due to difficulty eating or a loss of appetite.
Chest pain or discomfort – Some individuals experience pain or pressure in the chest, especially while eating.
Hoarseness or persistent cough – Changes in the voice or chronic coughing can occur if the cancer affects the throat or nearby nerves.
Heartburn or indigestion – Though common in many other conditions, persistent or worsening acid reflux can be a warning sign.
Vomiting or regurgitation – In more advanced cases, food or liquids may come back up due to obstruction in the esophagus.
In 2025, hepatocellular carcinoma remains a uniquely challenging cancer, with survival hinging not only on tumor stage but also on the underlying condition of the liver, particularly the presence of cirrhosis. Although advanced disease
has traditionally been associated with survival measured in months, the therapeutic landscape has been reshaped by dual‑agent immunotherapy combinations such as atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, which are establishing new survival standards
for patients who are not candidates for surgery. For localized tumors—where five‑year survival approaches 37%—curative strategies like liver transplantation or surgical resection offer the strongest long‑term outcomes, especially when
paired with modern interventional radiology techniques such as radiofrequency ablation. By 2025, the growing use of targeted therapies and the continued improvement in viral hepatitis management are steadily shifting the field away from
purely palliative approaches and toward genuine long‑term disease control.
In 2025, stomach cancer remains a formidable clinical challenge, largely because its early symptoms resemble everyday digestive discomfort, allowing the disease to advance unnoticed until survival is often measured in months. Yet the
outlook for advanced cases has improved with the widespread adoption of immunotherapies such as nivolumab and the rise of targeted treatments for HER2‑positive and Claudin 18.2‑positive tumors, which push survival beyond what traditional
chemotherapy alone could achieve. For the smaller group diagnosed early through upper endoscopy, curative approaches like endoscopic mucosal resection or gastrectomy offer a strong chance of long‑term survival. As precision oncology
continues to evolve in 2025, molecular profiling has become central to care, enabling treatments tailored to each tumor’s genetic signature and transforming a once‑bleak prognosis into a more strategic and manageable fight.
Stomach cancer has a low survival rate and is often diagnosed at an advanced stage. Stomach cancer can be tricky because its early symptoms often mimic common digestive issues.
Persistent indigestion or heartburn
Unexplained weight loss
Loss of appetite
Feeling full quickly when eating
Nausea or vomiting
Abdominal pain or discomfort
Bloating after meals
Difficulty swallowing
Fatigue or weakness
Blood in stool or black, tarry stools
In 2025, mesothelioma remains an aggressive cancer closely tied to asbestos exposure, yet a striking prognostic divide has emerged between its major subtypes. For the roughly 80% of patients with pleural mesothelioma, median survival typically
falls between 12 and 21 months, though the 2024–2025 adoption of frontline immunotherapy—such as nivolumab with ipilimumab or pembrolizumab paired with chemotherapy—is beginning to push these numbers modestly upward. In contrast, peritoneal
mesothelioma offers a far more favorable outlook, with five‑year survival reaching up to 65% in patients eligible for cytoreductive surgery followed by heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC). Cutting‑edge 2025 research is now turning
toward targeted metabolic therapies like pegargiminase, designed to deprive tumor cells of essential nutrients, alongside liquid biopsy technologies that enable earlier detection of recurrence. Together, these advances are reshaping mesothelioma
care into a more personalized, proactive, and durable therapeutic effort.
In 2025, gallbladder cancer remains a formidable diagnosis, largely because the organ’s lack of a protective serosal layer—combined with its close proximity to the liver—allows tumors to spread quickly and quietly before symptoms emerge.
Advanced cases still carry a prognosis measured in months, with metastatic five‑year survival often falling below 5%, yet the standard of care has improved through chemo‑immunotherapy combinations such as durvalumab or pembrolizumab paired
with cisplatin and gemcitabine. These dual‑agent regimens are extending survival beyond historical expectations, particularly in patients with biomarkers like MSI‑H or dMMR. For the roughly 20% diagnosed early—frequently discovered incidentally
during gallstone surgery—radical resection remains the only curative option, offering a markedly better five‑year survival of around 66%. As targeted therapies and genomic profiling continue to advance, the field is shifting toward uncovering
precise molecular vulnerabilities, transforming what was once a uniformly grim outlook into a more strategic and potentially life‑extending fight.
Bladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells form a tumor in the lining of the bladder, and in more advanced cases, the tumor can invade the surrounding muscle tissue. The most common and often earliest symptom is painless blood in
the urine (hematuria), which may appear intermittently and should never be ignored. Other symptoms can include pain during urination, frequent urges to urinate, or a weak urine stream. If blood is noticed in the urine—even if it
disappears—it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly for evaluation. Diagnosis typically involves procedures like cystoscopy, urine cytology, and imaging tests such as CT urograms to assess the bladder and urinary tract.
Treatment options vary depending on the stage and grade of the cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiation therapy.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer among men in the United States; about 9 out of 10 people diagnosed with bladder cancer are over the age of 55. Bladder cancer is most common in white men.
Men are about four times more likely to develop bladder cancer compared to women. There were around 63,100 new cases of bladder cancer in men for 2024, compared to 20,120 new cases in women.
Exposure to arsenic in drinking water is a known risk factor for bladder cancer. Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that can contaminate groundwater, and long-term exposure to high levels of arsenic has been linked to an
increased risk of bladder cancer, which is rare, and accounts for just 5% of all new cancers in the U.S.
In the U.S. for 2025, the cancers causing the highest number of deaths are led by lung cancer, with an estimated 124,730 fatalities, making it the most lethal by sheer volume. Colorectal cancer follows with 52,900 deaths, closely trailed
by pancreatic cancer at 51,980—both known for their late detection and aggressive nature. Prostate cancer, despite being highly treatable when caught early, is expected to claim 35,770 lives, while liver cancer, often linked to chronic
hepatitis and cirrhosis, rounds out the list with 30,090 deaths. These figures underscore the devastating impact of these widespread and often fatal diseases.
In 2025, pancreatic cancer stands as one of medicine’s most elusive foes, often advancing quietly behind the stomach until it has already secured a dangerous foothold—earning its reputation as oncology’s “silent” challenge. Survival
hinges on a race against time, with the ultimate milestone being surgical removal, a possibility reserved for roughly 20% of cases discovered before the tumor infiltrates major vessels or distant organs. Classic warning signs such as jaundice
or persistent back pain typically emerge only after the disease has progressed, prompting a shift toward deeper biological investigation to expose weaknesses hidden within the tumor’s genetic code. This evolution in strategy has opened the
door to more tailored treatments, from potent regimens like FOLFIRINOX that can shrink previously inoperable tumors to targeted therapies designed for mutations such as BRCA. With AI‑driven imaging sharpening detection and clinical trials
pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, the field is steadily transforming fleeting treatment windows into meaningful gains, redefining what survival can look like for this once‑unyielding disease.
Pancreatic cancer has a 5-year survival rate of only 12.5%; it's often diagnosed at an advanced stage because early symptoms are vague and hard to detect. Pancreatic cancer is notoriously difficult to diagnose early, which
contributes to its low survival rate. Symptoms like abdominal pain, jaundice, weight loss, and digestive issues can be subtle and often mistaken for other conditions. Unfortunately, by the time it's detected, it's frequently at
an advanced stage where treatment options are limited.
Pancreatic cancer is a silent killer, notorious for its five-year survival rate of just 12%—and for those diagnosed at Stage IV, that number plummets to a harrowing 1%, with most living less than a year. Its stealthy nature means symptoms
like back pain or jaundice often appear only after the disease has spread to vital organs, rendering surgery impossible and leaving chemotherapy as the primary defense. Regimens like FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine may slow its march, but the odds
remain grim. In rare cases where early detection allows for surgical removal, survival rates can climb dramatically, offering a glimmer of hope. Yet for most, pancreatic cancer remains a ruthless adversary, striking hard before it’s even seen.
Pancreatic cancer is exceptionally lethal because it hides in plain sight, often producing no symptoms until it has already spread beyond the pancreas, making early detection a rarity. Its aggressive nature allows it to metastasize rapidly
and resist many conventional treatments, leaving few effective options once diagnosed. Only 10–20% of patients are candidates for surgery—the only potentially curative approach—due to the advanced stage at which the disease is typically found.
While promising therapies like immunotherapy and targeted treatments are beginning to emerge, they have yet to significantly shift the survival curve, which remains stubbornly low.
Pancreatic cancer stands out as the most lethal, notorious for its stealthy onset and dismal five-year survival rate of just 12.8%, often leaving patients with less than a year after diagnosis. While lung cancer claims the highest number
of lives annually—over 124,000 in the U.S. alone—pancreatic, liver, and esophageal cancers trail closely behind, each marked by aggressive progression and limited treatment options. These malignancies are frequently diagnosed late, resist
conventional therapies, and offer few surgical opportunities, making them formidable adversaries in modern oncology. Despite emerging innovations like immunotherapy and targeted drugs, survival remains grim, underscoring the urgency for
breakthroughs in early detection and intervention.
Pancreatic cancer unfolds like a stealthy antagonist deep in the abdomen, where malignant cells quietly take hold in the pancreas—an organ essential for digestion and blood‑sugar control—before announcing themselves with vague signs
such as abdominal or back pain, jaundice, weight loss, fatigue, or unexpected changes in diabetes. Its risk grows with age, smoking, chronic pancreatitis, obesity, certain genetic mutations, and family history, while diagnosis often relies
on imaging, biopsies, and blood markers because the pancreas hides behind other organs. Treatment ranges from complex surgery to chemotherapy, radiation, and clinical trials, with palliative care playing a vital role in comfort and quality
of life. The disease’s reputation for late detection and resistance to therapy makes early awareness crucial, turning this quiet adversary into one of the most formidable challenges in modern oncology.
Lung and bronchus cancer holds a five-year survival rate of just 26.7%, with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) standing out as particularly aggressive and fast-spreading. Often linked to smoking, SCLC tends to grow rapidly and metastasize early,
making it difficult to catch in its early stages. Even with chemotherapy and radiation, recurrence is common and prognosis remains poor. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), while more common, also poses a serious threat when diagnosed late.
Symptoms like persistent cough, chest pain, or shortness of breath often appear only after the disease has advanced, contributing to its high mortality. Despite advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapy, lung cancer remains the leading
cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) strikes fast and hard, with a five-year survival rate of just 31.9% and a reputation for rapid progression that leaves little room for delay. Originating in the bone marrow, AML floods the bloodstream with abnormal
white blood cells, crowding out healthy ones and triggering symptoms like fatigue, fever, and easy bruising. Treatment typically begins immediately with intensive chemotherapy, but options remain limited, especially for older adults or those with
high-risk genetic mutations. Even after remission, relapse is common, and long-term survival hinges on factors like age, overall health, and access to stem cell transplantation. AML’s aggressive nature and resistance to standard therapies make it
one of the most challenging blood cancers to overcome.
Liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer carries a bleak five-year survival rate of just 21.7%, with global mortality rates soaring due to its strong ties to chronic hepatitis B and C infections. Often developing silently over years, these
cancers typically emerge in regions with limited access to early screening and antiviral treatments. By the time symptoms like abdominal pain, jaundice, or unexplained weight loss appear, the disease is frequently advanced, leaving few curative
options. Even with surgical resection or liver transplantation, recurrence is common, and long-term survival remains elusive. This cancer’s deadly reputation stems not only from its biology but from the global disparities in prevention and care.
Cancer is a complex and varied group of diseases, each with its own behavior, prognosis, and response to treatment. Some types—especially when caught early, like Stage One skin or testicular cancer—can often be cured through surgery,
radiation, or chemotherapy. However, others, particularly those diagnosed at advanced stages or with aggressive biology, may resist treatment and lack a definitive cure. In such cases, therapies aim to control the disease, extend life, and
improve quality of living, often leading to remission rather than complete eradication. The term “cancer” encompasses everything from slow-growing tumors to fast-spreading malignancies, making its curability a matter of timing, type, and
individual biology.
Primary bone cancer is a rare form of cancer that originates directly in the bone tissue, with types such as osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing sarcoma being the most common. These cancers typically affect children, adolescents,
and young adults, and may cause symptoms like localized pain, swelling, and increased risk of fractures. In contrast, secondary bone cancer, also known as metastatic bone cancer, occurs when cancer cells spread to the bones from other
parts of the body—most often from the breast, prostate, lung, or kidney—and is far more common than primary bone cancer. Understanding the distinction between these two types is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning,
as primary bone cancers are treated differently and often more aggressively than secondary ones.
The most dangerous cancers are those with the lowest survival rates and highest mortality; pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), brain cancer, stomach cancer, ovarian cancer,
myeloma, and laryngeal cancer are the most deadliest cancers. In 2022, approximately 608,366 Americans died from cancer, making it the second leading cause of death after heart disease. The most common types of cancer leading to
death include lung, breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers; in 2024 approximately 125,070 people are expected to die from lung cancer; 42,250 women from breast cancer; 35,250 men from prostate cancer; and 53,010 deaths from
colorectal cancers.
Lung cancer in non-smokers often presents differently, with adenocarcinoma being the most common type. It’s also more frequently diagnosed at later stages because symptoms can be subtle or mistaken for other condition.
Lung cancer can develop in non-smokers due to various risk factors, including genetic mutations, environmental exposures, and lifestyle influences.
Radon exposure: This naturally occurring radioactive gas can seep into homes and buildings, increasing lung cancer risk.
Secondhand smoke: Breathing in smoke from others can still expose a person to harmful carcinogens.
Air pollution: Long-term exposure to pollutants, especially in urban areas, has been linked to lung cancer.
Occupational hazards: Exposure to asbestos, diesel exhaust, and other industrial chemicals can contribute to lung cancer.
Genetic predisposition: Some individuals inherit gene mutations that make them more susceptible to lung cancer.
Cooking fumes: In some regions, prolonged exposure to smoke from cooking fuels and oils has been associated with lung cancer.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death, with a high mortality rate due to late diagnosis when treatment options are more limited, and aggressive nature spreading quickly. Lung cancer has several major risk factors, many of which
can be controlled, while others are beyond one's influence.
Smoking: The leading cause, responsible for most lung cancer cases. The risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked and the duration of smoking.
Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to smoke from others can also increase the risk significantly.
Radon Gas: A naturally occurring radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes, increasing lung cancer risk.
Occupational Exposure: Prolonged exposure to asbestos, arsenic, diesel exhaust, or other harmful chemicals can elevate risk.
Air Pollution: Living in areas with high air pollution can slightly increase the likelihood of lung cancer.
Genetic Factors: A family history of lung cancer may increase susceptibility.
Previous Lung Disease: Certain lung conditions, like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), can contribute to a higher risk.
Liver cancer is difficult to treat and has a low survival rate; it can be incredibly challenging to treat, and its prognosis is often poor, especially in later stages. One of the major issues is that symptoms tend to
appear only when the disease has progressed, making early detection difficult. Risk factors like chronic hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis, excessive alcohol consumption, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease all increase
the likelihood of developing liver cancer. However, prevention efforts—such as vaccination for hepatitis B, lifestyle changes to reduce alcohol intake, and maintaining liver health—can significantly lower the risk.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a type of blood cancer that progresses rapidly and has a low survival rate. AML starts in the bone marrow and quickly spreads into the bloodstream. It affects the myeloid cells, which normally
develop into various types of blood cells, including white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. Because AML progresses rapidly, early diagnosis and treatment are critical. Despite its severity, advancements in medical
research have led to improved treatments, including chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and bone marrow transplants. While survival rates can be low, especially in older adults, some patients respond well to treatment, and
new therapies continue to emerge.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), an aggressive type of blood cancer, can cause a variety of symptoms, often developing rapidly.
Fatigue and Weakness – Due to anemia from low red blood cell production.
Frequent Infections – A weakened immune system makes fighting infections harder.
Easy Bruising and Bleeding – Caused by a drop in platelets, which help with blood clotting.
Shortness of Breath – Resulting from low oxygen levels in the blood.
Bone or Joint Pain – As leukemia cells multiply in the bone marrow.
Swollen Gums or Lymph Nodes – Some subtypes of AML can cause swelling.
Unexplained Weight Loss or Fever – Due to the body’s response to cancer.
Paleness or Skin Rash – Changes in blood cell production can affect the skin.
Brain cancer (including Glioblastoma) are particularly aggressive and difficult to treat, with a low survival rate. The median survival time for adults diagnosed with glioblastoma is around 15 months.
Only about 5.6% of affected adults survive for five years or more. Brain cancer symptoms can vary depending on the tumor's location, size, and growth rate.
Persistent headaches that worsen over time, especially in the morning or when lying down.
Nausea and vomiting, often unrelated to food intake.
Seizures, even in individuals with no prior history of epilepsy.
Vision problems, such as blurred or double vision.
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
Weakness or numbness in one side of the body.
Personality or behavioral changes, including confusion or memory loss.
Loss of balance or coordination.
Ovarian cancer is often detected late, contributing to its high mortality rate. Early symptoms of ovarian cancer can be subtle and often mistaken for common digestive or menstrual issues. Because these symptoms can be vague,
they often go unnoticed until the cancer has progressed.
Abdominal bloating or swelling
Feeling full quickly when eating
Unexplained weight loss
Discomfort or pain in the pelvic area
Fatigue
Back pain
Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
Frequent need to urinate
Multiple myeloma is a rare blood cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow. These cancerous plasma cells crowd out healthy blood cells, leading to low blood counts. Because these cells are found in the bone marrow, myeloma cancer can weaken bones, disrupt blood cell production, and impair the body's ability to fight infections. The survival rate for multiple myeloma is relatively low.
Multiple myeloma is a type of blood cancer that affects plasma cells, which are a part of the immune system. In its early stages, it may not cause noticeable symptoms, but as it progresses, common signs can include:
Bone pain, especially in the spine, chest, or hips.
Fatigue due to anemia.
Frequent infections because of weakened immunity.
Weight loss and loss of appetite.
Mental fogginess or confusion.
Kidney problems, sometimes leading to kidney failure.
High calcium levels, which can cause excessive thirst, nausea, and constipation.
Weakness or numbness, particularly in the legs, due to nerve damage.
Laryngeal cancer affects the larynx and has a low survival rate due to late detection. Laryngeal cancer is a serious condition that affects the voice box, often leading to challenges in speech and breathing. One of the biggest
concerns is that symptoms like hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, or persistent throat pain can be overlooked, leading to late-stage diagnosis when treatment options are more limited.
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer, especially among women over 50, though it can also affect younger women and, in rare cases, men. The earliest and most typical symptom is a lump or thickened area of breast tissue,
but other warning signs include changes in breast size or shape, nipple discharge (possibly blood-streaked), swelling in the armpits, skin dimpling, rashes around the nipple, or a sunken appearance of the nipple. While most breast lumps
are not cancerous, any unusual changes should be evaluated by a doctor. Notably, breast pain on its own is not considered a symptom of breast cancer. Early detection through awareness and screening is key to improving outcomes.
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death among women; around 246,660 American women are diagnosed with breast cancer each year and over 40,000 die annually.
Breast cancer in men is rare; however, around 2,600 American men were diagnosed with breast cancer each year and approximately 440 died annually.
Breast cancer survivors who take aspirin regularly may be less likely to die or have their cancer return. Aspirin has relatively benign adverse effects compared with cancer chemotherapeutic drugs and may also prevent
colon cancer, cardiovascular disease, and stroke.
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed among women in the U.S.; the 5-year relative survival rate for breast cancer is about 91%; some risk factors for
breast cancer include age, family history, genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1 and BRCA2), and lifestyle factors such as obesity and alcohol consumption. Breast cancer symptoms can vary,
signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape,
dimpling of the skin, fluid coming from the nipple, or a red scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be
bone pain , swollen lymph nodes ,
shortness of breath , or yellow skin .
Common symptoms of breast cancer include:
A new lump in the breast or armpit that doesn’t go away.
Changes in breast size, shape, or texture.
Skin changes, such as redness, dimpling, or a rash resembling an orange peel.
Swelling in the armpit or near the collarbone, which may indicate cancer spreading to lymph nodes.
Nipple changes, including inward pulling, burning, itching, or unusual discharge.
Pain or tenderness in the breast, though lumps don’t usually hurt.
Increased risk for getting liver cancer when a person has symptoms that may include discomfort in the upper abdomen on the right side, a swollen abdomen, a hard lump on the right side just below the rib cage, pain near
the right shoulder blade or in the back, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), easy bruising or bleeding, unusual tiredness, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, and/or weight loss for no known reason.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the U.S., about 6 in 10 cases diagnosed in men aged 65 or older; the 5-year relative survival rate for prostate cancer is about 97.5%. Prostate cancer often develops without
noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, when symptoms do appear, they may include:
Difficulty urinating or a weak urine stream
Frequent urination, especially at night
Blood in urine or semen
Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
Erectile dysfunction
Bone pain if the cancer has spread
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men. Each year, roughly 300,000 men in the U.S. receive this diagnosis; prostate cancer can be a serious disease, and while many cases are caught early and successfully treated,
it remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among men aside from skin cancer. About 1 of 44 men has died of prostate cancer annually. While it can be serious, early detection through screenings like PSA tests and digital
rectal exams can significantly improve outcomes.
Around 1 in 7 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. There was a study published in 2014 that suggested men who had more than 20 female
sexual partners in their lifetime had a 28% lower risk of developing prostate cancer overall, and a 19% lower risk of aggressive prostate cancer, compared to men with fewer partners. However, a 2020 analysis published by Harvard Health
pointed out that men with 10 or more sexual partners were actually more likely to develop cancer, not less. The discrepancy may come down to confounding factors—like smoking, alcohol use, or sexually transmitted infections—that
weren’t fully accounted for in earlier research.
Prostate cancer is cancer that occurs in the prostate, which is a small walnut-shaped gland in
males that produces the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer is diagnosed with a biopsy. The most common reason for a man to undergo a prostate biopsy is due to an elevated prostate-specific
antigen level (PSA), determined by a blood test. It's not clear what causes prostate cancer. Prostate cancer may cause no signs or symptoms in its early stages; when it's more advanced, signs and symptoms may include
trouble urinating, decreased force in the stream of urine blood in the urine and the semen, and/or erectile dysfunction.Prostate cancer, which is the most commonly diagnosed type of cancer, is the second leading cause of cancer in men. One in 8 men has been diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point in their lives.
Prostate cancer incidence increases with age, the older men are, the greater their chance of developing this disease. Around 60% of all prostate cancers are diagnosed in men over the age of 65
(1 in 55 for ages 50 to 59, 1 in 20 for ages 60 to 69, and 1 in 12 for ages 70 and older).
According to the American Cancer Society, an estimated 313,780 new cases of prostate cancer will be diagnosed in 2025, and approximately 35,770 men will die from the disease. It remains the most common cancer among American
men after skin cancer and is the second-leading cause of cancer death, following lung cancer. While the death rate has declined significantly over the past few decades due to better screening and treatment, the number of
advanced-stage diagnoses has been rising again in recent years.
All dangerous tumors share a core set of traits that define malignant behavior: they arise from uncontrolled, irreversible cell growth, the hallmark of a malignant neoplasm; they possess the ability to invade nearby tissues, breaking
through normal biological boundaries; they carry the potential to metastasize through blood or lymphatic pathways, allowing them to seed new tumors far from their origin; and they are often resistant to standard treatments such as surgery,
chemotherapy, and radiation, making them especially challenging to manage once they gain momentum.
Dangerous tumors form a shadowy spectrum of malignant growths, each defined by its ability to invade tissue and spread with ruthless efficiency, from lung cancer—one of the deadliest killers worldwide—to pancreatic cancer, whose subtle
early signs help fuel its reputation as one of the most lethal malignancies; colorectal cancer adds to the toll as a global leader in cancer‑related deaths, while aggressive breast cancer subtypes such as triple‑negative forms accelerate
rapidly, and advanced prostate cancers metastasize with alarming speed; even more formidable are tumors like glioblastoma, esophageal cancer, liver cancer, ovarian cancer, and stomach cancer, all known for their fast growth and resistance
to treatment, creating a landscape where malignant neoplasms turn uncontrolled cell division into a biological force capable of reshaping entire organ systems.
Lung cancer stands out as one of the deadliest cancers worldwide, a malignancy that often hides in plain sight until it has already advanced, making late diagnosis common and giving it the opportunity to spread rapidly through the body.
Pancreatic cancer ranks among the most lethal malignancies, largely because its early symptoms are so subtle that the disease often advances unnoticed, allowing it to progress with remarkable speed; by the time it is detected, it is frequently
resistant to treatment, creating a clinical challenge that makes this cancer one of the most formidable in modern medicine.
Colorectal cancer is a major global cause of cancer‑related death, a malignancy that can grow in near silence for years before detection, allowing tumors to advance unnoticed and making early diagnosis one of the most challenging—
and critical—factors in managing this disease.
Breast cancer includes many treatable forms, but certain aggressive subtypes—most notably triple‑negative breast cancer—break from that pattern by growing rapidly, spreading early, and resisting many standard therapies, turning
what is often a manageable disease into one that demands swift, intensive intervention.
Prostate cancer in its advanced forms includes variants that break from the typically slow‑growing pattern of the disease, instead progressing rapidly and metastasizing early, turning a usually manageable malignancy into one capable
of spreading with striking speed and demanding far more aggressive clinical attention.
Other highly aggressive tumors form a particularly dangerous group of cancers known for growing and spreading with unusual speed, including glioblastoma, a brain tumor that infiltrates surrounding tissue with remarkable stealth;
esophageal cancer, which often advances before symptoms become noticeable; liver cancer, driven by rapid cellular turnover and a tendency to metastasize early; ovarian cancer, notorious for remaining hidden deep in the abdomen until
it reaches advanced stages; and stomach cancer, which can progress swiftly and invade nearby organs, making this cluster of malignancies especially challenging to detect and treat before they gain momentum.
Cholesterol influences cancer development in distinct ways depending on the type. In prostate cancer, high cholesterol fuels androgen production and tumor growth, while lower levels are linked to reduced risk of aggressive forms.
Colorectal cancer cells exploit cholesterol to activate growth pathways like PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin, making elevated levels a risk factor, though statins may suppress tumor progression. In breast cancer, high total and LDL cholesterol
contribute to hormone-driven growth and inflammation, with statins showing potential to reduce recurrence and mortality. Pancreatic cancer cells are highly cholesterol-dependent, though some aggressive subtypes resist statin therapy by
bypassing cholesterol biosynthesis. Overall, cholesterol plays a critical role in supporting cancer cell proliferation, hormone signaling, and inflammation, while statins may offer protective effects in several cancers.
Cholesterol levels appear to influence the development and progression of several types of cancer, though the relationship is complex and varies by cancer type. Elevated cholesterol, particularly in the form of
hypercholesterolemia, has been linked to increased risks of colorectal, prostate, breast, and pancreatic cancers. This may be due to cholesterol’s role in promoting chronic inflammation, altering hormone signaling in
hormone-sensitive cancers, and producing oxidized cholesterol molecules that can damage DNA1. Cancer cells often reprogram their cholesterol metabolism—boosting synthesis, uptake, and storage—to support rapid growth and survival,
making them “cholesterol-addicted”. For example, in melanoma, higher expression of cholesterol synthesis genes correlates with poorer patient outcomes. On the other hand, low cholesterol levels have also been studied as potential
indicators of certain cancers, though it's unclear whether they are a cause or a consequence of disease. Statins, which lower cholesterol, have shown promise in reducing the risk or progression of cancers like melanoma, non-Hodgkin
lymphoma, endometrial, breast, and colorectal cancers2. Overall, maintaining balanced cholesterol levels is considered important for both cardiovascular and cancer-related health.
Research suggests that men with total cholesterol levels below 200 mg/dL may have a lower risk of developing prostate cancer, particularly its more aggressive forms, possibly due to cholesterol’s role in hormone production
and cell membrane structure. However, extremely low LDL cholesterol levels—especially in individuals not taking statins—have been associated with a higher incidence of cancer, which may reflect underlying health issues rather
than a direct cause. Interestingly, statins, the drugs commonly used to lower cholesterol, have shown potential in reducing the risk of certain cancers such as colorectal, pancreatic, and skin cancers by influencing inflammatory
and cellular signaling pathways. These findings highlight a nuanced relationship between cholesterol levels and cancer risk, suggesting that maintaining balanced cholesterol may support both cardiovascular and cancer prevention goals.
Black or African American men face a significantly higher burden when it comes to prostate cancer. They are more likely to be diagnosed with the disease, often at a younger age, and tend to present with more advanced stages by
the time it's detected. Tragically, they also experience higher mortality rates from prostate cancer compared to other racial and ethnic groups. These disparities reflect a complex interplay of genetic factors, access to care,
socioeconomic conditions, and systemic inequities in healthcare—making targeted awareness, early screening, and equitable treatment strategies essential for improving outcomes.
When prostate cancer is slow-growing or unlikely to spread quickly, many doctors recommend a strategy known as active surveillance or watchful waiting. This approach involves regular monitoring—such as PSA tests, imaging, and
biopsies—to keep tabs on the cancer without jumping into treatment right away. If the disease progresses or symptoms worsen, treatment options may include surgery to remove the prostate, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other
targeted therapies. Each option carries potential side effects, including urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and bowel issues, making it essential to weigh the risks and benefits carefully with a healthcare provider.
Prostate cancer often develops silently, with most men experiencing no noticeable symptoms in its early stages. When signs do appear, they may include frequent urination, difficulty starting or maintaining a steady stream,
blood in the urine or semen, or persistent pain in the back, hips, or pelvis. While these symptoms can be alarming, they are not exclusive to prostate cancer and may stem from other, less serious conditions. It's important to
consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and peace of mind if any of these issues arise.
In 2025, prostate cancer stands as the most frequently diagnosed cancer among men in the U.S., with an estimated 313,780 new cases—making up 15.4% of all male cancer diagnoses—and 35,770 deaths, accounting for 5.8% of male cancer
fatalities. After a sharp decline in incidence from 2007 to 2014 due to reduced PSA screening, the trend has reversed, with rates climbing 3% annually since 2014, particularly among younger men under 55 and those presenting with advanced-
stage disease. While the five-year survival rate remains high at nearly 98%, the rise in late-stage diagnoses and the slowing decline in mortality signal a troubling shift. These patterns underscore the evolving landscape of prostate
cancer, where early detection, disparities in outcomes, and the need for refined screening strategies are once again at the forefront of public health attention.
In the U.S. prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men in the U.S., especially as they age. About 313,780 new cases
of prostate cancer are expected in 2025. Around 35,770 deaths are projected this year. Roughly 6 in 10 cases are diagnosed in men aged 65 or older, with the average age at diagnosis being 67. The lifetime risk of
being diagnosed is about 1 in 8, while the risk of dying from it is about 1 in 44. There are some symptoms of this disease: urinary problems (e.g.; urgency, frequency, hesitancy, pain during urination), difficult
in penile erection, painful ejaculation, blood in urine or semen, pelvic discomfort, frequent pain in lower back, belly or hip, swelling in the legs. Many of these symptoms can also be caused by benign prostatic
hyperplasia (BPH) or infections, so they don’t always mean cancer—but they should definitely prompt a medical check.
The PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test was once widely used as a routine screening tool for prostate cancer. However, over time, experts realized that PSA testing can lead to overdiagnosis and
overtreatment—identifying slow-growing cancers that might never cause harm, yet prompting invasive biopsies or treatments with serious side effects like incontinence or impotence. Because of this, major health
organizations now recommend a shared decision-making approach:
Men aged 55–69 should talk with their doctor about the benefits and risks of PSA screening and make an individual choice based on personal values and risk factors.
Men 70 and older are generally not advised to undergo routine PSA screening, unless they’re at high risk or have specific concerns.
Men can develop the breast cancer disease; male breast cancer is rare but very real, and awareness is crucial. In the U.S., breast cancer in men accounts for less than 1% of breast cancer cases, and tends to
strike men aged 60 and older, and risk factors include family history of breast cancer (especially BRCA2 mutations), radiation exposure to the chest, hormonal imbalances, such as elevated estrogen levels, liver disease,
obesity, or testicular disorders. Symptoms in men are similar to those in women: a lump in the breast, nipple discharge, or changes in breast shape or skin. According to the American Cancer Society, in 2025,
about 2,800 men in the U.S. will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, and approximately 510 will die from it.
Bowel cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, refers to malignancies that begin in the large bowel, which includes the colon and rectum. The specific name—colon or rectal cancer—depends on the exact location of the tumor within
the large intestine. It is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide, particularly in older adults. While cancer can also originate in the small bowel (small intestine), this form is significantly rarer, accounting for only
about 3% of gastrointestinal cancers. Small bowel cancers include types like adenocarcinomas, carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). In contrast, colorectal cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related
deaths and is often detected through screening methods such as colonoscopy, which can identify precancerous polyps before they develop into invasive cancer.
People with Cowden syndrome have a significantly increased risk of developing several types of cancer—including colon and rectal cancer—often
at a younger age than the general population2. This rare genetic condition is linked to mutations in the PTEN gene, which normally helps regulate cell growth. When this gene is altered, it can lead to uncontrolled
cell division and tumor formation, both benign and malignant.
Cancer that begins in the colon is called colon cancer, and cancer that begins in the rectum is called rectal cancer. Cancer that starts in either of these organs may also be called colorectal cancer. Each year around 143,000 people
in the U.S. are diagnosed with colorectal cancer . It is the fourth most common cancer in men, after
skin ,
prostate , and
lung cancer.
About 154,270 people in the U.S. were diagnosed with colon and rectal cancer in 2025, and about 52,900 deaths are expected from the disease. While incidence rates have declined in older adults, rates are rising in people under 50,
increasing by about 2.4% per year. It's recommended that for people between age 50 and 75 colonoscopy should be screening once every 10 years, sigmoidoscopy every five years, an annual FIT (Fecal Immunochemical Test) / stool blood test,
an annual gFOBT (Guaiac-based Fecal Occult Blood Test), and FIT-DNA (Cologuard) for every 1 to 3 years.
Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths when numbers for men and women are combined; the 5-year relative survival rate for colorectal cancer is about 65%; age is a significant risk factor, with
most cases diagnosed in people aged 50 and older.
The colon and rectum make up the large intestine (or large bowel), which is part of the digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal (GI) system. Colon cancer, which is a type of cancer that begins in the large intestine (colon),
is sometimes called colorectal cancer (CRC), a term that combines colon cancer and rectal cancer, which begins in the rectum.
CRC, which typically affects 33% of older adults (male or female), usually begins as small, noncancerous (benign) clumps of cells called polyps that form on the inside of the colon. Over time some of these polyps can become CRC.
Finding and removing polyps can prevent CRC. When abnormal tissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the US; 1 out of 20 people will develop CRC in their lifetime . CRC often has no obvious signs or
symptoms; when symptoms appear, they'll likely vary, depending on the cancer's size and location in the large intestine. If CRC develops, many treatments are available to help control it, including surgery, radiation therapy and drug treatments,
such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy; when detected early people with CRC have a greater than 90% 5-year survival rate.
In 2024, colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, with an estimated 53,010 deaths—a slight increase from 52,550 in 2023. While overall death rates have declined among older
adults due to better screening and treatment, there's growing concern about rising incidence and mortality in younger adults under 50, where rates have been increasing by about 1–2% per year
Around 48,330 Americans were diagnosed with oral cavity
or oropharyngeal cancer each year and approximately 9,570 died annually.A multi-cancer early detection test, Galleri , developed by Grail, Inc. , an American healthcare company, can detect over 50 types of cancers — over 45 of which lack recommended
screening today — with a low false positive rate, through a single blood draw. The Galleri test looks for signals present in the blood that may be associated with cancer at the time of the blood draw. If a cancer signal is detected, Galleri results can point to where in the body the cancer is coming from. However, the Galleri
test does not diagnose cancer and not all cancers may be detected in the blood. A bone marrow biopsy , which involves removing a small sample of the bone marrow inside bones for testing, may also help confirm a diagnosis of a blood cancer.
Liver cancer is the 6th most common cancer in the world, and
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for 90% of primary liver cancer cases. This type of cancer occurs more often in men than women,
and is usually diagnosed in people age 50 or older. Almost any cancer, such as,
breast cancer ,
colorectal cancer ,
esophageal cancer ,
lung cancer ,
melanoma ,
pancreatic cancer , and
stomach cancer ,
can spread to the liver.Most cases of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), occur in people who already have signs and symptoms of chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis
caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. The risk of HCC for people with
type 2 diabetes is greater (from 2.5 to 7.1 times the non-diabetic risk) depending on the duration of diabetes and treatment
protocol. HCC often doesn’t show symptoms until the advanced stages of the disease, but some people may experience abdominal pain or tenderness, easy bruising or bleeding, enlarged abdomen, unexplained weight loss,
and jaundice. HCC remains associated with a high mortality rate, in part related to initial diagnosis commonly at an advanced stage of disease.
Globally, each year over 750,000 people are diagnosed with liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), most often in late stages of the disease. Almost 50% of all cases are diagnosed in China in large part due to the prevalence of hepatitis B and C, fatty foods and obesity, alcohol, and aflatoxin (a carcinogenic mould found in contaminated food, especially rice).
There are limited treatments available for people across all stages of liver cancer, and even less if diagnosed at the advanced stage. Despite the high prevalence of HCC, people with the disease still have few options and a low survival rate. In fact, less than 50% of people diagnosed with advanced HCC will survive more
than a year after diagnosis. Treatments currently available across different stages of the disease include surgery to remove masses, radiation, liver transplant, transarterial chemoembolisation , chemotherapy,
freezing or heating the cancer cells, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
The most common types of cancer in males are lung cancer , prostate cancer ,
colorectal cancer and stomach cancer . In females, the most common types are
breast cancer , colorectal cancer, lung cancer and cervical cancer. Cancer
is the second leading cause of death globally, and was responsible for 8.8 million deaths in 2015. Globally, nearly 1 in 6 deaths is due to cancer .
Approximately 70% of deaths from cancer occur in low- and middle-income countries.
Cervical cancer is a malignant condition that begins in the cervix—the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina—and is most often caused by persistent infection with high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV). In its early
stages, cervical cancer typically presents no symptoms, making regular screening through Pap tests and HPV testing essential for early detection. When symptoms do occur, the most common is unusual vaginal bleeding, which may happen after
sexual intercourse, between menstrual periods, or following menopause. Other signs can include watery or bloody discharge, pelvic pain, or pain during sex. While abnormal bleeding doesn’t necessarily mean cancer, it should always be evaluated
by a healthcare provider. If cervical cancer is suspected, patients are usually referred to a specialist within two weeks for further testing, which may include colposcopy, biopsy, and imaging to determine the stage and guide treatment options
such as surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
In the U.S., each year there are about 56,000 new cases of thyroid cancer , and the majority of those diagnoses are papillary
thyroid cancer — the most common type of thyroid cancer. Some thyroid cancer signs and symptoms include a hoarse voice, neck pain, and enlarged lymph nodes. Although as much as 75% of the population will have thyroid nodules,
the vast majority are benign. Thyroid cancer can occur in any age group and its aggressiveness increases significantly in older patients. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer at a ratio of 3:1. Fewer than 1% of all
thyroid nodules are malignant (cancerous). A nodule that is cold on scan is more likely to be malignant. However, the majority of these are benign as well.
Thyroid cancer does not always cause symptoms; often, the first sign of thyroid cancer is a thyroid nodule. Most thyroid cancers are very curable. In fact, the most common types of thyroid cancer (papillary and follicular thyroid cancer)
are the most curable. In younger patients, both papillary and follicular cancers have a more than 97% cure rate if treated appropriately.
Cancer has a major impact on society in the U.S. and across the world. People who have cancer may have questions about how serious their cancer is and the chances of survival. The answer depends on
the type of cancer, the stage of the cancer, cancer's grade, age, how healthy they are, and how they respond to treatment. The period of time may be 1 year, 2 years, 5 years, etc. In the U.S. the average number of new cases
of cancer is 440 per 100,000 men and woman per year, and the average number of cancer deaths is 163.5 per 100,000 people. In 2018, there were around 1,735,350 new cases of cancer, and 609,640 people died from the disease.
In 2017, there were 15,270 children and adolescents ages 1 to 19 were diagnosed with cancer and 1,790 died of the disease. Understanding of
cancer prognosis is important.
The most common cancers :
Breast cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 89.9%),Lung and bronchus cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 19.4%),Prostate cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 98%),Colon and rectum cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 64.4%),Melanoma of the skin (percent surviving 5 years: 92.2%),Bladder cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 77.1%),Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (percent surviving 5 years: 72.0%),Kidney and renal pelvis cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 74.8%),Endometrial cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 19.9%),Leukemia (percent surviving 5 years: 62.7%),Pancreatic cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 9.3%),Thyroid cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 92.3%),Liver cancer (percent surviving 5 years: 18.4%).
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. Signs and symptoms usually depend on the size and type of cancer.
Breast cancer Endometrial cancer Cervix cancer Ovarian cancer Lung cancer Head and neck cancer Brain cancer Thyroid cancer Oesophageal cancer Stomach cancer Colon & rectal cancer Liver cancer Pancreatic cancer Skin cancer Kidney cancer Bladder cancer Prostate cancer Testis cancer Bone cancer Lymphoma Blood cancer
Cancer is a collection of related diseases in which some of the body’s cells begin to divide without stopping and spread into surrounding tissues.
Different cancers can require different treatments, like chemotherapy , radiation therapy , or
immunotherapy.
There are many types of cancer ,
breast cancer ,
lung and bronchus cancer ,
prostate cancer ,
colon and rectum cancer ,
melanoma of the skin ,
bladder cancer ,
non-Hodgkin lymphoma ,
kidney cancer ,
renal pelvis cancer ,
endometrial cancer ,
leukemia ,
pancreatic cancer ,
thyroid cancer , and
liver cancer
are the most common cancers. There is an estimated 1,740,000 new cases of cancer each year in the United States and around 610,000 people
die from the disease.There are a number of cancer symptoms that
men are likely to ignore. These include upset stomach or stomachache; chronic "acid stomach" or feeling full after a small meal; unexplained weight loss; jaundice; wheezing or shortness of breath;
chronic cough or chest pain; frequent fevers or infections; difficulty swallowing; chronic heartburn; swelling of facial features; swollen lymph nodes or lumps on the neck; underarm, or groin, excessive bruising or bleeding that doesn't stop;
weakness and fatigue; rectal bleeding or blood in stool; bowel problems; difficulty urinating or changes in flow; pain or burning during urination; blood in urine or semen; erection problems; pain, aching, or heaviness in the groin, hips, thighs, or abdomen;
testicular swelling or lump; unexplained back pain; scaly or painful nipple or chest, nipple discharge; a sore or skin lump that doesn't heal, becomes crusty, or bleeds easily; and changes in nails.
There are a number of cancer symptoms women are likely to ignore. These include wheezing or
shortness of breath; chronic cough or chest pain; swallowing problems or hoarseness; frequent fevers or infections swollen lymph nodes or lumps on the neck, underarm, or groin; bloating or abdominal weight gain --
the "my jeans don't fit" syndrome; feeling full and unable to eat; pelvic or abdominal pain;unusually heavy or painful periods or bleeding between periods; rectal bleeding or blood in stool; upset stomach or stomachache; a red,
sore, or swollen breast; nipple changes; excessive bruising or bleeding that doesn't stop;weakness and fatigue; unexplained weight loss; swelling of facial features; a sore or skin lump that doesn't heal, becomes crusty,
or bleeds easily; changes in nails; and pain in the back or lower right side.
Cancer develops when cells in the body grow uncontrollably due to changes (mutations) in their DNA. Mutations in DNA disrupt the normal processes that regulate cell growth and division. This can lead to the formation of tumors,
which can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Malignant tumors invade surrounding tissues and can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system—a process called metastasis. The causes of
these DNA mutations can vary widely, from inherited genetic factors to environmental exposures and even random errors during cell division. It's a complex and multifaceted disease, which is why research into its prevention, treatment,
and cure is so vital.
Cancer is a condition where cells in a specific part of the body grow and reproduce uncontrollably. The cancerous cells can invade and destroy surrounding healthy tissue, including organs. Untreated, these cells can potentially
spread to other tissues in the body, including organs, which is known as secondary or metastatic cancer.
Late effects of cancer treatment can come from any of the main types of
cancer treatment :
chemotherapy ,
hormone therapy ,
radiation therapy ,
surgery ,
targeted therapy and
immunotherapy .
For the cancer treatment using chemotherapy, late effects may include dental problems, early menopause, eye problems, hair loss, hearing loss, heart problems, increased risk of other cancers, infertility, loss of taste,
lung disease, nerve damage, osteoporosis (bone loss), and reduced lung capacity.
For the cancer treatment using hormone therapy, late effects may include blood clots, hormonal change, hot flashes, increased risk of other cancers, menopausal symptoms, osteoporosis, and sexual side effects.
For the cancer treatment using radiation therapy, late effects may include cavities and tooth decay, dry mouth, early menopause, hair loss, heart and vascular problems, hypothyroidism, increased risk of other cancers,
increased risk of stroke, infertility, intestinal problems, lung disease, lymphedema, memory problems, and osteoporosis.
Late side effects from surgery depend on the type of cancer and the surgery location in the body; lymphedema is most commonly caused by the removal of or damage to a lymph node as a part of this cancer treatment.
Late effects are unknown for the cancer treatment with targeted therapy or immunotherapy.
Cancer , an incurable disease , is a deadly terminal disease known worldwide.
There are over 200 different types of cancers. While 1 in every 3 women in her lifetime, is likely to die because of breast cancer, colo-rectal cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and lung and bronchial cancer,
1 in every 2 men in his life time, mostly dies because of lung & bronchus cancer, prostate cancer, colon & rectum cancer, pancreas cancer, and liver & intrahepatic bile duct cancer.In the US, cancer usually develops in older people ; 86% of all cancers are diagnosed in people 50 years of age or older.
Lifetime risk refers to the probability that an individual will develop or die from cancer over the course of a lifetime. The lifetime risk of developing cancer is 42% in men and 38% in women.
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth
with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Many cancers can be prevented by not smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, not drinking too much alcohol ,
eating plenty of vegetables, fruits and whole grains, vaccination against certain infectious diseases, not eating too much processed and red meat, and avoiding too
much sunlight exposure. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths, Another 10% is due to obesity ,
poor diet , lack of physical activity and drinking
alcohol . Other factors include certain infections , exposure to
ionizing radiation and environmental pollutants.There are more than 200 different types of cancer, the most common ones are breast, lung, prostate and bowel. Each cancer is diagnosed and treated in a particular way. One in two people develop some kind of cancer during their lifetime,
most cases of cancer are in people aged 50 and over. Changes to the body's normal processes or unusual, unexplained symptoms can sometimes be an early sign of cancer, such as a lump that suddenly appears on the body, unexplained bleeding,
and changes to your bowel habits.
Many cancers are found too late and most of them show no symptoms until later stages, and treatment options may be limited and the outcomes are often deadly. Cancer blood tests and other laboratory tests may help doctors make a cancer diagnosis.
Common blood tests used to diagnose cancer include
Complete Blood Count (CBC) (used to detect if too many or too few of a type of blood cell or abnormal cells are found in blood);
Blood Protein Testing (used to detect certain abnormal immune system proteins (immunoglobulins) that are sometimes elevated in people with multiple myeloma;
Tumor Marker Tests (used to detect chemicals made by tumor cells in blood); and
Circulating Tumor Cell Tests (used to detect cells that have broken away from an original cancer site and are floating in the bloodstream).
Nearly 2 million Americans have been diagnosed with cancer in 2023, and around 610,000 people have died of the disease; anyone can develop cancer, but 88% of those in the U.S. diagnosed with cancer are 50 or older,
and 57% are 65 or older, the American Cancer Society said.
In 2023, an estimated 609,820 people in the United States died from cancer, while in 2024, that number rose slightly to 611,720 deaths, averaging about 1,680 deaths per day. Lung cancer continued to be the top killer,
followed by colorectal, pancreatic, breast, prostate, and liver/intrahepatic bile duct cancers. In 2024, the U.S. also saw a record-breaking 2 million new cancer cases, driven by rising incidence in prostate, breast, pancreatic,
kidney, and melanoma cancers.
Cancer was the second leading cause of death, after heart disease, in the United States. In 2024, there were 611,720 cancer deaths. Lung cancer remains the deadliest, followed by colorectal and pancreatic cancers.
Breast and prostate cancers are the leading gender-specific causes of death, while liver cancer continues to show a sharp gender disparity.
125,070 people died of lung cancer (55,440 females and 69,630 males).
53,010 people died of colorectal cancer (23,440 females and 29,570 males).
51,750 people died of pancreatic cancer (24,360 females and 27,390 males).
42,250 females died of breast cancer.
35,250 males died of prostate cancer.
29,290 people died of liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer (10,030 females and 19,260 males).
Cancer was the second leading cause of death, after heart disease, in the United States. In 2020, there were 602,350 cancer deaths; 284,619 were among females and 317,731 among males.
136,084 people died of lung cancer (63,135 females and 72,949 males).
51,869 people died of colorectal cancer (23,826 females and 28,043 males).
46,774 people died of pancreatic cancer (22,495 females and 24,279 males).
42,275 females died of breast cancer.
32,707 males died of prostate cancer.
28,227 people died of liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer (9,591 females and 18,636 males).
Cancer treatments and cancer can cause side effects , which are problems that occur when treatment affects healthy tissues or organs. These may include:
anemia ,
appetite loss ,
bleeding and bruising (thrombocytopenia) ,
constipation ,
celirium ,
ciarrhea ,
edema (swelling) ,
fatigue ,
fertility issues in men ,
fertility issues in women ,
flu-like symptoms ,
hair loss (alopecia) ,
infection and neutropenia ,
lymphedema ,
memory or concentration problems ,
mouth and throat problems ,
nausea and vomiting ,
nerve problems (peripheral neuropathy) ,
immunotherapy and organ-related inflammation ,
pain ,
sexual health issues in men ,
sexual health issues in women ,
skin and nail changes ,
sleep problems and insomnia , and
urinary and bladder problems .
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled
cell growth in tissues of the
lung .The most common symptoms are coughing (including
coughing up blood ), weight loss, shortness of breath, and chest pains .
Lung cancer is caused by tobacco use (cigarette smoking), secondhand smoke, radon, poor diet, alcohol intake, sedentary lifestyle,
asbestos exposure, arsenic, and air pollution.The vast majority (85%) of cases of lung cancer are due to long-term tobacco smoking . More than half of people with lung cancer die within one year of
being diagnosed. The lung cancer five-year survival rate (18%) is lower than many other leading cancer types, such as the colon (65%), breast (90%) and prostate (99%).
The five-year survival rate for lung cancer is 55% for cases detected when the disease is still localized (within the lungs). However, only 16% of lung cancer cases are diagnosed at an early stage.
For distant tumors (spread to other organs) the five-year survival rate is only 4%. Lung cancer occurred in around 1.8 million people globally and resulted in approximate 1.6 million deaths annually.
There are around 415,000 Americans living with lung cancer today, and approximately 158,080 die annually. The age-adjusted death rate for
lung cancer is higher for men (51.7 per 100,000 persons) than for women (34.7 per 100,000 persons).However, lung cancer mortality has declined by 19% for women and 45% for men over years, due to advances in screening,
newly established oncologic treatments, and reductions in smoking.
Lung, liver, stomach, colorectal and breast cancers cause the most cancer deaths each year worldwide, accounting for 8.2 million deaths in 2012;
about 30% of cancer deaths are due to high body mass index, low fruit and vegetable intake, lack of physical activity, tobacco use, alcohol use.
When cancer cells spread from one organ to another, they are called metastases. Cancer from other organs also may spread to the lungs. When cancer starts in the lungs, it is called
lung cancer . Lung cancer begins in the lungs and may spread to lymph nodes or other organs in the body, such as the brain.
In 2024 and 2025, lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States, with an estimated 235,000 new diagnoses and 125,000 deaths in 2024, followed by 226,650 new cases and 124,730 deaths
projected for 2025. Encouragingly, the five-year survival rate has risen to 28.1% in 2025, up from 18.6% in earlier years, reflecting improved treatments and early detection. For cases diagnosed when the disease is
still localized within the lungs, the survival rate climbs to 64.7%, but only 22.6% of cases are detected at this early stage. Lung cancer continues to show gender disparities, with death rates higher among men—previously
46.7 per 100,000—than women, at 31.9 per 100,000. Although mortality rates are trending downward, at 31.5 per 100,000 in 2025, early diagnosis and enhanced screening remain vital to improving outcomes.
In the United States, lung cancer statistics from earlier years show a higher incidence among men, with a rate of 46.7 per 100,000 persons, compared to 31.9 per 100,000 for women. In 2016, approximately 148,945
Americans died from lung cancer, and by 2018, that number was increased to 154,050. At the time, the five-year survival rate for lung cancer stood at just 18.6%, significantly lower than for colorectal
cancer (64.5%), breast cancer (89.6%), and prostate cancer (98.2%). When lung cancer is detected at a localized stage—confined to the lungs—the survival rate improves to 56%, but only 16% of cases were diagnosed
that early, underscoring the critical need for better screening and earlier detection strategies.
The two main types of lung cancer are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. These categories refer to what the cancer cells look like under a microscope. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small
cell lung cancer. People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery (an operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue), chemotherapy (using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer), radiation therapy (using high-energy rays
(similar to X-rays) to kill the cancer), targeted therapy (using drugs to block the growth and spread of cancer cells), or a combination of these treatments. People with small
cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Doctors from different specialties often work together to treat lung cancer. Pulmonologists are doctors who are experts in diseases of the lungs.
Surgeons are doctors who perform operations.
Thoracic surgeons
specialize in chest, heart, and lung surgery. Medical oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with medicines.
Radiation oncologists are doctors who treat cancers with radiation.
The five year survival rate for all
cancers combined is approximately 65 percent.
Surgery ,
radiation and
chemotherapy are the forms of cancer treatment.
Lung cancer , a serious illness, is the major cause of death in the U.S. Early screening for this disease is not as effective as it is with
breast ,
colon or
prostate cancers. It is also more resistant to treatment than some other cancers.In the United States, the most common types of cancer that lead to death in men include lung cancer —which remains the leading cause and accounts
for roughly 22% of male cancer deaths—followed by prostate cancer, colorectal cancer ,
liver cancer , pancreatic cancer,
and esophageal cancer . While stomach cancer was previously more prominent
worldwide, it is less common as a cause of death among men in the U.S. today. These cancers vary in incidence and mortality depending on factors such as age, genetics, lifestyle choices, and access to early detection and treatment.
The most common types of cancer that kill women are breast cancer ,
lung cancer , stomach cancer ,
colorectal cancer , and cervical cancer ; breast, cervical and colorectal cancer
can be cured if detected early and treated adequately.
According to the latest data from the American Cancer Society, the lifetime risk of developing colorectal cancer in the United States is approximately 1 in 24 (4.1%) for men and 1 in 26 (3.8%) for women. These figures reflect
average risk across the population but can vary based on individual factors such as age, genetics, lifestyle habits, and adherence to recommended screening protocols. Early detection and preventive measures—like maintaining a healthy diet,
exercising regularly, and undergoing routine colonoscopies—can significantly reduce both the risk and mortality associated with colorectal cancer.
Most colorectal cancers start
as growths in the colon or rectum called polyps . But some screening tests allow doctors to find and remove polyps before they turn into cancer.
Leukemia , a cancer of the blood cells, not only causes the overproduction of white
blood cells , which help your body fight infection, but also reduces red blood cells , which carry oxygen to all parts of your body. In children ages 0 to 14, the most common cancers are acute leukemias, particularly acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), followed by brain and other central nervous system (CNS) tumors, and lymphomas. ALL accounts for the majority
of childhood leukemia cases and arises from immature white blood cells in the bone marrow. CNS tumors, including gliomas and medulloblastomas, are the second most frequent, while lymphomas—such as Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin—affect the
lymphatic system and are more common in older children. These cancers differ significantly from those seen in adults, both in type and behavior, and are treated using specialized pediatric oncology protocols.
There are 7.6 million people died of cancer annually - 13% of all deaths worldwide. Lung (1.37 million deaths), stomach (736,000 deaths), liver (695,000 deaths), colorectal/colon (608,000 deaths), breast (458 000 deaths), and
cervical cancer (275,000 deaths) caused the most cancer deaths. The most common types of cancer that kill men are lung, stomach, liver, colorectal and oesophagus and the most common types of cancer that kill women are breast, lung,
stomach, colorectal and cervical.
The most common cancers among adolescents ages 15-19 are Hodgkin lymphoma (15%),
thyroid carcinoma (11%), brain and
central nervous system (CNS) (10%), and
testicular germ cell tumors (8%).
The death rate for cervical cancer dropped by 70% between 1955 and 1992 as early detection and screening became more prevalent. From 1993 to 2025, the death rate for cervical cancer in the U.S. has continued to decline, though at
a slower pace than the dramatic drop seen between 1955 and 1992. While the overall trend is positive, disparities persist. Black and Native American women continue to face significantly higher mortality rates than white women,
often due to differences in access to screening and follow-up care.
1990s–2000s: Mortality rates steadily decreased thanks to widespread Pap smear screening and early treatment; by the early 2000s, the death rate had fallen to around 2.8 per 100,000 women.
2010s: The decline began to level off, with rates hovering between 2.2 and 2.4 per 100,000; HPV vaccination, introduced in 2006, started to show early signs of impact, especially among younger women.
2020s: The death rate has remained relatively stable, with an estimated 4,320 deaths expected in 2025, according to the American Cancer Society; that’s about 0.7% of all cancer deaths in the U.S.
Colon cancer patients may live longer by taking aspirin . Some studies suggest
that daily low-dose aspirin may help colon cancer patients live longer by reducing the risk of recurrence and improving disease-free survival, particularly in those with genetic mutations like PIK3CA. For instance, research has
shown up to a 55% lower recurrence risk and a 45% increase in disease-free survival among aspirin users in certain subgroups. However, findings are mixed—other trials, such as the ASAC study, found no significant survival
benefit and even reported slightly lower outcomes with aspirin use among patients with liver metastases. Additionally, aspirin carries potential side effects like gastrointestinal bleeding, so it’s not universally recommended.
Its effectiveness may depend on individual patient characteristics, genetic markers, and overall treatment plans.Radiation from a CT scan can slightly increase a child’s cancer risk, as children are more sensitive to ionizing radiation due to their rapidly dividing cells and longer expected lifespan. This heightened vulnerability
means there’s more time for potential radiation-induced changes to manifest. While the overall risk remains low, repeated scans or high doses can amplify it, which is why pediatric CT protocols are tailored to deliver the minimum
necessary dose. Physicians often consider alternatives like MRI or ultrasound when possible, since they don’t involve radiation. Ultimately, when medically necessary, the benefits of a CT scan—such as diagnosing serious injuries
or conditions—generally outweigh the small risk, but care is taken to ensure it's used judiciously.
Chlorotoxin , a component found in scorpion venom, is being used in innovative cancer research to target aggressive brain tumors like glioblastoma.
It may shrink brain cancers by helping spread therapeutic genes
throughout the brain gene therapy. Rather than delivering the toxin itself, scientists have engineered CAR T cell therapies—specifically CLTX-CAR T cells—that use chlorotoxin’s unique ability to bind to tumor cells to guide
immune cells precisely to cancerous regions. This targeted approach enhances the delivery of therapeutic genes throughout the brain without damaging healthy tissue. Early studies in lab and animal models show promising results,
marking a major step forward in using gene therapy to treat complex and hard-to-reach brain cancers.The brain cancer symptoms may include headaches , seizures ,
problem with vision , vomiting ,
and mental changes. Around 87,000 Americans are diagnosed
annually with brain cancer and the median age at diagnosis is 60 . An estimated 700,000 Americans are living with a primary brain tumor, of which
69% tumors are benign and 30% tumors are malignant . The average survival rate for all malignant
brain tumor patients is 35%.
Brain tumor or intracranial neoplasm occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain . There are two main types of tumors: malignant or
cancerous tumors and benign tumors.
Cancerous tumors can be divided into primary tumors that start within the brain, and
secondary tumors that have spread from somewhere else, known as
brain metastasis tumors. Secondary or metastatic brain tumors
are more common than primary brain tumors with about half of metastases coming from lung cancer .
A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor ) that
lacks the ability to invade neighboring tissue or metastasize .
Primary brain tumors occur in around 250,000 people a year globally; there are around 689,000 Americans having brain tumor,
and approximately 78,000 people are diagnosed annually. Brain tumors have the highest per-patient initial cost of care (around $100,000) for any cancer group.
Brain tumors can be deadly, significantly impact quality of life. A tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue that has
formed a lump; it’s called a benign tumor if it grows slowly and is self-limiting. Benign tumors need no treatment, but they can
become dangerous if they grow large enough to press on vital organs, blood vessels or nerves. A malignant or cancerous tumor , is innately
dangerous because its cells can divide uncontrollably and produce virtually immortal daughter cells.Doctors now can detect pre-cancerous growths in the stool for a colon cancer test; this new test can potentially be an alternative to colonoscopies .
Colorectal cancer is a treatable disease if caught early.
▷ Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, when not well-controlled, can lead to serious long-term complications due to chronic high blood sugar damaging blood vessels and organs. Among the most critical risks are kidney failure, as diabetes is a
leading cause of end-stage renal disease; cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, coronary artery disease, and peripheral artery disease; and stroke, often resulting from accelerated atherosclerosis and hypertension.
People with type 1 diabetes are nearly twice as likely to develop heart disease or stroke compared to those without diabetes. Fortunately, maintaining tight glycemic control, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, and adopting
healthy lifestyle habits—like regular exercise and a balanced diet—can dramatically reduce these risks.
Diabetes increases the risk of developing ulcers ; about 15–25% of people with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer at some point.
People with diabetes, especially those with poorly controlled blood sugar, are more prone to diabetic ulcers, particularly on the feet. This happens because (1) high blood sugar damages nerves (called peripheral neuropathy),
reducing sensation—so small injuries may go unnoticed; (2) diabete impairs blood circulation, slowing wound healing, and weakens the immune system, making infections more likely. These factors combine to make even minor
cuts or blisters potentially serious.
As of 2024, roughly 589 million adults worldwide—about 1 in 9—are living with diabetes, underscoring a growing global health challenge fueled by aging populations, lifestyle changes, and urbanization. Diabetes now causes an
estimated 3.4 million deaths annually, or one every nine seconds. Looking ahead, projections suggest that by 2050, the number of people affected will reach approximately 853 million. The countries with the largest number of cases remain
consistent: China (~140.9 million), India (~74.2 million), the United States (~38.4 million), followed by Pakistan, Indonesia, Brazil, Bangladesh, Japan, Russia, and Italy. These figures reflect both population size and increasing
exposure to risk factors such as obesity and physical inactivity.
As of 2024, an estimated 38.4 million Americans—roughly 11.6% of the population—are living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, up from 30.3 million in 2020. This increase reflects trends in aging, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles.
Among these individuals, about 12 million are aged 65 and older, and approximately 193,000 are younger than 20. Each year, nearly 1.5 million Americans are newly diagnosed. Diabetes prevalence varies widely by race and ethnicity:
about 6.9% among non-Hispanic whites; 9.1% among non-Hispanic Asians (with subgroup rates previously reported at 4.3% for Chinese, 8.9% for Filipinos, 11.2% for Asian Indians, and 8.5% for other Asian Americans); 11.7% among Hispanics
(including higher rates for Puerto Ricans and Mexican Americans); 12.1% among non-Hispanic Blacks; and 13.6% among American Indian/Alaska Native adults. These disparities underscore the importance of targeted prevention and equitable
access to healthcare.
Between 2012 and 2024, diabetes prevalence in the United States rose sharply from an estimated 22.3 million to 38.4 million people of all ages, representing about 11.6% of the total population. The surge is largely due to increases
in type 2 diabetes, driven by aging demographics, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles. Among adults aged 18 and older, approximately 38.1 million are affected, including 8.7 million undiagnosed cases. In older adults aged 65 and above,
prevalence climbs even higher, reaching 29.2%—nearly one in three. This dramatic growth reflects both improved detection and widening exposure to risk factors across all age groups.
As of 2024, the most recent estimates indicate that approximately 98 million U.S. adults aged 18 and older have prediabetes, which still accounts for more than 1 in 3 adults nationwide.
Among U.S. adults ages 18 years or older, 96 million—more than 1 in 3—had prediabetes in 2019 as below.
32.2 million adults ages 18 to 44 years old
37.4 million adults ages 45 to 64 years old
26.4 million adults ages 65 or older
Diabetes is the 7th leading cause of death in the United States in 2015, with 79,535 people listing it as the underlying cause of death, and a total of 252,806 death certificates listing diabetes as an underlying
or contributing cause of death. In 2021, 103,294 deaths listed diabetes as the underlying cause; 399,401 death certificates mentioned diabetes as either an underlying or contributing cause. In 2022 and 2023, diabetes remained a
significant cause of death in the United States, continuing to rank among the top 10 leading causes. In 2022, underlying cause of death is approximately 103,294 deaths, and contributing cause is around 399,401 death certificates.
The death rate from diabetes in 2023 aligns closely with 2022 levels.
People with the type 1 form of diabetes have an autoimmune disorder and are unable to produce sufficient amounts of the hormone insulin ,
which is made by the pancreas ; type 1 diabetes accounts for
about 5% of all diabetes cases. The vast majority of Americans with diabetes have type 2 form of the disorder, in which the body does not manage its insulin levels correctly;
type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90% to 95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes. People are at risk for developing prediabetes or type 2 diabetes
if they are overweight and age 45 or older, and physically active less than 3 times a week, or if they have a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes.
As of 2024, approximately 38.4 million people in the U.S.—or 11.6% of the total population—are living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, marking a sharp rise from the 22.3 million reported in 2012. Among adults aged 18 and older,
14.7% have diabetes, and about 8.7 million of them are undiagnosed despite meeting lab criteria. The prevalence is especially high among older adults: nearly 1 in 3 Americans aged 65 and over (29.2%) are affected. This surge
is largely driven by increases in type 2 diabetes, fueled by aging demographics, rising obesity rates, and sedentary lifestyles.
Approximately 90% of individuals with type 2 diabetes are either overweight or obese, highlighting excess weight as a major risk factor for the disease. One increasingly recognized treatment option is bariatric surgery,
also known as metabolic or gastric surgery, which not only promotes substantial weight loss but also leads to significant improvements—or even remission—in type 2 diabetes for many patients. Procedures like gastric
bypass have shown superior outcomes compared to lifestyle changes and medication alone, with many patients achieving glycemic control without the need for diabetes drugs for years after surgery.
Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar , levels are too high.
Most of the food you eat is broken down into sugar (also called glucose) and released into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to
release insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose (blood sugar) get into your body’s cells for use as energy
With type 1 diabetes , your body does not make insulin .
With type 2 diabetes , the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose stays in your blood.
Diabetes can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease , vision loss , and
kidney disease .The longer a person lives with diabetes, the greater their risk of experiencing a stroke—particularly an ischemic stroke. Studies have shown that individuals who’ve had diabetes for 10 years or more face nearly triple
the stroke risk compared to those without the condition. Even after accounting for factors like age, blood pressure, and cholesterol, each additional year with diabetes increases stroke risk by approximately 3%. This elevated danger
stems from chronic high blood glucose levels, which gradually damage blood vessels, leading to impaired circulation and potential clot formation in the brain. Fortunately, proactive management through lifestyle changes and proper
medication can significantly reduce this risk and support long-term vascular health.
As of 2025, an estimated 53.1 million Americans are living with diabetes—38.7 million with a diagnosis and 14.4 million unaware they have it. The overwhelming majority of these cases are type 2 diabetes, a condition
strongly associated with poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and obesity.
As of 2025, 14.4 million adults in the United States are living with undiagnosed diabetes, highlighting a pressing public health concern. Notably, significant racial disparities persist: African-Americans are nearly 1.8 times
more likely, and Hispanic-Americans approximately 1.5 times more likely, to be diagnosed with diabetes than non-Hispanic whites. These inequities are driven by a complex interplay of genetic factors, socioeconomic barriers, and unequal
access to healthcare resources.
Diabetes stands as the seventh-leading cause of death in the United States and leads to serious complications, including kidney failure, non-injury-related amputations of the legs and feet, and more new cases of
blindness among adults under 75 than any other condition. These outcomes stem from long-term damage to blood vessels and nerves caused by chronically high blood sugar levels.
Diabetes is a long-term condition that causes high blood sugar levels; approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1,
for which the body does not produce insulin; the rest 90% are type 2, for which the body does not produce enough insulin for proper function. The most common diabetes symptoms include
frequent urination , intense thirst and hunger, weight gain, unusual weight loss,
fatigue , cuts and bruises that do not heal,
male sexual dysfunction , numbness and tingling in hands and feet.
Mississippi (U.S.) has some of the country's highest rates of obesity, diabetes, hypertension and infant mortality. According to Mississippi’s 2024 Public Health Report Card, the state ranks among the worst nationally for several
key health indicators: 48th in obesity and diabetes, 49th in hypertension, and 50th in infant mortality. These conditions contribute to high rates of preventable deaths, with over 195,000 years of life lost before age 75 in 2024 alone.
While there have been modest improvements in some areas, such as declining opioid deaths and tuberculosis rates, health officials continue to call these outcomes “absolutely unacceptable” and urge stronger action to improve access to
care and preventive services.
Bleeding gums and bone loss around the teeth can be early warning signs of diabetes, as elevated blood sugar levels weaken the immune system and increase glucose in saliva, fostering bacterial growth and plaque buildup.
This can trigger gingivitis and progress to periodontitis, a more advanced form of gum disease that damages the bone supporting the teeth. Individuals with diabetes are also more susceptible to oral infections such as thrush and
dry mouth, which can further compromise oral health and make blood sugar harder to control. Because oral complications can both signal and worsen diabetes, maintaining good oral hygiene and scheduling regular dental checkups
are essential components of overall diabetes care.
Diabetes occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use and store glucose, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This chronic condition is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and
other vascular complications. People over the age of 40 who are overweight face a significantly higher likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, especially when combined with sedentary lifestyles and poor dietary habits.
As of 2023, an estimated 38.1 million adults in the United States had diabetes, with over 90% diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Of these, 29.4 million were formally diagnosed, while 8.7 million remained undiagnosed.
Additionally, approximately 96 million adults had pre-diabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are elevated but not yet within the diabetic range. These rising figures reflect a growing public health crisis and
emphasize the urgent need for widespread awareness, early detection, and preventive strategies to curb the diabetes epidemic.
Approximately 90% of individuals with type 2 diabetes are either overweight or obese, highlighting excess weight as a major risk factor for the disease. One increasingly recognized treatment option is bariatric
surgery, also known as metabolic or gastric surgery, which not only promotes substantial weight loss but also leads to significant improvements—or even remission—in type 2 diabetes for many patients. Procedures like gastric
bypass have shown superior outcomes compared to lifestyle changes and medication alone, with many patients achieving glycemic control without the need for diabetes drugs for years after surgery.
As of 2024, diabetes remains one of the top 10 leading causes of death in the United States, with its rising prevalence reflecting both improved detection and growing risk factors like obesity and aging. An estimated 38.4 million
people of all ages—about 11.6% of the total population—are living with diabetes. Among adults aged 18 and older, the rate climbs to roughly 14.7%, encompassing both diagnosed and undiagnosed cases. When broken down by sex, 15.4% of men
have diabetes (12.6% diagnosed, 2.8% undiagnosed), compared to 14.1% of women (10.2% diagnosed, 3.9% undiagnosed), illustrating notable gender disparities in detection and disease burden.
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native adults in the U.S. experience significantly higher rates of diabetes compared to non-Hispanic white adults. The age-adjusted prevalence stands at 13.6% for
American Indian/Alaska Native adults, 12.1% for non-Hispanic Black adults, and 11.7% for Hispanic adults, while non-Hispanic white adults have a lower rate of 6.9%. These disparities are shaped by a complex interplay of factors
including limited access to healthcare, socioeconomic challenges, food insecurity, higher rates of obesity and hypertension, and potentially cultural or genetic influences—underscoring the urgent need for targeted interventions
and equitable health resources across vulnerable communities.
One in 10 Chinese adults already have diabetes, the finding surpasses other Western nations, including Germany and Canada. As of 2023, China’s adult diabetes prevalence reached approximately 13.7%, up from 7.5% in 2005.
That means over 230 million people in China are living with diabetes, making it the country with the largest diabetic population in the world. In comparison, Germany has a prevalence of about 6.9% and Canada sits at around 7.7%.
The rise is largely attributed to rapid urbanization, dietary changes, sedentary lifestyles, and an aging population.
Type 2 diabetes is often called a “silent” disease because it can develop gradually and go unnoticed for years. Although the early signs may seem minor individually, together they can signal an underlying issue. Common symptoms
include unexplained weight loss despite normal or increased eating, frequent urination and excessive thirst due to fluid being pulled from tissues, and persistent fatigue and irritability caused by cells struggling to absorb glucose.
Other warning signs include blurry vision from sugar buildup in the eye’s lenses, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet—a sign of nerve damage—increased hunger, dry or itchy skin with dark patches, slow-healing wounds due to
poor circulation, and frequent infections such as Candida, which flourish in high-sugar environments. Recognizing and addressing these symptoms early is crucial for preventing more serious complications.
▷ Heart Disease & Strokes
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a chronic condition where the heart struggles to pump blood effectively, and its impact on life expectancy becomes even more severe when paired with other illnesses like diabetes
or psychosis. A large-scale study found that individuals who developed diabetes, psychosis, and CHF in that sequence experienced the greatest reduction in life expectancy—about 13 years on average. Interestingly, CHF
alone was associated with a mean loss of 12.4 years, and when combined with psychosis (in any order), the effect was similarly devastating. These findings highlight how the order and timing of disease onset can shape
outcomes, and they underscore the importance of early intervention and coordinated care for people with multiple chronic conditions.
A stroke, also known as a "brain attack", occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients.
This can lead to brain cell death. There are two main types of strokes, ischemic (caused by a blockage in a blood vessel supplying the brain) and hemorrhagic (caused by a blood vessel in the brain bursting).
Symptoms of a stroke can include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side of the body), confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech, difficulty seeing in one or both eyes,
trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, and a severe headache with no known cause.
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked for a long enough time that part of the heart muscle is damaged or dies.
This is usually caused by a blockage in one or more of the coronary arteries. Symptoms of a heart attack can include chest pain or discomfort (which may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain),
pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach, shortness of breath, cold sweat, nausea, or lightheadedness.
When the heat beats, blood is drawn into its two upper chambers, stayed there briefly and then pumped out forcefully through its two lower chambers. An arrhythmia ,
or irregular heartbeat (a problem with the rate or rhythm of heartbeat) occurs when the heart beats too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular rhythm, and it can lose coordination among its chambers; this breakdown can lead to fatigue,
shortness of breath, a heart attack or stroke. People who have Type 2 diabetes are 34% more
likely to develop an arrhythmia (or Afib) than people without diabetes.
The heart beats about 100,000 times per day (roughly 3 billion times during the course of an average lifetime); an adult heart beats about 60 to 80 times per minute (between 60 and 100 beats per minute is normal).
The heart pumps about 5.7 liters of freshly oxygenated blood every minute (it can rise to more than 35 liters per minute when exercising), leaves the heart and enters the bloodstream throughout the body.
The human heart beats over 100,000 times a day—specifically, around 103,680 times on average, assuming a typical resting heart rate of about 72 beats per minute. Over the course of a lifetime, that adds up to more than 2.5 billion
heartbeats, tirelessly pumping blood to sustain every cell in the body.
In the U.S. about 40 children a year die from heatstroke , either because they were left or became trapped in a car. That's about one child every 10 days killed in a hot car.
There were over 940 child hot car deaths since 1998.
Young people with the kind of irregular heartbeat (known as a trial fibrillation) may be better off undergoing surgery to fix the problem
instead of taking medication first.
Stents , small mesh tubes used to keep blood vessels open, have revolutionized the treatment of
coronary artery disease and other vascular conditions. The concept began in the 1960s with the development of balloon angioplasty, a procedure to widen narrowed arteries. The first coronary stent was implanted in
a human patient in 1986; these early stents were bare-metal, which helped prevent artery collapse but still had limitations, such as the risk of restenosis. The introduction of drug-eluting stents,
which release medication to reduce the risk of restenosis in 2000's; this innovation significantly improved patient outcomes. The modern bioresorbable stents, which dissolve over time, have been developed to further
reduce long-term complications.Mechanically
removing a blood clot from a stroke patient’s brain is no more useful than the older treatment of giving an IV dose of a clot-dissolving drug to the body. This medical technique is suitable for large artery blockages, mechanical
thrombectomy remains a gold standard—especially when performed within 24 hours of symptom onset; it can significantly improve outcomes when IV drugs alone aren’t enough to restore blood flow. A recent 2025 study found that for
medium- or small-sized artery blockages, mechanical clot removal (thrombectomy ) was no more effective at reducing disability 90 days
after stroke than standard care, which includes IV clot-busting drugs like alteplase; so in those cases, the older IV treatment holds its ground. It’s not a one-size-fits-all answer. The best approach depends on stroke severity, timing,
and vessel size.The most dangerous disease in the world is ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease). It occurs when the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked.
This reduces blood flow and oxygen to the heart muscle, which can lead to chest pain (angina), heart attacks, arrhythmias, and other serious complications. Its symptoms may include
chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, pain in the upper body (neck, jaw, shoulders, arms, back), sweating, nausea or vomiting, dizziness or lightheadedness, and fast or irregular heartbeat.
Ischemic heart disease is the leading cause of death globally, responsible for millions of deaths each year. Other highly dangerous diseases include stroke, respiratory infections,
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cancers.
Cholesterol plays a central role in many diseases beyond cancer, particularly in cardiovascular, neurological, and metabolic disorders. In cardiovascular disease, excess LDL cholesterol contributes to atherosclerosis by
building up in artery walls, narrowing blood vessels and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes2. In the brain, cholesterol is essential for synapse formation, myelin integrity, and neuronal signaling, but imbalances—either
excess or deficiency—are linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis46. Metabolically, cholesterol dysregulation is associated with conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance, and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In particular, cholesterol stored in liver fat droplets can trigger inflammation and fibrosis, accelerating the progression of metabolic liver disease8. These findings underscore cholesterol’s
dual nature: while vital for cellular function and hormone synthesis, its mismanagement can drive chronic disease across multiple organ systems.
LDL cholesterol , often called “bad” cholesterol, plays a central role in the development of atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Below is how LDL targets are defined based on risk level. These targets reflect a shift from “normal” ranges to personalized, goal-based thresholds that better protect against future cardiovascular events. Lowering LDL through lifestyle
changes, statins, or combination therapies like adding ezetimibe has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of recurrent heart attacks.
For most people, LDL should be under 130 mg/dL to reduce cardiovascular risk.
For high-risk individuals—such as those with diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or a strong family history of heart disease—the target is under 100 mg/dL.
For the highest-risk patients, including those who have survived a heart attack or have established cardiovascular disease, the goal is under 70 mg/dL, and in some cases, even below 55 mg/dL.
Low levels of HDL (the “good” cholesterol) appear connected
to many health risks, not just heart disease ; LDL cholesterol reduction with drugs such as statins has been demonstrated to reduce cardiovascular risk.type-2 diabetes are more
likely than the general population to develop
cardiovascular disease and have lower levels of heart-protective HDL cholesterol.
Exercise and
a heart healthy diet are the way to go and might decrease some of the health risks seen
in people with low HDL cholesterol levels.
High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides are major contributors to cardiovascular disease, even though both substances are essential for life. Cholesterol supports cell function and hormone production, while triglycerides serve
as fuel for body cells. However, imbalances pose serious risks. Total cholesterol (TC)—a calculated measure combining LDL ("bad" cholesterol), HDL ("good" cholesterol), and triglycerides (TC = LDL + HDL + [Triglycerides ÷ 5])—should remain
below 200 mg/dL. LDL carries cholesterol to tissues and, when elevated, promotes plaque buildup in artery walls (atherosclerosis); target levels should be under 100 mg/dL. In contrast, HDL transports cholesterol away from arteries to
the liver for elimination, with levels ideally above 60 mg/dL. Triglycerides, another type of fat in the blood, can contribute to artery wall thickening and increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, and heart disease when levels
exceed 150 mg/dL. Common medications used to manage cholesterol include statins such as Crestor, Lescol, Lipitor, Pravachol, and Zocor.
As of 2024, global estimates indicate that approximately 9.2 million people died from ischemic heart disease, while around 6.6 million deaths were attributed to stroke and other cerebrovascular disease. In 2015, ischemic heart
disease caused 8.76 million deaths, while stroke and other cerebrovascular diseases accounted for 6.2 million, underscoring the long-standing global burden of these conditions.
The hardest working muscle is the heart. It pumps out 2 ounces (71 grams) of blood at every heartbeat. Daily the heart pumps at least 2,500 gallons (9,450 liters) of blood. The heart has the ability to beat over 3 billion times
in a person’s life.
Heart problems often show up in unexpected ways, especially in women and older adults. In addition to the chest pain, the other
surprising signs of an unhealthy heart include neck pain, sexual problems, dizziness,
faintness, or shortness of breath, indigestion, nausea, or heartburn, jaw and ear pain. Other subtle signs include fatigue, cold sweats, swelling in the legs, or even persistent coughing.
Neck, jaw, or ear pain: These can be referred pain from the heart, especially during a heart attack.
Sexual dysfunction: In men, erectile dysfunction can be an early warning sign of vascular issues. In women, reduced libido or discomfort may also be linked to poor circulation.
Dizziness or fainting: These may signal arrhythmias, low blood pressure, or heart valve problems.
Shortness of breath: Especially during mild exertion or while lying down, this can indicate heart failure or coronary artery disease.
Indigestion, nausea, or heartburn: These are surprisingly common heart attack symptoms, particularly in women.
About 500,000 heart stent procedures are performed each year in the United States, and the researchers estimate that about a fifth
of those are for people with stable heart disease. Of those, about a quarter — or an estimated 23,000 procedures — are for people without any chest pain.
A stent is placed in a weak artery to improve blood flow and help prevent the artery from bursting, but it is not better at preventing a
heart attack or prolonging survival than lifestyle changes, such as exercising and taking statins to lower cholesterol.As of 2025, cardiovascular disease affects approximately 612 million people globally, with an estimated 19.2 million deaths attributed to it in 2023—up from 18 million in 2015. Ischemic heart disease, stroke, and hypertensive heart
disease remain the leading causes, and the age-adjusted death rate stands at about 235 per 100,000 people. The burden is unevenly distributed, with the highest mortality rates found in Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and parts of Africa
and the Middle East, while high-income regions like Australasia and Asia Pacific report the lowest. This growing toll reflects aging populations, lifestyle risks, and disparities in healthcare access.
Cardiovascular diseases (CDVs) are the number one cause of death worldwide and accounts for 30% of all deaths,
more people die annually from CVDs than from any other cause. An estimated 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2016, representing 31% of all global deaths. Of these deaths,
85% are due to heart attack and stroke . Over three quarters of CVD deaths take place in low- and middle-income countries.
South Asians (from Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka) with around 2 billion people comprise 60% of the world’s heart disease
cases, even though they make up only a quarter of the planet’s population. Asian descent, a growing population of about 5.4 million,
have disproportionately higher risk of stroke, heart attacks
and other cardiovascular ailments that are not explained by widely known risk factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes or smoking.Most cardiovascular diseases can be prevented by addressing behavioral risk factors such as tobacco use, unhealthy diet and obesity, physical inactivity and harmful use of alcohol using population-wide strategies.
A family history of early heart disease is a risk factor for coronary heart disease. Over time, unhealthy lifestyle habits increase higher risk of coronary heart disease because they can lead to plaque buildup in the heart’s blood vessels. These include being physically inactive,
not getting enough good quality sleep, smoking tobacco or long-term exposure to secondhand smoke, stress, and unhealthy eating patterns.
Coronary heart disease is a type of heart disease that develops when the arteries of the heart cannot deliver enough oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
Coronary heart disease is often caused by the buildup of plaque, a waxy substance, inside the lining of larger coronary arteries. This buildup can partially or totally block blood flow in the large arteries of the
heart. The risk of coronary heart disease goes up with the number of risk factors and how serious they are. Some risk factors such as high blood pressure
and high blood cholesterol can be changed through heart-healthy lifestyle changes .
Other risk factors, such as sex, older age, family history and genetics, and race and ethnicity, cannot be changed. The risk for coronary heart disease starts to increase around age 45 for men and 55 for women. People who deal with toxins, radiation, or other hazards, have a lot of stress at work,
sit for long periods, work more than 55 hours a week, work long, irregular, or night shifts that affect their sleep, have at higher risk of coronary heart disease.Over 65% of patients who experience a myocardial infarction (heart attack) during or shortly after
non-cardiac surgery do not have ischemic symptoms .
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally; most cardiovascular disease affects older adults. Cardiovascular diseases caused 17.9 million deaths (32.1%) worldwide in 2015,
up from 12.3 million (25.8%) in 1990. In the United States 11% of people between 20 and 40 have cardiovascular disease, while 37% between 40 and 60, 71% of people between 60 and 80, and 85% of people over 80 have cardiovascular disease. The average age of death from coronary artery disease in the developed world is around 80 while it is around 68 in the developing world.Cardiovascular disease onset is typically seven to ten years earlier in men as compared to women; cardiovascular disease symptoms may be different for men and women; men are more likely to have
chest pain; women are more likely to have other symptoms along with chest discomfort, such as shortness of breath, nausea and extreme fatigue.
There are many risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, which include age, gender, tobacco use ,
physical inactivity , excessive alcohol consumption ,
unhealthy diet , obesity , genetic predisposition and family history of cardiovascular disease, raised blood pressure (hypertension) , raised blood sugar
(diabetes mellitus) , raised blood cholesterol (hyperlipidemia) , undiagnosed celiac disease ,
psychosocial factors , poverty and low educational status, and air pollution .
Older people who take a low-dose aspirin (100 mg or less) daily may be 20 percent more likely to develop anemia than those who do not. Anemia develops when a person's blood produces a lower-than-normal amount of healthy red blood cells, which are needed to carry oxygen to tissues throughout the body.
Anemia causes the lack of oxygen can make people feel tired or weak, shortness of breath, dizziness, headaches, or an irregular heartbeat. People often took low-dose aspirin, which can thin the blood and help prevent clots, in hopes of preventing a heart attack or stroke. However, taking low-dose aspirin is not effective for most people who have not already had a cardiovascular issue.
Heart attacks are about three times more likely to occur in the morning , when blood pressure and platelet activity are typically at their highest levels. Taking a daily aspirin helps thin the blood and prevent platelets from clumping, lowering the likelihood of heart attacks and stroke.
However, aspirin users were about 30 percent more likely to have a serious gastrointestinal bleeding event, a side effect of frequent aspirin use.Heart attack, cardiac arrest and stroke generally often occur in early morning hours (between 5:00 AM and 12:00 PM) when the agreeability of thrombocytes is higher. A daily baby aspirin pill (81 mg), often recommended to lower the risks of heart disease,
can also reduce high blood pressure -- but only if it's taken at bedtime.
For people who have recently had a stent implanted in a blocked heart artery, the risk of developing a blood clot
may be higher early in the morning than other times of day. Stent patients generally take aspirin plus another anti-clotting medication (e.g.; Plavix) for some time after the procedure -- a year or more if they have drug-coated stents.
A highly anticipated trial results show that invasive procedures, stents and bypass
surgery are no more effective than drugs for stable heart disease , these should be used more sparingly in patients with stable heart disease and the decision to use them should be less rushed. The ability to implant
stents using a catheter inserted through blood vessels in the arm or groin have been clearly demonstrated to save lives in people who are suffering from a heart attack;
however, as heart medicines such as statins have improved, there has been active debate about whether stents and other invasive procedures are
more effective for people who aren’t in the throes of a heart attack but have stable heart disease .
Heart disease or cardiovascular disease (CDV), which affects more than 1 in 3 adults, is responsible for 35.3 percent of all deaths in the U.S. Today, the chance of dying in few days immediately after of a
heart attack is around 6 percent. CDV deaths declined by 26.4 percent from 1995 to 2005. In 1994, it was about 10 percent. In 1984, it was 19 percent. In the 1960s, it was 30 to 40 percent. The lifetime risk of developing coronary artery disease after age 40 is more
than 50 percent for men without symptoms.Cardiovascular disease (CDV) killed 864,480 American in 2005; 151,000 of CDV deaths were under age 65. 16.8 million Americans
had a heath attack or angina; 6.5 million Americans had a stroke; 5.7 million live with heart failure; 309,000 Americans died from sudden heart attack. About 6 million people each year go to hospitals with chest pain; however, only a small fraction are truly having a heart attack. CT scans are increasingly used to diagnose heart attack, but they put out a lot of radiation, which may raise a person's chances of developing cancer.
About 10,000 blood centers in 168 countries report collecting a total of 108 million blood donations globally, of which around 50% is collected in the high-income countries, home to 18% of the world’s population.
As per American Heart Association , 1,314,000 angioplasties , in which a plastic catheter is
snaked into the blocked artery and a small balloon is inflated, opening the vessel, were done in the United States in 2006. Of these 1,313,000 were
percutaneous coronary interventions (PCIs) . 855,000 men and 459,000 women had angioplasties.
448,000 cardiac revascularizations (also known as coronary artery bypass graft or CABG operations) were done in the United States in 2006.
CABG was performed on 323,000 men and 125,000 women. In 2007, American cardiologists performed 721,000 angioplasties. Patients were often given out of the hospital a year of
clopidogrel (Plavix) and a life time of stain,
ACE inhibitor ,
beta blockers and
aspirin . The cost of a heart attack treatment was about $5,700 in 1977 to $54,400 in 2007.
In 2025, angioplasty remains a cornerstone of cardiac care in the U.S., with over 965,000 procedures performed annually—a notable increase from 721,000 in 2007. This growth reflects both an aging population and advances in minimally
invasive techniques that make angioplasty more accessible and effective. As for post-heart attack treatment, the medication regimen still typically includes Clopidogrel (Plavix) or other antiplatelet agents for up to a year, and Statins,
ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and aspirin—often for life. These medications have been joined by newer options like GLP-1 receptor agonists (e.g., semaglutide), which have shown added cardiovascular benefits in high-risk patients.
Regarding cost, the average price tag for treating a heart attack in 2025 has climbed significantly. While exact figures vary by insurance and hospital, estimates suggest total treatment costs can now exceed $80,000, especially when
factoring in emergency care, hospitalization, stenting, and follow-up medications. This rise is driven by inflation, advanced technologies, and longer hospital stays in complex cases.
Heart disease is the number one killer of American of all ages while
cancer is the number one killer of Americans under 85. 46% of women and 22% of men
heart attack survivors will be disabled with heart failure within six years. 435,000 American women have heart attacks annually; 42% die within 1 year;
which kill six times as many women as breast cancer .Congestive heart failure ,
protein deficiency ,
circulatory problems ,
fluid in the lungs ,
kidney disease ,
lupus ,
lead poisoning and more can all cause changes to your nails or nail bed. For example,
nails that have turned completely white may be a sign of liver disease, and if the skin beneath nails has turned red,
it could indicate heart problems.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that not only affects joints but also significantly elevates cardiovascular risk due to persistent systemic inflammation. This inflammation accelerates atherosclerosis,
impairs endothelial function, and alters lipid metabolism—contributing to conditions like heart failure, stroke, and myocardial infarction. Studies show that RA patients have a 48% increased risk of cardiovascular disease, with
68% higher risk of heart attacks and 41% higher risk of strokes compared to the general population. The longer and more active the disease, the greater the risk, especially in those with extra-articular manifestations or positive
rheumatoid factor. Managing RA with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and lifestyle interventions can help reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular outcomes.
More than 1.36 million U.S. adults are currently living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
That’s about 0.6% to 1.0% of the adult population. RA is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and potential joint damage.
It’s more common in women than men, and it can strike at any age—though it most often begins between ages 30 and 60.
Sleep disturbances are extremely common among people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Studies show that
between 50% and 75% of RA patients experience some form of sleep problem; some have trouble falling or staying asleep; others wake up feeling less than refreshed or battle drowsiness during the day.
When people, who had a combination of jaw/left hand and chest pain, were brought to a hospital, they often had a
EKG , a chest X-ray, an ultrasound test and a
CT scan within the first hour; the possibilities the doctors mentioned were terrifying, heart attacks.
About 1 million people in the U.S. go to the hospital with a heart attack every year; 2 in 3 people survive their heart attacks, and 1 in 5 heart attack survivors develop major
depression .
Nervous system disorders , diabetes, heart disease and high blood pressure are ones of many physical or medical conditions that contribute to
sexual dysfunction and diminish sexual desire.Heart disease or lung problems can cause
chest pain.
Heartburn , gastroesophageal
reflux (GERD) , stomach ulcer (burning pain occurs when stomach is empty and feels better when eating food), or
gallbladder (pain often gets worse after a meal, especially a fatty meal) can also cause chest pain.Many commonly performed surgeries—while useful in certain contexts—are often flagged as overused or unnecessary when safer, more effective alternatives exist. Procedures like stent placement for stable angina, complex spinal
fusion for stenosis, hysterectomy for uterine fibroids, and knee arthroscopy for osteoarthritis may offer limited benefit in specific cases. For example, stents don't reduce heart attack or death risk more than medication and lifestyle
changes in stable angina patients, and complex spinal fusions have higher risks without clear advantages over simpler decompression surgery. Likewise, many uterine fibroids can be managed through less invasive treatments such as
embolization or focused ultrasound, and knee arthroscopy generally shows no greater benefit than physical therapy for osteoarthritis, targeting symptoms rather than the root cause. These surgeries aren't inherently harmful—but they
underscore the importance of evidence-based decision-making and exploring all available options before proceeding with invasive treatment.
Stents for stable angina - Studies show that for people with stable (not emergency) angina, stents don’t reduce the risk of heart attack or death more than medication and lifestyle changes. They may relieve chest pain,
but often not more effectively than non-surgical options.
Complex spinal fusion for stenosis - This surgery is frequently performed for back pain, but evidence suggests it’s no more effective than simpler procedures like decompression alone, and it carries higher risks and costs.
Hysterectomy for uterine fibroids - While sometimes necessary, many fibroids can be managed with less invasive treatments like embolization, focused ultrasound, or medication. Hysterectomy is a major surgery with long-term
hormonal and reproductive consequences.
Knee arthroscopy for osteoarthritis - Once a go-to procedure, research now shows it often provides no more benefit than physical therapy for osteoarthritis. It treats symptoms, not the root cause, and recovery can be lengthy.
The first heart transplant and subsequent ongoing research in cardiac transplantation at the University of Cape Town's Groote Schuur Hospital, where
Christiaan Barnard with his team performed the world’s first human-to-human heart transplant operation on 3 December 1967. The first heart transplant
patient survived only 18 days, four of first 10 patients survived for more than one year, two living for 13 and 23 years. Forty-nine consecutive heterotopic heart transplants were performed in Cape Town between 1974 and 1983,
with moderately good results for that era; three of the first five patients of this 49-patient group survived more than 10 years.
Dr. Robert Jarvik implants a permanent artificial heart , the Jarvik 7,
into retired dentist Barney Clark at the University of Utah on December 2, 1982. The heart, powered by an external compressor, keeps Dr. Clark alive for 112 days. The next several implantations of the Jarvik-7 heart were conducted by
Humana , a large health care insurance company. The second patient,
William J. Schroeder , survived 620 days. In 1953 Dr. John H. Gibbon (September 29, 1903 – February 5, 1973) an American surgeon,
performs the first successful open heart surgery in which the blood is artificially circulated and oxygenated by a heart-lung machine.
Dr. Gibbon died in 1973, ironically from a heart attack , while playing tennis.
Dr. Norman Edward Shumway (February 9, 1923 – February 10, 2006) was a pioneer of heart surgery at
Stanford University . Norman Shumway is widely regarded as the father of heart transplantation;
he successfully transplants a heart into 54-year-old steelworker Mike Kasperak, who survives for 14 days in 1968.Dr. Bruce Reitz performed the first successful the world's first
combined heart and lung transplant in a landmark in 1981 on Mary Gohlke at Stanford Hospital .Stroke is the number three killer in the US, affecting almost 800,000 people each year.
Top risks for a stroke include high-fat diet, being single, being unhappy, being obese, smoking,
and being born in the wrong demographic.To maintain healthy eyes, ears, and teeth, it's essential to follow a daily routine that includes wearing protective eyewear, practicing the 20-20-20 rule to reduce eye strain, staying hydrated, and scheduling regular eye exams. For ear care,
avoid inserting objects into the ear canal, dry ears gently after swimming, limit exposure to loud noise, and get hearing checks if symptoms arise. Dental health requires brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, avoiding sugary and
acidic foods, and visiting the dentist every six months. Using mouthguards for sports or grinding and choosing desensitizing toothpaste can further protect teeth. Together, these habits help prevent common conditions like glaucoma, otitis media,
cavities, and gum disease, while supporting overall well-being.
▷ Common Eyes, Ears & Teeth Diseases
Medicare’s glaucoma‑screening rules become a lot more engaging when framed as a snapshot of who lands in the program’s “high‑risk” spotlight: anyone living with diabetes, anyone with a family tree marked by glaucoma,
African Americans who’ve reached age 50, and Hispanic adults 65 and older all fall into the group that qualifies for a fully covered screening every 12 months. Medicare Part B picks up the cost of the screening, provided the appointment
is with an eye doctor who agrees to Medicare’s payment terms.
Glaucoma can’t be cured, but it can be managed effectively. The condition causes permanent damage to the optic nerve, and once that damage occurs, it can’t be reversed. What treatment can do is slow or stop further vision loss by lowering
eye pressure through medications, laser procedures, or surgery. Early detection and consistent follow‑up care make a major difference in preserving vision over time.
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that quietly damage the optic nerve—often due to increased pressure inside the eye—and can gradually steal vision without early warning, making it one of the most insidious causes of blindness worldwide.
Open‑angle glaucoma tends to creep in slowly with subtle peripheral vision loss, while angle‑closure glaucoma can erupt suddenly with intense eye pain, blurred vision, halos around lights, headache, nausea, and a red, distressed eye,
turning it into a true medical emergency. Other forms, such as normal‑tension or childhood glaucoma, may bring cloudy eyes, light sensitivity, or gradual blurring, but all share the same underlying threat: progressive optic nerve damage
that often goes unnoticed until significant vision is lost.
Refractive errors form the broad category of vision problems that occur when the eye’s shape prevents light from focusing properly on the retina, creating a world that looks blurred, distorted, or harder to bring into sharp focus.
They include nearsightedness, where distant scenes fade into a soft blur; farsightedness, where close‑up details slip out of clarity; astigmatism, which bends light unevenly and makes objects at any distance look skewed or smeared; and
presbyopia, the age‑related stiffening of the lens that turns reading menus and phone screens into a stretching‑arm exercise. These conditions are extremely common and, according to major medical sources, affect more than 150 million
people in the United States alone. They’re typically diagnosed during a routine eye exam and corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or, in some cases, refractive surgery.
Refractive errors are the most common type of vision problem, occurring when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing properly on the retina. This leads to blurry or distorted vision, depending on the type. Myopia (nearsightedness)
makes distant objects appear blurry because light focuses in front of the retina. Hyperopia (farsightedness) causes nearby objects to look blurry as light focuses behind the retina. Astigmatism results from an irregularly shaped cornea or lens,
causing both near and far objects to appear distorted or fuzzy. These conditions can develop at any age and are often inherited. Symptoms include squinting, eye strain, headaches, and difficulty seeing clearly. Treatment typically involves eyeglasses,
contact lenses, or refractive surgery like LASIK to correct how light enters the eye.
Several eye conditions show up far more often than others, and the major health organizations highlight a consistent group. The most common include cataracts, refractive errors (like nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and
presbyopia), glaucoma, age‑related macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. These conditions account for a large share of vision impairment worldwide and in the United States.
Age‑related macular degeneration unfolds as a slow erosion of the macula—the tiny but powerful center of the retina responsible for sharp, straight‑ahead vision—gradually turning once‑crisp details into waviness, dimness, or blank
spots. Medical sources describe two main forms: the far more common dry AMD, where the macula thins and accumulates drusen deposits over time, and the more aggressive wet AMD, where abnormal blood vessels leak beneath the retina and
accelerate central vision loss. Risk rises with age, family history, smoking, high blood pressure, and diets high in saturated fatsmy.clevelandclinic.org+2. While no cure exists, early detection through regular dilated eye exams can
slow progression, and treatments such as AREDS2 nutritional supplements for certain dry AMD cases or anti‑VEGF injections and laser‑based therapies for wet AMD can help preserve remaining vision and delay further decline.
Diabetic retinopathy emerges as a slow, often silent reshaping of the retina’s delicate blood vessels, driven by long‑term effects of diabetes and the strain high blood sugar places on the eye’s internal network. In its early,
nonproliferative stage, tiny vessels weaken and leak, creating swelling and subtle vision changes; in its advanced proliferative form, fragile new vessels grow and bleed, setting the stage for more serious complications such as
retinal detachment or sudden vision lossmayoclinic.org. Risk climbs with longer duration of diabetes, poorly controlled blood sugar, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, pregnancy, and tobacco use. While the condition can’t be
cured, early detection through regular dilated eye exams and strong diabetes management can slow its progression, and treatments such as anti‑VEGF injections, laser therapy, or vitrectomy can help preserve remaining vision and reduce
further damage.
In 1748, Jacques Daviel (11 August 1696 – 30 September 1762), a French ophthalmologist , was the first modern European physician to successfully extract cataracts
from the eye. In the 1940s Harold Ridley (10 July 1906 – 25 May 2001), an English ophthalmologist, invented the intraocular lens and pioneered intraocular lens surgery for cataract patients, he introduced the concept of implantation of
the intraocular lens which permitted more efficient and comfortable visual rehabilitation possible after cataract surgery.
Cataracts unfold like a slow fog drifting across the eye’s natural lens, caused by age‑related changes that make the once‑clear lens turn cloudy and dim the world. Vision gradually blurs, colors lose their punch, glare becomes harsher,
and nighttime scenes grow harder to navigate. The likelihood of developing cataracts rises with age, diabetes, long‑term sunlight exposure, smoking, certain medications such as steroids, and family history. While brighter lighting or updated
glasses can help early on, the true solution is cataract surgery—a widely performed procedure that replaces the clouded lens with a clear artificial one and restores clarity that everyday life depends on.
Cataracts are a common eye condition where the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, leading to blurred vision, glare sensitivity, and difficulty seeing at night. This clouding is typically caused by aging, as proteins in the lens break down and
clump together, but it can also result from eye injuries, diabetes, long-term steroid use, or genetic factors. Symptoms often develop gradually and may include faded colors, double vision in one eye, and frequent changes in eyeglass prescriptions.
In early stages, brighter lighting and updated glasses may help, but as cataracts progress, surgery to replace the cloudy lens with a clear artificial one is often recommended and highly effective.
Cataracts are most commonly due to aging , but may also occur due to
trauma , radiation exposure, be present from birth ,
occur following eye surgery, having diabetes , smoking tobacco, or prolonged exposure to sunlight ,
and alcohol. About 20 million people globally are blind due to cataracts .
Cataract removal/surgery is one of the most common operations performed in the United States.
It also is one of the safest and most effective types of surgery. In about 90 percent of cases, people who have cataract surgery have better vision afterward.Cataract surgery (or lens replacement surgery) is the removal of the natural lens of the
eye (also called "crystalline lens") that has developed an opacification,
which is referred to as a cataract , and its replacement with an intraocular lens .
Metabolic changes of the crystalline lens fibers over time lead to the development of the cataract, causing impairment or loss of vision . During cataract
surgery, a patient's cloudy natural cataract lens is removed, either by emulsification in place or by cutting it out.
An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted in its place. Over 90% of cataract operations are successful in restoring useful vision,
with a low complication rate. Day care, high volume, minimally invasive, small incision phacoemulsification with quick post-op recovery has become
the standard of care in cataract surgery all over the world.
Cataracts can develop in one or both eyes, but they’re not contagious and can’t spread from one eye to the other. By age 80, more than 68% of Americans either have
cataracts or have undergone cataract surgery. Cataract surgery is one of the most common and successful procedures in the U.S., with about 3.7 million surgeries performed annually. It boasts a 95–98% success rate in restoring or
significantly improving vision. Modern cataract surgery is quick, minimally invasive, and often done on an outpatient basis.Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased pressure inside the eye (intraocular pressure), and it can lead to gradual or even sudden vision loss if left untreated. The pressure builds up
when fluid in the eye (aqueous humor) doesn’t drain properly, damaging the nerve that transmits visual information to the brain. There are several types, including open-angle glaucoma—the most common form, which progresses slowly and painlessly—
and angle-closure glaucoma, which can cause sudden symptoms like severe eye pain, headache, nausea, and blurred vision. Because early stages often show no symptoms, regular eye exams are crucial for early detection. Treatment may include eye
drops, oral medications, laser therapy, or surgery to reduce pressure and prevent further damage.
Macular degeneration is an age-related eye condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. It primarily impacts central vision, making tasks like reading, driving, and recognizing
faces difficult, while peripheral vision remains intact. There are two main types: dry macular degeneration, which is more common and progresses slowly due to thinning of the macula and buildup of protein deposits called drusen; and wet macular
degeneration, which is less common but more severe, caused by abnormal blood vessels leaking fluid or blood under the retina. Risk factors include aging, genetics, smoking, high blood pressure, and poor diet1. While there's no cure, treatments
like anti-VEGF injections, laser therapy, and nutritional supplements can help slow progression and preserve vision.
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva—the thin, transparent membrane that lines the eyelid and covers the white part of the eye. This condition causes the small blood vessels in the conjunctiva
to become swollen, making the eye appear red or pink, and is often accompanied by itching, burning, tearing, and discharge that may form a crust overnight. Conjunctivitis can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergies, or irritants like smoke
or chlorine. Viral and bacterial forms are highly contagious and often spread through direct contact. Treatment depends on the cause: antibiotic drops for bacterial infections, antihistamines for allergies, and supportive care like warm compresses
and hygiene for viral cases, which usually resolve on their own.
Dry Eye Syndrome is a common condition where the eyes don’t produce enough tears or the tears evaporate too quickly due to poor quality, leading to inadequate lubrication of the eye’s surface. This tear instability can cause symptoms like
burning, stinging, grittiness, blurred vision, light sensitivity, and even watery eyes—a paradoxical response to dryness. The tear film consists of three layers: oily, watery, and mucus, and disruptions in any of these can trigger dry eye. Causes
range from aging, hormonal changes, screen overuse, environmental factors, and certain medications, to autoimmune conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome. Treatment often includes artificial tears, prescription eye drops, lifestyle adjustments, and in
some cases, procedures to block tear drainage for better moisture retention.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, due to prolonged high blood sugar levels from diabetes. It typically affects both eyes
and progresses through two stages: non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), where weakened blood vessels leak fluid and cause retinal swelling, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), where abnormal new blood vessels grow and may bleed
into the eye, potentially leading to vision loss. Symptoms may include floaters, blurred vision, dark or empty areas in sight, and difficulty seeing at night, though early stages often show no symptoms. Managing diabetes effectively and getting
regular eye exams are key to preventing or slowing its progression.
Amblyopia, commonly known as lazy eye, is a vision development disorder that typically begins in early childhood, where one eye fails to achieve normal visual acuity—even with glasses or contact lenses. It occurs when the brain favors one eye
over the other, often due to strabismus (misaligned eyes), refractive errors (like nearsightedness or farsightedness), or visual deprivation from conditions like cataracts. As the brain suppresses input from the weaker eye, that eye’s vision
deteriorates further. Symptoms can be subtle and may include poor depth perception, squinting, head tilting, or an eye that drifts inward or outward. Early detection is crucial, as treatment—such as patching the stronger eye, corrective lenses,
or vision therapy—is most effective when started before age 7.
The Argus II Retinal Prosthesis System (“Argus II”) is the world’s first approved device intended to restore some functional vision for people suffering from blindness. Argus II is approved for use in the United States
and the European Economic Area.
In the early 2010s, 285 million people are visually impaired worldwide, of whom, 39 million are blind and 246 million have low vision. As of June 2025, the World Health Organization and other global sources report that more than 2.2 billion
people live with some form of vision impairment, including both low vision and blindness. Of these, at least 1 billion cases could have been prevented or are yet to be addressed, often due to lack of access to basic eye care.
Blindness (profound vision loss): affects tens of millions globally, though exact updated figures vary by source.
Low vision (moderate to severe impairment): makes up the majority of cases.
Women and people in low- and middle-income countries are disproportionately affected.
In the early 2010s, about 82% of those with blindness were over age 50, and 90% of people with visual impairments lived in low- and middle-income countries. By 2025, 2.2 billion people worldwide are affected by vision impairment,
including 43 million with complete blindness. The burden remains highest in underserved regions with limited access to eye care. Yet over 80% of visual impairments are now preventable or treatable through solutions like cataract
surgery and corrective lenses. Women make up 55% of cases, shaped by longevity and unequal healthcare access. With aging populations driving up total cases, most individuals with blindness are still older adults. But progress is
underway—technological innovation, awareness, and global health efforts are helping reduce avoidable vision loss and build a more equitable future.
After an eye exam, the doctor must give you a copy of your prescription for free and with no strings attached; for glasses, the patient must receive a copy of their prescription after the exam; for contacts, the doctor must provide
it after the fitting is complete - whether the patient asks for it or not, it’s the law, required by The Federal Trade Commission’s Contact Lens Rule and the Eyeglasses Rule.
Ear issues span a wide spectrum—from infections and tinnitus to hearing loss—and each one brings its own mix of sensations, challenges, and potential complications. Recognizing the early signs and knowing the general approaches to
treatment can make a meaningful difference in how these conditions are managed, whether it’s easing discomfort, protecting long‑term hearing, or reducing the impact on daily life.
Ear infections, or otitis media, often unfold as a small drama inside the ear, beginning with swelling or blockage of the Eustachian tubes after a cold or allergy flare‑up, trapping fluid that becomes a breeding ground for bacteria
or viruses. The result can be a mix of ear pain, fever, irritability, and muffled hearing in children, while adults may notice pressure, discomfort, and occasional fluid discharge. Although many infections fade on their own, relief
often comes from managing pain, and antibiotics may be used when symptoms are intense or persistent. When these infections keep returning, clinicians may explore additional treatments to break the cycle and restore calm to the middle ear.
Earwax buildup can turn the ear canal into an unexpectedly troublesome space, creating itching, discomfort, a sense of fullness, or even temporary hearing loss when too much wax blocks sound from passing through. This usually happens
when earwax accumulates faster than the body can naturally clear it, forming a plug that disrupts the ear’s normal function. Relief often comes from gentle softening drops, while more stubborn or impacted wax is best handled by a healthcare
professional who can remove it safely and restore the ear’s clarity.
Hearing loss is associated with depression among American adults, especially women and those younger than age 70.
Adults with hearing impairment were more likely to report moderate to severe depression. Women with hearing loss had a higher prevalence of depression than men. The association was strongest in adults aged 18 to 69, suggesting that younger
individuals may be more affected emotionally by hearing difficulties.Meniere’s disease often unfolds in dramatic waves, bringing sudden episodes of vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss, persistent tinnitus, and an uncomfortable sense of fullness deep within the ear. Although its exact origin remains a
mystery, the condition is tied to abnormal fluid buildup in the inner ear, which disrupts balance and hearing signals. Management focuses on reducing the intensity and frequency of these episodes through approaches such as dietary
adjustments, targeted medications, and, when symptoms are especially stubborn, surgical options designed to restore stability and improve quality of life.
Eustachian tube dysfunction can feel like the ear is stuck between pressure zones, creating fullness, discomfort, and shifts in hearing that often become more noticeable during altitude or weather changes. It typically develops when
allergies, colds, or sinus infections cause swelling that prevents the Eustachian tubes from opening and equalizing pressure properly. Management usually focuses on reducing that congestion with options like decongestants or nasal sprays,
and in more persistent cases, surgical procedures may be considered to help the tubes function more smoothly again.
Otitis Media is a common middle ear infection, especially in young children, caused by bacteria or viruses that inflame the space behind the eardrum. It often follows a cold or respiratory illness, when fluid builds up and becomes infected
due to poor drainage through the eustachian tubes. Symptoms include ear pain, fever, trouble hearing, irritability, and sometimes fluid drainage from the ear if the eardrum ruptures2. While many cases resolve on their own, treatment may involve
pain relievers, antibiotics, or ear tubes for recurrent infections3. Children are more susceptible due to their developing immune systems and shorter, less efficient eustachian tubes.
Otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, is an infection of the outer ear canal—the passage that runs from the outer ear to the eardrum. It’s often caused by bacteria or fungi thriving in a moist environment, especially after
swimming, bathing, or exposure to humid conditions. Symptoms typically include itching, redness, pain that worsens when pulling the ear, fluid or pus drainage, and sometimes muffled hearing or swollen lymph nodes around the ear2. The infection
can become severe if untreated, potentially spreading to nearby tissue. Risk factors include frequent water exposure, use of cotton swabs or earbuds, and skin conditions that affect the ear canal. Treatment usually involves antibiotic or
antifungal ear drops, keeping the ear dry, and avoiding further irritation.
Tinnitus is the perception of noise (heard can be soft or loud) or ringing in the ears, and it occurs when there is no outside source of the sounds.
It may also sound like blowing, roaring, buzzing, hissing, humming, whistling, or sizzling. A common problem, tinnitus affects about 1 in 5 people. Almost everyone notices a mild form of tinnitus once in a while. It only lasts
a few minutes; however, constant or recurring tinnitus is stressful and makes it harder to focus or sleep.Tinnitus often feels like an internal soundtrack that refuses to quiet down, producing ringing, buzzing, or roaring sensations that have no external source. It can emerge after years of loud noise exposure, a simple buildup of earwax,
age‑related hearing changes, or even as a side effect of certain medications. Although a definitive cure doesn’t exist, many people find relief through approaches such as sound therapy, hearing aids, and treating any underlying issues
that may be contributing to the noise.
Tinnitus is often more noticeable at night because surroundings are quieter. To make tinnitus less irritating, try to relax, get enough rest, and avoid loud places and sounds, and things that
may make tinnitus worse, such as caffeine, alcohol, and smoking. If these are not helpful, it may be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or a circulatory system disorder,
high blood pressure , an allergy, or
anemia (in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells). In rare cases, tinnitus is a sign of a serious problem,
such as a tumor or aneurysm . Other risk factors for tinnitus include
temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ), diabetes, thyroid problems, obesity, and head injury.
Tinnitus is the perception of sound—such as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or clicking—in one or both ears without any external source. It’s not a disease itself but a symptom of underlying conditions like age-related hearing loss, ear injuries,
exposure to loud noise, earwax blockage, or even certain medications. Tinnitus can be subjective (heard only by the person) or objective (rare, and audible to a doctor during examination). For some, it’s a mild annoyance; for others, it can
interfere with sleep, concentration, and emotional well-being. While there’s no cure, treatments such as sound therapy, hearing aids, behavioral therapy, and medications can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Ménière’s disease is a chronic inner ear disorder that disrupts both balance and hearing, often causing sudden episodes of vertigo, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and progressive hearing loss, typically in one ear. These episodes may last
from 20 minutes to several hours and can be accompanied by nausea, ear pressure, and a sensation of fullness. The condition is linked to a buildup of endolymph, a fluid in the inner ear that interferes with normal sensory signals. While the
exact cause remains unknown, potential contributors include genetics, autoimmune reactions, viral infections, and poor fluid drainage. Treatment focuses on symptom management through dietary changes, medications, vestibular therapy, and in
some cases, surgery to relieve pressure or reduce vertigo episodes.
Hearing loss occurs when the ear’s ability to detect or process sound is impaired, and it’s typically classified into two main types: conductive and sensorineural. Conductive hearing loss involves problems in the outer or middle ear, such as
earwax buildup, fluid from infections, or damage to the eardrum or tiny bones that transmit sound. This type often causes muffled hearing and can sometimes be treated with medication or surgery. Sensorineural hearing loss, on the other hand,
results from damage to the inner ear—specifically the cochlea or auditory nerve—and is usually permanent. It’s commonly caused by aging, noise exposure, or certain illnesses and medications. A third type, mixed hearing loss, combines elements
of both. Symptoms may include difficulty understanding speech, asking people to repeat themselves, or struggling in noisy environments. Treatment options range from hearing aids and cochlear implants to assistive listening devices, depending on
the severity and type.
As of 2025, about 60.7 million Americans aged 12 and older experience some degree of hearing loss. That’s nearly 1 in 5 people, and the numbers are expected to rise as the population ages and noise exposure increases.
Note that 115 decibels (dB) is how loud the average MP3 player is playing music at maximum volume; and listening to an MP3 player at 100db for just 15 minutes can cause hearing loss. The National Institute on Deafness and
Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) warns that sounds above 85 dB can cause permanent hearing loss with prolonged exposure. MP3 players, concerts, and even lawnmowers fall into this risky range.
Ear barotrauma is a condition caused by pressure changes between the inside and outside of the ear, often triggered by flying, scuba diving, or rapid altitude shifts. It occurs when the eustachian tube, which helps equalize ear pressure,
becomes blocked or fails to open properly. This imbalance can lead to symptoms like ear pain, fullness, dizziness, temporary hearing loss, and in severe cases, eardrum rupture or nosebleeds. While mild cases often resolve on their own, chronic
or intense episodes may require treatment such as decongestants, nasal sprays, or even surgical intervention in rare cases. Preventive techniques include yawning, swallowing, chewing gum, or using specialized earplugs during pressure changes.
Cavities, also known as tooth decay or dental caries, occur when plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—builds up on the teeth and produces acids that erode the enamel, the tooth’s hard outer layer. Over time, this erosion creates holes or pits
in the teeth, which can lead to pain, sensitivity, and even infection if left untreated. Early cavities may not cause symptoms, but as they progress, you might notice toothaches, visible discoloration, or pain when eating or drinking. Treatment
depends on severity: fillings are used to restore minor decay, crowns for more extensive damage, and root canals if the decay reaches the tooth’s pulp.
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, caused by plaque and tartar buildup that leads to inflammation of the gums, resulting in redness, swelling, bleeding, and bad breath2. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a
more severe form where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that trap bacteria and debris. This triggers an immune response that breaks down the bone and connective tissue supporting the teeth, potentially leading to gum recession,
loose teeth, and tooth loss. Risk factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes, and genetic predisposition1. Treatment ranges from improved brushing and flossing to professional cleanings and, in advanced cases, surgical
intervention.
A toothache is a common dental symptom that can range from mild discomfort to intense, throbbing pain, often caused by tooth decay, infection, trauma, or gum disease. The pain may be sharp, dull, or pulsating and can worsen with chewing,
temperature changes, or pressure. If the discomfort persists, it may indicate a more serious issue like a dental abscess, cracked tooth, or nerve damage, which could require urgent treatment. Other symptoms may include swelling, fever, bad breath,
or a foul taste, especially if an infection is present. Treatment depends on the cause and may involve fillings, root canals, antibiotics, or even tooth extraction in severe cases.
Cracked or chipped teeth occur when the enamel—the hard outer layer of the tooth—is damaged due to trauma, teeth grinding (bruxism), or biting down on hard objects like ice or candy. A chip typically involves a small fragment breaking off,
while a crack can run deeper, sometimes reaching the gum line or even the root. Symptoms may include sharp pain when chewing, sensitivity to hot or cold, or a visible jagged edge on the tooth. Treatment depends on severity: bonding for minor chips,
crowns for larger fractures, and root canals if the crack exposes the pulp or causes nerve damage.
Impacted teeth are teeth that fail to erupt properly through the gums, often remaining partially or fully trapped in the jawbone. This condition most commonly affects wisdom teeth (third molars), but can also involve upper canines. Causes
include insufficient jaw space, misalignment, or genetic factors, and symptoms may include pain, swelling, red or bleeding gums, bad breath, difficulty opening the mouth, and crowding of nearby teeth. There are different types of impaction—soft
tissue, partial bony, and full bony—depending on how much of the tooth is trapped. Treatment varies based on severity and symptoms, ranging from monitoring to surgical extraction, especially if the impacted tooth causes infection or affects
surrounding teeth.
Tooth erosion is the gradual loss of enamel, the hard outer layer of your teeth, caused by exposure to acidic foods and drinks, stomach acid from conditions like GERD, frequent vomiting, or even brushing too aggressively. As enamel wears away,
teeth become more vulnerable to sensitivity, discoloration, rough edges, and eventually cracks or decay. Early signs include a sandblasted appearance, transparent tooth tips, and increased pain with hot or cold stimuli. While enamel loss is
irreversible, you can slow or stop erosion with fluoride treatments, gentle brushing, dietary changes, and regular dental checkups.
A tooth abscess is a painful condition caused by a bacterial infection in or around the pulp or root of a tooth, leading to a pocket of pus that can cause swelling, throbbing pain, fever, and sometimes facial swelling or difficulty swallowing.
There are different types: periapical abscess (at the tip of the root), periodontal abscess (in the gums), and gingival abscess (on the surface of the gum). Common causes include deep cavities, cracked teeth, gum disease, or trauma, which allow
bacteria to invade the inner tooth structures. If untreated, the infection can spread to the jaw, neck, or even vital organs, making prompt treatment essential. Management typically involves antibiotics, drainage of the abscess, and often a root
canal or tooth extraction to eliminate the source of infection.
Tooth sensitivity, or dentin hypersensitivity, is a common dental issue where pain or discomfort arises when teeth are exposed to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. This happens when the enamel wears down or gums recede, exposing
the underlying dentin, which contains tiny tubules that lead to the tooth’s nerve center. These tubules allow stimuli to reach the nerve, triggering sharp or sudden pain. Causes include brushing too hard, acidic diets, teeth grinding, gum disease,
and recent dental procedures. Treatment options range from desensitizing toothpaste and fluoride varnishes to dental bonding, sealants, or even root canal therapy in severe cases.
Stained teeth refer to discoloration that can range from yellow and brown to gray or even purple, depending on the cause. There are two main types: extrinsic stains, which affect the outer enamel due to foods, drinks (like coffee, tea, and
red wine), tobacco, and poor oral hygiene; and intrinsic stains, which originate within the tooth and are often caused by medications (like tetracycline), trauma, fluorosis, or aging. Treatment varies based on the type and severity: whitening
products like toothpaste and over-the-counter kits can help with surface stains, while professional bleaching, veneers, or bonding may be needed for deeper discoloration.
▷ Mental Illness
Mental illness can reveal itself through a vivid mix of emotional shifts, changes in thinking, and disruptions in daily life, ranging from persistent sadness or overwhelming worry to sudden mood swings, withdrawal from social
connections, loss of interest in once‑enjoyed activities, difficulty concentrating, altered perception of reality, sleep or appetite changes, unexplained physical discomfort, and a noticeable decline in work or school performance;
when several of these signs begin to shape someone’s days, it often signals that professional support could make a meaningful difference.
Mental illness refers to a wide range of health conditions that affect a person’s thinking, mood, behavior, and ability to function in daily life. These conditions can vary in severity and duration, and include disorders such as
depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, eating disorders, and substance use disorders. Mental illness is not a sign of weakness—it’s a medical condition, just like diabetes or heart disease, and it can affect anyone
regardless of age, gender, background, or social status. Symptoms may include persistent sadness, confusion, extreme mood changes, withdrawal from social activities, fatigue, sleep problems, and even physical symptoms like headaches or
stomach pain1. While mental illness can be distressing and disruptive, effective treatments—including therapy, medication, and support systems—can help individuals manage symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
Mental illness remains more commonly reported among women and younger adults in the U.S.. In 2024, about 26.5% of women and 20% of men experienced some form of mental illness, according to the National Institute of Mental Health.
Young adults aged 18–25 had the highest prevalence at roughly 36%, followed by adults aged 26–49 at 29%. In contrast, those aged 50 and older reported the lowest rate, around 14%. These patterns highlight persistent mental health challenges,
especially for younger individuals facing increasing pressures from social, economic, and digital environments. The gender gap also remains consistent, shaped by a complex interplay of biological and sociocultural factors.
Mental illness encompasses a wide range of conditions that affect a person’s thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and ability to function in daily life, including disorders like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, eating
disorders, and substance use disorders. These conditions are medical in nature—not signs of weakness—and can impact anyone regardless of age, gender, or background. Symptoms may include persistent sadness, extreme mood changes, confusion,
withdrawal from social activities, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and even physical complaints like headaches or stomach pain. With effective treatments such as therapy, medication, and strong support systems, individuals living with mental
illness can manage symptoms and lead fulfilling, meaningful lives.
Delusional disorder is a rare psychotic condition in which a person maintains one or more persistent false beliefs—called delusions—for at least a month, despite clear evidence to the contrary. Unlike schizophrenia, individuals with delusional
disorder typically function well in daily life and do not experience hallucinations or disorganized thinking outside the delusional theme. These delusions can be non-bizarre and fall into categories such as erotomanic (believing someone is in
love with them), grandiose (believing they possess exceptional abilities), jealous, persecutory, somatic, or mixed. Causes may include genetic factors, brain chemistry imbalances, personality traits, or stressful life events. Treatment often
involves antipsychotic medications, cognitive behavioral therapy, and supportive care to help manage symptoms and improve insight.
Repeated lying, especially when it becomes habitual or compulsive, may reflect deeper psychological patterns and is often associated with pathological lying—also known as pseudologia fantastica or mythomania—where individuals fabricate
elaborate stories without clear motive, even when easily disproven. This behavior can be linked to personality disorders such as antisocial, narcissistic, or histrionic personality disorder, though not all pathological liars meet diagnostic
criteria. In contrast, compulsive lying is typically driven by habit rather than intent, with individuals lying about even trivial matters to boost self-image or gain attention, often showing little remorse. In some cases, this behavior may
serve as a coping mechanism rooted in childhood trauma, emotional insecurity, or a need for control.
Compulsive lying is a behavioral pattern in which a person habitually tells frequent and often elaborate lies, even when there's no clear benefit or reason to do so. These lies may contain distorted truths and are typically used to boost
self-image, avoid discomfort, or gain attention, with little remorse or awareness of their impact on others. The behavior often stems from deeper psychological needs—such as a desire for acceptance or control—and may be associated with mental
health conditions like borderline, narcissistic, or antisocial personality disorders. Treatment usually involves psychotherapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which helps individuals recognize and change their lying habits,
and in some cases, medication may be prescribed to address related issues like anxiety or depression.
Pathological lying, also known as pseudologia fantastica or mythomania, is a psychological phenomenon where individuals compulsively tell exaggerated or fabricated stories, often without clear motive or benefit. Unlike ordinary lying,
which is typically intentional and goal-driven, pathological lying is persistent, often elaborate, and may span years or even decades. People with this condition may present themselves as heroes, victims, or individuals with extraordinary
experiences, and while they may know the stories are false, they often cling to them as part of their identity. Though recognized since the late 1800s, pathological lying is not classified as a standalone mental disorder in the DSM-5. Instead,
it’s considered a symptom that may appear in conditions like antisocial, narcissistic, or histrionic personality disorders, or even factitious disorder. The underlying causes are still debated, but theories suggest links to low self-esteem,
childhood trauma, and neurological differences, such as increased white matter in the prefrontal cortex, which may enhance storytelling ability.
Mood disorders are mental health conditions that primarily affect a person’s emotional state and energy levels, often leading to prolonged periods of sadness, irritability, or elevated mood. The two most common types are depression and
bipolar disorder. Depression involves persistent feelings of hopelessness, fatigue, and loss of interest in daily activities, while bipolar disorder is marked by extreme mood swings—alternating between depressive episodes and manic or
hypomanic episodes, which may include elevated energy, impulsivity, and reduced need for sleep. These disorders can significantly impact relationships, work, and overall quality of life, but with proper treatment—such as medication, therapy,
and lifestyle adjustments—many people can manage symptoms effectively and lead fulfilling lives.
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions marked by excessive fear, worry, or nervousness that can interfere with daily life. Common types include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), which involves persistent and unrealistic
worry about everyday things; panic disorder, characterized by sudden and intense episodes of fear known as panic attacks; and phobias, which are irrational fears of specific objects, situations, or activities. These disorders can cause both
emotional and physical symptoms, such as restlessness, rapid heartbeat, sweating, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances. While anxiety is a normal response to stress, anxiety disorders go beyond typical nervousness and often require
treatment through therapy, medication, or lifestyle changes to help individuals manage symptoms and regain control.
Psychotic disorders are a group of serious mental health conditions characterized by a loss of contact with reality, often involving hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking or behavior. One of the most well-known psychotic
disorders is schizophrenia, which typically presents with persistent false beliefs (delusions), sensory experiences that others don’t perceive (hallucinations—most commonly hearing voices), and speech or behavior that may seem illogical or
erratic. People with schizophrenia may also experience negative symptoms, such as reduced emotional expression, lack of motivation, or social withdrawal. These disorders can severely impact daily functioning, but with early diagnosis and
consistent treatment—including medication, therapy, and support—many individuals can manage symptoms and lead meaningful lives.
Personality disorders are a group of mental health conditions that deeply affect how individuals think, feel, and behave—especially in relation to others. Two notable examples are borderline personality disorder (BPD) and antisocial
personality disorder (ASPD). BPD is marked by intense emotional instability, fear of abandonment, impulsive behavior, and turbulent relationships, often accompanied by self-harming tendencies2. ASPD, on the other hand, involves a persistent
disregard for others’ rights, manipulative or deceitful behavior, and a lack of remorse or empathy. While both fall under the Cluster B category of personality disorders—known for dramatic and erratic traits—they differ significantly in
emotional expression and social behavior. Treatment can be challenging but possible, often involving psychotherapy, behavioral interventions, and in some cases, medication.
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of conditions that affect how the brain develops and functions, often emerging in early childhood and influencing behavior, learning, and social interaction. Two of the most well-known examples
are Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Autism typically involves challenges with communication, social cues, sensory processing, and repetitive behaviors, while ADHD is characterized by difficulties
with attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. Though distinct, these disorders can share overlapping traits and sometimes co-occur, making diagnosis and treatment more complex. Support often includes behavioral therapy, educational
interventions, medication, and family support, tailored to each individual's unique strengths and needs.
Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of cognitive impairments that disrupt memory, reasoning, language, and decision-making to the point where daily life becomes difficult or impossible. It’s not a single disease, but rather a
syndrome caused by various underlying conditions—Alzheimer’s disease being the most common, responsible for 60–80% of cases. Other types include vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal disorders, each with distinct
patterns of progression and symptoms. Dementia results from damage to brain cells that interferes with their ability to communicate, leading to changes in behavior, mood, and personality. While aging increases risk, dementia is not a
normal part of growing older.
Dementia is a broad term used to describe a decline in cognitive function that interferes with daily life, affecting memory, thinking, behavior, and decision-making. Among its many forms, Alzheimer’s disease is the most common,
accounting for 60–80% of dementia cases. Alzheimer’s typically affects people over the age of 65, but it can also occur in younger individuals—a condition known as younger-onset Alzheimer’s, which impacts approximately 200,000 Americans
under 65. The disease progresses gradually, beginning with memory loss and advancing to confusion, disorientation, and difficulty with basic tasks. It affects slightly more women than men, possibly due to women’s longer average lifespan.
Alzheimer’s is not a normal part of aging, and while age is the greatest known risk factor, genetics, lifestyle, and overall health also play significant roles in its development.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It occurs when nerve cells in a part of the brain called the basal ganglia become damaged or die, leading to a drop in dopamine, a chemical that
helps control smooth, coordinated muscle activity. Early symptoms often include tremors, slowed movement (bradykinesia), muscle stiffness, and balance problems, which gradually worsen over time. People may also experience speech changes,
facial masking, and non-motor symptoms like depression, sleep disturbances, and memory issues. While the exact cause is unknown, Parkinson’s is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and it’s more common
in people over 60. Though there’s no cure, treatments such as medications (like levodopa), physical therapy, and in some cases deep brain stimulation surgery can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Memory loss refers to difficulty in remembering information, events, or experiences that were previously accessible. It can be temporary or progressive, and may affect short-term or long-term memory. Common causes include aging, stress,
depression, sleep deprivation, head injuries, stroke, nutritional deficiencies (especially B vitamins), and neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Medications, substance use, and emotional trauma
can also interfere with memory function. Symptoms may range from forgetting names or appointments to repeating questions, misplacing items, or getting lost in familiar places. While occasional forgetfulness is normal, persistent or worsening
memory issues should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out treatable conditions or identify early signs of dementia.
Parkinson’s primarily targets the substantia nigra, a region in the midbrain that produces dopamine, the chemical responsible for smooth, coordinated movement. As dopamine-producing neurons degenerate, motor symptoms emerge—such as tremors,
rigidity, slowness of movement (bradykinesia), and postural instability. Over time, non-motor symptoms like sleep disturbances, depression, and cognitive decline may also appear, reflecting broader changes in brain regions like the frontal and
temporal lobes.
According to the Alzheimer’s Association, early Alzheimer’s signs of Alzheimer’s include memory loss that disrupts daily life, difficulty completing
familiar tasks, confusion with time or place, trouble with visual or spatial understanding, language problems, poor judgment, and social withdrawal. If you’re experiencing one or more of these—especially frequent memory lapses,
disorientation in familiar settings, or trouble managing routine tasks—it may be an early indicator of Alzheimer’s and worth discussing with a healthcare provider.
As of 2025, approximately 7 million Americans aged 65 and older are living with Alzheimer’s disease, and that number is projected to nearly double to 13 million by 2050. Women continue to be disproportionately
affected—nearly two-thirds of those diagnosed are women, largely due to longer life expectancy. Alzheimer’s disease now causes around 140,000 deaths annually in the U.S., and its mortality rate has increased by 145%
since 2000, making it one of the leading causes of death.
Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and, eventually, the ability
to carry out the simplest tasks. Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia, a general term for memory loss and other cognitive abilities serious enough to interfere with daily life. People with Alzheimer’s have
trouble doing everyday things like driving a car, cooking a meal, or paying bills. They may ask the same questions over and over, get lost easily, lose things or put them in odd places, and find even simple things confusing.
As the disease progresses, some people become worried, angry, or violent. In most people with Alzheimer’s, symptoms first appear in their mid-60s. One in 9 people over age 65 and nearly half of people over 85 have Alzheimer's disease.
The time from diagnosis to death varies — as little as 3 or 4 years if the person is older than 80 when diagnosed to as long as 10 or more years if the person is younger.Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. Alzheimer's
disease and changes in a person's sleeping behavior were linked , people who develop Alzheimer's show changes in sleep years before their memory begins to decline. Memory problems are typically one of the first signs of Alzheimer’s,
though initial symptoms may vary from person to person. A decline in other aspects of thinking, such as finding the right words, vision/spatial issues, and impaired reasoning or judgment, may also signal the very early stages of Alzheimer’s
disease.
Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease are both progressive neurodegenerative disorders, but they affect the brain in distinct ways. Parkinson’s primarily impacts movement due to the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the
substantia nigra, leading to symptoms like tremors, stiffness, and slowed motion, while Alzheimer’s targets memory and cognitive function, beginning in the hippocampus and cortex and causing confusion, memory loss, and language difficulties.
Parkinson’s may eventually lead to dementia, but Alzheimer’s always results in cognitive decline. The two conditions also involve different abnormal proteins—alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s and beta-amyloid and tau in Alzheimer’s—and require
different treatment approaches, with Parkinson’s focusing on motor symptom management and Alzheimer’s aiming to slow cognitive deterioration.
Postpartum depression (PPD) , also called postnatal depression, is a type of
mood disorder associated with childbirth , which can affect both sexes. Postnatal
depression is a type of depression that many parents experience after having a baby; it's a common problem, affecting more than 1 in every 10 women within a year of giving birth, and one in 20 fathers experienced postnatal depression
in the weeks after their child was born. A girl is more at risk of developing mental health problems if her father has experienced postnatal depression. Symptoms may include extreme sadness, low energy, anxiety, crying episodes,
irritability, and changes in sleeping or eating patterns.Between 2018 and 2025, suicide has remained a major public health crisis in the U.S., with troubling trends—especially among healthcare professionals.
General Suicide Trends (2018–2025)
Suicide deaths peaked in 2022 and 2023, with over 49,000 deaths each year—roughly one every 11 minutes.
After a brief decline between 2018 and 2020, rates returned to their highest levels by 2022.
Men continue to die by suicide nearly four times more often than women, and firearms remain the most common method.
Older adults (85+) have the highest suicide rates, followed by those aged 75–84.
Physician and Surgeon Suicide - The annual estimate of 400 physician suicides still holds as the same in 2021, making it one of the highest suicide rates among any profession. Surgeons, in particular, continue to face elevated
risk due to high-stakes decision-making, long hours and physical strain, emotional toll of patient outcomes, reproductive health challenges, especially among female surgeons. While more recent data on physician suicide is limited,
the underlying stressors—burnout, stigma around seeking help, and systemic pressures—remain largely unchanged.
In 2025, suicide remains a major global public health concern, responsible for more than 720,000 deaths worldwide each year—equivalent to roughly one death every 45 seconds.
It accounts for over 1 in every 100 deaths globally and is among the leading causes of death for individuals aged 15–29, particularly affecting young women and men. The vast majority of suicides—about 73%—occur in low- and middle-income countries,
highlighting the urgent need for equitable mental health support and prevention strategies1. Doctors are dying by suicide at higher rates than the
general population. Around 400 physicians ended their own life a year in the US, the equivalent of one medical
school graduating class annually. Surgeons, who often suffer high rates of burnout ,
ergonomic injuries ,
miscarriages and infertility and are expected to take responsibility for what happens to their patients, have some of the highest known
rates of suicide; of 697 physician suicides reported to the CDC between 2003 and 2017, at least 71 were surgeons.
American attempt suicide an estimated 1 million time annually, and women are 3 times more likely to attempt suicide. For every 13 minutes one
American dies by suicide, over 40,000 people die by suicide every year. For every woman who dies by suicide, four men die by suicide, but women are 3 times more likely to attempt suicide. 90% of Americans who die by suicide
had a diagnosable psychiatric disorder at the time of their death. Suicide is the 10th leading cause
of death in the U.S.; 2nd leading cause of death for ages 10 to 24, and 5th leading cause of death for age 45 to 59. Firearms were the most common method of death by suicide, accounting for 51% of all suicide deaths, followed by suffocation (including hangings) at 25%
and poisoning at 17%.
As of 2025, approximately 7 million Americans aged 65 and older are living with Alzheimer's disease . The disease claims around 140,000 lives annually,
and its impact continues to rise as the population ages. Based on a recent study, every 33 seconds, one American develops Alzheimer's disease, and by 2050, that interval is expected to shrink to every 27 seconds as the number of
cases nearly doubles.
As of 2014 the U.S. annually spent about $317 billion (which comes from medical expensive and disability payments) on caring for over 9.6 million adults with a serious
mental illness . As of 2024, to address serious mental illness, the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
received $2.187 billion in funding for 2024, a $75 million increase from the previous year; the Veterans Affairs Mental Health and Suicide Prevention Programs were allocated $16.24 billion, up by $2 billion; and the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline
received $519.6 million, reflecting continued federal commitment to crisis response infrastructure. Additionally, the Biden-Harris administration earmarked $68.5 million in new grants to expand the mental health workforce and improve access
in underserved communities.
▷ Depression & Stress
Depression and stress are both emotional responses that can affect your mental and physical health, but they differ significantly in cause, duration, and intensity. Stress is typically a short-term reaction to external pressures—like
work deadlines, financial strain, or relationship issues—and may cause symptoms such as irritability, sleep disturbances, muscle tension, and difficulty concentrating. It can be motivating in small doses but harmful when chronic. Depression,
on the other hand, is a clinical mental health disorder marked by persistent sadness, hopelessness, loss of interest in activities, fatigue, and changes in sleep or appetite that last for at least two weeks and interfere with daily functioning.
While stress may resolve once the stressor is removed, depression often requires professional treatment such as therapy or medication. The two can overlap, and chronic stress may even trigger depression, but recognizing their differences is
key to getting the right support.
Depression is a causal risk of coronary heart disease for people with smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
People with depression have a 64% higher risk of developing coronary artery disease compared to those without depression. Among those already diagnosed with depression causes coronary heart disease (CHD), depression increases the risk of
adverse cardiovascular events like heart attacks or cardiac death by nearly 59%. The biological mechanisms are complex and may involve inflammation, autonomic nervous system dysfunction, platelet activation, and hormonal imbalances.
Depression in women has been linked to a significantly higher risk of developing chronic health conditions, including abdominal obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and even certain cancers. This connection stems from both
biological and behavioral factors: depression can elevate cortisol levels, promote unhealthy eating patterns, reduce physical activity, and disrupt immune and metabolic functions. These combined effects not only worsen mental
health but also contribute to inflammation, poor glycemic control, and cardiovascular strain—creating a ripple effect across multiple systems in the body.
In 2023, depression remained a major public health concern in the United States, with an estimated 13.1% of individuals aged 12 and older experiencing depressive symptoms. Women continued to report higher rates than men
(16.0% vs. 10.1%), and young people aged 12–19 had the highest prevalence at 19.2%, while adults aged 60 and over reported the lowest at 8.7%. Rates of depression were also strongly influenced by socioeconomic status, with those
living below the poverty line experiencing significantly higher rates. While earlier surveys from 2013–2016 reported an average 8.1% of adults over 20 with depression in a given two-week period—10.4% of women and 5.5% of men—by 2024,
updated methods showed about 5.0% of adults over 18 reporting regular feelings of depression. Though this 2024 figure appears lower, it's important to note that measurement approaches and timeframes vary. Consistent with past trends,
women, young adults, and individuals from Black, Hispanic, and multiracial backgrounds remain disproportionately affected, while non-Hispanic Asian adults continue to report the lowest rates.
Depression is a serious medical condition that makes you feel restless, irritable, sad, anxious, numb, hopeless, shame, guilt,
worthlessness, and powerlessness. It makes you lose interest in activities, hobbies, appetite and drastic changes in weight, and have little energy and feeling fatigued, trouble sleeping or sleeping too much, and physical problems,
such as headaches, stomachaches, and back pain. Depression ,
stress and anxiety have been linked
to memory problems, such as forgetfulness or confusion; it can make you difficult to focus on work and tasks, make decisions, or think clearly. About 30.0%
of American adults with depression reported moderate or extreme difficulty with work, home, or social activities because of their depression symptoms.
About a quarter of suicides in the US are felt to be due to undiagnosed, or misdiagnosed major depression.Depression (major depressive disorder or clinical depression) is a common but serious mood disorder. It causes severe symptoms
that affect how you feel, think, and handle daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. Depression is one of the most common mental disorders that often lead to attempt suicide. 1 out of 6 people in the U.S. succumb
to clinical depression during their lifetime. Experiences with major depressive disorder includes depressed moods, decreased energy, trouble concentrating, lost interest in activities, guilt of feelings of hopelessness, sleep disturbances,
appetite changes and suicidal thoughts or attempts.People who had depression at some point in their lives were about a third more likely to suffer a stroke than those who haven't been depressed. This is supported by
a research . A 2024 meta-analysis of 44 studies found that people with a history of depression had a 41%
higher risk of stroke compared to those without depression. The link appears across different types of stroke that includes ischemic stroke (30% higher risk), hemorrhagic stroke (33% higher risk) and fatal stroke (39% higher risk).
This connection may stem from chronic inflammation, changes in the nervous system, and behavioral factors like poor sleep, inactivity, or medication nonadherence—all of which can elevate stroke risk.
Stress is the body’s natural response to challenges or demands, triggering the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that prepare you to react through the fight-or-flight system. While short-term stress can enhance focus and
performance, chronic stress can lead to serious health issues such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, anxiety, and depression. Symptoms may include headaches, fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbances, digestive problems, and
social withdrawal. Managing stress effectively involves regular exercise, relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing, maintaining healthy sleep and nutrition habits, connecting with others, and setting boundaries to reduce
overload.
Stress symptoms commonly include exhaustion, irritability, muscular tension, inability to concentrate and a variety of physiological reactions,
such as sleeplessness, headache and elevated heart rate. Stress is hurting physical and emotional health and contributing to some of the leading causes of death. Today 1 out of every 4 American are dealing with extremely high stress
levels. The top 10 stress factors are money, work, economy, family responsibilities, relationships, personal health concerns, housing costs, job stability, health problems affecting the family, and personal safety.The brain’s stress response is activated by corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), a key hormone produced in the hypothalamus that signals the adrenal glands to release cortisol, the body’s main stress hormone. Acting as a biological
on-off switch, this process is carefully regulated by a protein called Otp, which governs CRH production through two distinct receptor forms generated by alternative splicing of the PAC1 gene. The short receptor variant stimulates
CRH release and initiates the stress response, while the long variant suppresses it, helping the body return to a state of equilibrium once the stressor has passed. This elegant neurochemical mechanism illustrates how precise
molecular interactions in the brain help maintain emotional and physiological balance.
Dealing with stress during middle age is increasingly recognized as a risk factor for dementia later in life. Women who experienced high levels of
stress in middle age had a significantly higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia decades later. Chronic psychological stress has been shown to accelerate cognitive decline by affecting sleep,
increasing inflammation, and disrupting brain health over time. While stress is a normal part of life, persistent or poorly managed stress in midlife can have long-term consequences for brain health. Fortunately, interventions
like mindfulness, therapy, social support, and physical activity may help buffer these effects.Certain antidepressants —especially SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors)—have been
linked to an increased risk of bleeding, including rare cases of intracranial hemorrhage,
the absolute risk remains very low for most people. The risk increases significantly when SSRIs are combined with NSAIDs, antiplatelet drugs, or anticoagulants.
Anxiety or panic attacks are often accompanied by
chest pain , most likely caused by muscle contractions in the chest wall. The common external factors can cause anxiety panic attacks are stress
at work/school, stress in a personal relationship (e.g.; marriage, love), stress from an emotional trauma (e.g.; the death of a loved one), financial stress, stress from a serious medical illness, and side effect of medication.An anxiety attack is a sudden episode of intense fear or distress that can feel overwhelming and often comes with a surge of physical symptoms. While not a formal clinical diagnosis, the term is commonly used to describe acute bouts of
anxiety that may be triggered by stress, trauma, or specific situations. Symptoms can include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest tightness, dizziness, sweating, shaking, nausea, and a sense of impending doom or loss of control.
These episodes can last from a few minutes to an hour and may resemble panic attacks, though anxiety attacks are typically more gradual in onset and tied to identifiable stressors.
▷ Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive, long-term condition in which the kidneys gradually lose their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood effectively. In its early stages, CKD often causes no noticeable
symptoms and is typically detected through routine blood and urine tests that reveal reduced kidney function or elevated protein levels. As the disease advances, symptoms may become more apparent and include persistent tiredness,
swelling in the ankles, feet, or hands due to fluid retention, shortness of breath, nausea, and blood in the urine. These signs reflect the kidneys’ declining ability to maintain fluid balance, remove toxins, and regulate essential
bodily functions.
There are 7 symptoms that suggest you have kidney damage: swelling (edema), poor appetite, weight loss, weakness, feeling tired, nausea or vomiting, and trouble sleeping. Those are all recognized signs of kidney
damage—especially in the later stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD). When the kidneys aren’t filtering waste and fluids properly, it can affect nearly every system in the body. Below is how those symptoms connect.
These symptoms often develop gradually, so they’re easy to overlook. If you are experiencing several of them—especially with risk factors like diabetes or high blood pressure—it’s worth getting kidney function tested.
Swelling (edema): Damaged kidneys can’t remove excess fluid, leading to puffiness in the legs, ankles, feet, or even around the eyes.
Poor appetite & weight loss: Waste buildup in the blood can cause nausea and alter taste, making food unappealing.
Weakness & fatigue: Failing kidneys produce less erythropoietin, a hormone that helps make red blood cells—leading to anemia and low energy.
Nausea or vomiting: Toxin accumulation can irritate the digestive system.
Trouble sleeping: Discomfort, restless legs, or changes in body chemistry can disrupt sleep.
Urine is made up of excess water and waste products that have been filtered by kidneys from the body. Its natural light yellow color
is due to excretion of a pigment found in your blood called urochrome. If you are healthy, the color should be a pale yellow to gold. Normal urine color varies, depending on how much water you drink. Fluids dilute the yellow pigments
in urine, so the more you drink, the clearer your urine looks; when you drink less, the color becomes more dark or yellow. Most people need to empty their urine up to eight times a day; pregnant women and older people usually have to
go more often than others.If you notice you suddenly have to pee more often than usual, though, it could be a sign of a health problem like a urinary tract
infections (UIT) , diabetes, an enlarged prostate in men, vaginitis in women, or a problem with the wall of your bladder called interstitial cystitis.
Urine can turn colors far beyond what's normal, including bloody/red/pink, blue, green, dark brown and cloudy white .Bloody urine is common in urinary tract infections (UIT) and kidney stones. These problems usually cause pain; painless bleeding
might signal a more-serious problem, such as cancer. Red or pink urine can be caused by (1) diseases, such as urinary track infections, enlarged prostate, kidney cysts, and kidney or bladder stones; (2) foods, such as beets, blackberries
and rhubarb); and (3) medications, such as Rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane) used to treat tuberculosis, and phenazopyridine (Pyridium - a drug that numbs urinary tract discomfort), and laxatives containing senna. Red or pink color can also
be caused by your long-distance running.
Orange urine can result from medications, such as anti-inflammatory drug sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) ;
phenazopyridine (Pyridium) ; some laxatives; and certain chemotherapy drugs. Orange urine along with light-colored stools can indicate the liver disease or bile duct.
If your urine is dark or orange along with pale stools and yellow skin and eyes, your liver might be malfunctioning.
Blue or green urine can be caused by (1) colored food dyes and dyes used for some tests of kidney and bladder function; (2) medications, such as amitriptyline, indomethacin (Indocin, Tivorbex) and propofol (Diprivan); and
(3) medical conditions, such as familial benign hypercalcemia, and UIT caused by pseudomonas bacteria.
Brown urine can result from (1) food, such as fava beans, rhubarb or aloe; (2) medications, such as antimalarial drugs chloroquine and primaquine, antibiotics metronidazole (Flagyl)
and nitrofurantoin (Furadantin) , laxatives containing cascara or senna, and methocarbamol — a muscle relaxant; and
(3) medical conditions, such as liver and kidney disorders, kidney damage and urinary tract infections; and extreme exercise that leads to muscle injury.
Cloudy white urine can be caused by urinary tract infections and kidney stones.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) causes loss of kidney function over time and may lead to kidney failure or end-stage kidney disease. CKD can progress silently, and many people may not experience symptoms until the disease is advanced.
Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and a family history of kidney disease. Kidney diseases are a leading cause of death in the United States. More than 1 in 7 American adults may have CKD.
As many as 9 in 10 don't know they have it. About 360 people begin treatment for kidney failure (dialysis or kidney transplant) every day.
Few kidney diseases are known to be caused by direct viral infection of renal parenchymal cells. A kidney infection happens when bacteria or viruses get into kidneys; some kidney-tropic viruses, including the polyomaviruses BK and JC
and the herpesvirus CMV, are common in the general population world-wide. Dialysis fills the vital roles the kidneys play, cleaning the blood of toxins, balancing essential components including electrolytes, keeping blood pressure in
check and removing excess fluids. It can be a temporary measure while the kidneys recover, or it can be used long-term if they do not. Another unknown is whether the kidney damage caused by the virus is permanent.
A kidney stone is a solid piece of material which is formed in the kidneys from minerals
in urine . Kidney stones typically leave the body in the urine stream, and a small stone may pass without causing symptoms, otherwise it leads to
pain . About 9% of the U.S. population has a kidney stone, and in 2013 about 15,000 deaths globally because of kidney stone disease.Around 88,000 Americans need kidneys each year; however, only about 17,000 get kidneys, and more than 4,600 die because they did not get one in time.
▷ Lung & Liver Diseases
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that encompasses emphysema and chronic bronchitis, both of which cause airflow obstruction and breathing difficulties. Smoking is the leading cause,
responsible for up to 80% of COPD-related deaths in the U.S.2. The disease gradually worsens over time, with symptoms like persistent cough, excess mucus, wheezing, and shortness of breath becoming more severe. COPD significantly
reduces life expectancy, especially in advanced stages. For example, a 65-year-old smoker with stage 3 or 4 COPD may lose 5.8 years of life expectancy, while former smokers lose about 5.6 years. Quitting smoking is the most
effective way to slow disease progression and improve outcomes. Treatments include bronchodilators, pulmonary rehabilitation, supplemental oxygen, and vaccines to prevent respiratory infections1. Early diagnosis and lifestyle
changes can make a meaningful difference in quality of life.
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious, progressive lung disease marked by scarring and thickening of the tissue around and between the air sacs (alveoli), which makes it increasingly difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream.
This stiffened lung tissue impairs breathing, leading to symptoms like shortness of breath, dry cough, fatigue, and reduced exercise tolerance. Over time, the condition worsens, and many patients experience a decline in lung function
that can result in respiratory failure or complications like pulmonary hypertension and right-sided heart failure. The most common form, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), has a median survival of 3 to 5 years after diagnosis,
though some individuals live longer depending on disease progression and treatment response. While lung damage from fibrosis cannot be reversed, therapies such as antifibrotic medications, oxygen support, and pulmonary rehabilitation
can help slow progression and improve quality of life.
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) , which is a newly viral respiratory illness to humans since 2102; people infected
with MERS developed severe acute respiratory illness, including fever, cough, and shortness of breath, and many of them have died.The Tuberculosis (TB) , which is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs, is second only to HIV/AIDS as the greatest killer worldwide
due to a single infectious agent. In 2012, 8.6 million people fell ill with TB and 1.3 million died from TB. In 2024, 10.6 million new TB cases were reported, and 1.3 million deaths among HIV-negative individuals, and 160,000 deaths
among those with HIV. While the total number of TB cases has increased slightly since 2012, the death toll has remained relatively stable as a result of improved diagnosis and treatment access. However, TB still ranks among the top
infectious disease killers worldwide, alongside COVID-19 and HIV/AIDS.
About one-quarter to one-third—is estimated to be infected with latent TB, meaning they carry the bacteria but don’t show symptoms and aren’t contagious. Of those infected, only 5–10% will develop active TB during their lifetime,
typically when the immune system is weakened. As of the 2024 WHO Global Tuberculosis Report, India accounted for approximately 27% of global TB cases, and India and China together made up about 42% of the global burden.
The liver (located in the upper abdomen near the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, and pancreas), is essential for digesting food and ridding the body of toxic substances. It performs storing nutrients, removing
waste products and worn-out cells from the blood, filtering and processing chemicals in food, alcohol, and medications, and producing bile that helps digest fats and eliminates waste products.
A liver hemangioma is a noncancerous (benign) mass in the liver made up of a tangle of blood vessels; these lumps,
which consist of blood vessels and are usually harmless, are common and are estimated to occur in up to 20% of the population. An estimated 5% of American adults have small liver hemangiomas that cause no symptoms and do not need treatment;
larger hemangiomas can cause pain or discomfort.
The signs of liver disease (may not be liver cancer) may include abdominal pain and swelling,
skin and eyes that appear yellowish (jaundice), swelling in the legs and ankles, itchy skin, dark urine color, pale stool color, chronic fatigue, nausea or vomiting, loss of appetite, and/or tendency to bruise easily.
▷ Pregnancy
Around 12% of married women have trouble getting pregnant or sustaining a pregnancy. The chance of having a child is much higher for women younger than 35 years and men younger than 40 years than for older women and men.
A couple ages 29-33 has a 20-25% chance of conceiving in any given month; after six months of trying, 60% of couples will conceive without any medical assistance. As women get older, it takes longer to conceive and the chance
of having a baby decreases; the chance of pregnancy for a women at age 30 is around 20 percent, and by age 40 , the chance is around 5 percent.
The longest recorded pregnancy was 375 days (instead of the normal 280) , the
oldest recorded woman to have a baby was 66 years old, who gave birth by caesarean section to twin boys;
13% of women received infertility services in their lifetime.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantations (FMTs) or "poop transplants"
work as well as antibiotics to treat a common and deadly cause of diarrhea;
this was a small trial, but the initial results showed that fecal microbiota transplantation may be an alternative to antibiotic therapy in primary C. difficile infection, which kills 29,000 Americans a year and makes 450,000 sick
in the U.S. alone.Women ages 40 to 44 had 114,730 of the 3.8 million babies born in 2017, women 45 and older had 9,325.
When women undergo in vitro fertilization with their own eggs, the chance of having a baby in each attempt falls
from 41.5% before age 35 to 12.4% at ages 41–42. After age 44, the success rate is just 1%, which is why the vast majority of women who have babies after that age using eggs from younger donors.Women are given a lot of advice during pregnancy, including to take a vitamin D supplement to keep bones and teeth healthy for their babies.
There is no strong evidence that pregnant women should receive vitamin D supplementation to prevent low bone mineral content in their children ;
low vitamin D levels in the mothers do not affect their child’s bone health.
The pregnancy rate for U.S. women is around 85-90 per 1,000 women aged 15–44. The birth rate for married women was around 70% higher than the rate for unmarried women; in 2022, there were approximately 38 abortions per 100 live
births among unmarried women, compared to just 4 per 100 among married women.
In 2023, the total U.S. cesarean delivery rate was 32.3% of all live births. About 60% of those were primary cesareans, meaning they were the first
cesarean delivery for the mother. After a primary cesarean, the chance of a vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC) was 15.1 per 100 live births.
An estimated 650,000 people worldwide have multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) . A study found that
vitamin C can kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis in vitro by generating reactive
oxygen species (ROS) through a process known as the Fenton reaction. This oxidative stress damages the bacteria’s DNA and cell structures, leading to its death. However, while promising, these findings are mostly
from lab and animal studies—clinical trials in humans are still needed before vitamin C can be recommended as a standard treatment.
Each year around 132 million babies were born and around 62 million people die; approximate 117 billion humans throughout history on the Earth and about 8.2 billion people live today.
Woman who had at least one stillbirth or miscarriage will increase the risk of a heart attack by 3.5 times later in her life ;
and women who had more than 3 miscarriages during their childbearing years will have 9 times as likely to have a
heart attack .As of 2023, the World Health Organization and UNICEF report that around 13% of adolescent girls and young women globally give
birth before age 18. This translates to approximately 12 million births annually among girls aged 15 to 19, and at least 1 million births among girls under 15, though the latter is likely underreported due to stigma and lack of data.
The highest rates of adolescent births are concentrated in sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and parts of Latin America, where early marriage and limited access to reproductive health services remain significant challenges.
As of 2024, the twin birth rate in the United States is approximately 30.7 per 1,000 live births, which is consistent with the rate reported in 2023. This reflects a stabilization following decades of increase
driven by maternal age trends and the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). While ART continues to contribute to multiple births, recent medical guidelines promoting single-embryo transfers have helped curb the
rise in twin pregnancies. Older mothers—particularly those in their late 30s and 40s—still have a higher likelihood of twin births compared to younger women, maintaining the pattern observed in earlier years.
Twin Birth Rates (All Ages)
2022: 31.2 twin births per 1,000 live births (≈ 3.12%)
2023: 30.7 per 1,000 (≈ 3.07%)
2024: Around the 2023 level
By Maternal Age (2022 data)
Women 40 and older: ~4.0% (40 per 1,000 live births)
Women in their late 30s (35–39): ~3.9%
Women aged 20–24: ~2.4%
Teenagers (15–19): ~1.7%